Abstract
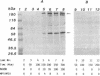
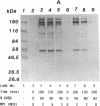
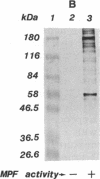
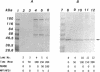
MPM-2, a monoclonal antibody specific for cells in mitosis, recognizes a family of proteins that share a common phosphorylated epitope. In this study we have shown that during the maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes induced by progesterone, phosphorylation of MPM-2 antigens coincided with the appearance of MPF activity. When MPM-2 (0.7-1.4 micrograms per oocyte) was injected into oocytes prior to progesterone stimulation, MPF activity failed to appear and induction of maturation was inhibited as judged by both germinal-vesicle breakdown and white-spot formation. Further, MPM-2 was able to neutralize as well as immunodeplete MPF activity from mitotic HeLa cell and mature oocyte extracts. These results suggest that MPM-2 recognizes either MPF itself or a protein(s) that regulates MPF activity and that the kinase that phosphorylates MPM-2 antigens may be a key component in the regulation of M-phase induction.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capoly J. P., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Labbé J. C., Dorée M. Changes in the activity of the maturation-promoting factor during meiotic maturation and following activation of amphibian and starfish oocytes: their correlations with protein phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyert M. S., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of MPF activity in vitro. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90380-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M., Peaucellier G., Picard A. Activity of the maturation-promoting factor and the extent of protein phosphorylation oscillate simultaneously during meiotic maturation of starfish oocytes. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90298-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Mitosis-inducing factors are present in a latent form during interphase in the Xenopus embryo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2047–2056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Laskey R. A. The transplantation of nuclei from single cultured cells into enucleate frogs' eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Sep;24(2):227–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Bravo R., Kirschner M. Phosphorylation changes associated with the early cell cycle in Xenopus eggs. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Kyes J. L., Maller J. L. Metaphase protein phosphorylation in Xenopus laevis eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):760–768. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J. Mitotic control by metaphase-promoting factor and cdc proteins. J Cell Sci. 1989 Feb;92(Pt 2):131–135. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J., Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):295–312. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Newport J., Kirschner M. Maturation-promoting factor induces nuclear envelope breakdown in cycloheximide-arrested embryos of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):81–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W. A mitotic inducer matures. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):207–208. doi: 10.1038/335207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Gia P., Bomsel M., Labrousse J. P., Gallien C. L., Weintraub H. Partial purification of the maturation-promoting factor MPF from unfertilized eggs of Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Dec 15;161(3):771–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandre D. D., Davis F. M., Rao P. N., Borisy G. G. Phosphoproteins are components of mitotic microtubule organizing centers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4439–4443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. Effects of cyclohexamide on a cytoplasmic factor initiating meiotic naturation in Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]