Abstract
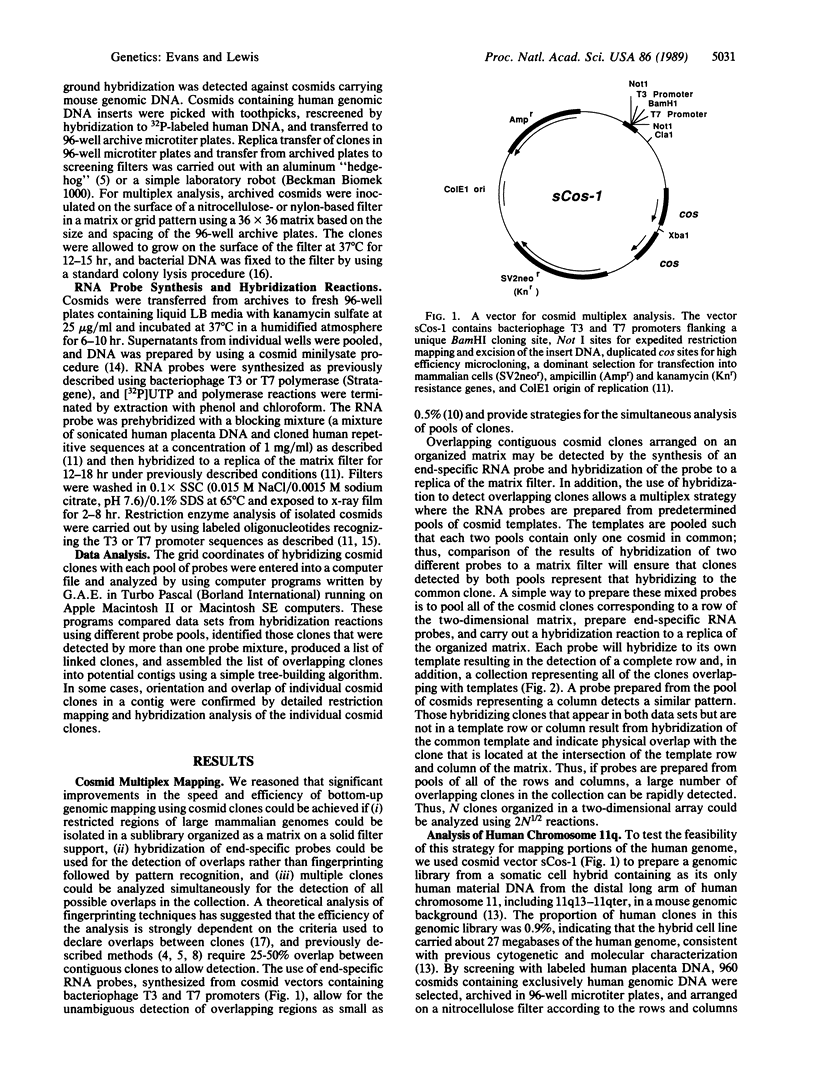
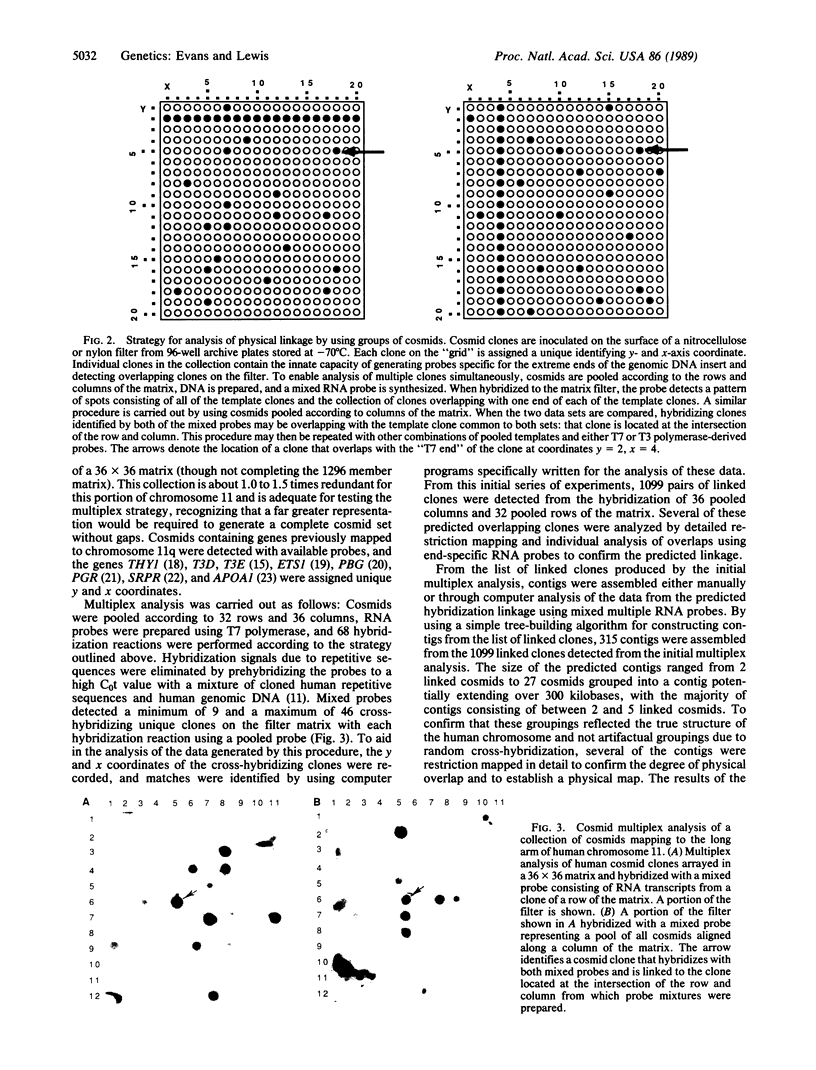
A rapid and powerful approach for linking individual clones of a cosmid library and the assembly of a large physical map is presented, which depends on the simultaneous analysis of many cosmid clones for overlapping regions. This method uses cosmid vectors that contain endogenous bacteriophage T3 and T7 promoters to allow for the identification of overlapping clones through the synthesis of end-specific RNA probes. A genomic library is constructed and organized as an ordered matrix such that each clone is assigned an identifying coordinate. DNA from mixtures of cosmid clones is pooled such that each pool contains only one common member with any other pool, RNA probes are prepared from mixtures of cosmid clones, and groups of clones overlapping with the constituents of the mixtures are determined by hybridization. Pooled probes are most simply prepared by grouping clones according to the rows and columns of the library matrix. The pairwise comparison of data generated by the hybridization of mixed probes can be decoded by using simple algorithms that predict the order and linkage of all clones in the collection and organize them into predicted contigs. To demonstrate the feasibility of multiplexed analysis of cosmids, a genomic library was prepared from a mouse-human somatic cell hybrid that contains a portion of the long arm of human chromosome 11. Preparation, arrangement on a matrix, and analysis of pooled cosmid clones from this collection resulted in the detection of 1099 linked pairs of cosmids, which could be assembled into 315 contigs. Thus, with a minimal amount of effort, a substantial portion of this genomic region has been linked in multiple overlapping contigs. This method may have practical applications in the large-scale mapping and sequencing of mammalian genomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Sulston J., Brenner S., Karn J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7821–7825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson A., Waterston R., Kiff J., Sulston J., Kohara Y. Genome linking with yeast artificial chromosomes. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):184–186. doi: 10.1038/335184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Lewis K. A., Lawless G. M. Molecular organization of the human CD3 gene family on chromosome 11q23. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(5):365–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00364236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Wahl G. M. Cosmid vectors for genomic walking and rapid restriction mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:604–610. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin C. A., McKeon C., Israel M. A., Gegonne A., Ghysdael J., Stehelin D., Douglass E. C., Green A. E., Emanuel B. S. Comparison of constitutional and tumor-associated 11;22 translocations: nonidentical breakpoints on chromosomes 11 and 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6122–6126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Waterman M. S. Genomic mapping by fingerprinting random clones: a mathematical analysis. Genomics. 1988 Apr;2(3):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Skogseid B., Oberg K., Nakamura Y., Nordenskjöld M. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 gene maps to chromosome 11 and is lost in insulinoma. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):85–87. doi: 10.1038/332085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer L., Garcia P. D., Harkins R. N., Coussens L., Ullrich A., Walter P. Topology of signal recognition particle receptor in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):334–338. doi: 10.1038/318334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Tang C. J., Watkins P. C., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Rapid detection of human chromosome 21 aberrations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9664–9668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslen C. L., Jones C., Glaser T., Magenis R. E., Sheehy R., Kellogg J., Litt M. Seven polymorphic loci mapping to human chromosomal region 11q22-qter. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):66–75. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misrahi M., Atger M., d'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guiochon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E. Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):740–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen C., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Santoni M. J., Goridis C., Jordan B. R. Localization of the human NCAM gene to band q23 of chromosome 11: the third gene coding for a cell interaction molecule mapped to the distal portion of the long arm of chromosome 11. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):711–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T., Barlow D. P., Zehetner G., Craig A., Michiels F., Ehrich E., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Molecular approaches to mammalian genetics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):131–139. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochazka M., Leiter E. H., Serreze D. V., Coleman D. L. Three recessive loci required for insulin-dependent diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):286–289. doi: 10.1126/science.2885918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyati J., Kucherlapati R. S., Skoultchi A. I. Activation of human beta-globin genes from nonerythroid cells by fusion with murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Kaytes P. S. Amplification, storage, and replication of libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:407–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. L., Arredondo-Vega F. X., Giampietro P. F., Smith M., Anderson W. F., Desnick R. J. Regional gene assignment of human porphobilinogen deaminase and esterase A4 to chromosome 11q23 leads to 11qter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Kozak C., Reeves R., Gearhart J., Nunn M. F., Nash W., Fowle J. R., 3rd, Duesberg P., Papas T. S. Conserved chromosomal positions of dual domains of the ets protooncogene in cats, mice, and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1792–1796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijs J., Giguère V., Hurst J., van Agthoven T., Geurts van Kessel A., Goyert S., Grosveld F. Chromosomal localization of the human Thy-1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5832–5835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]