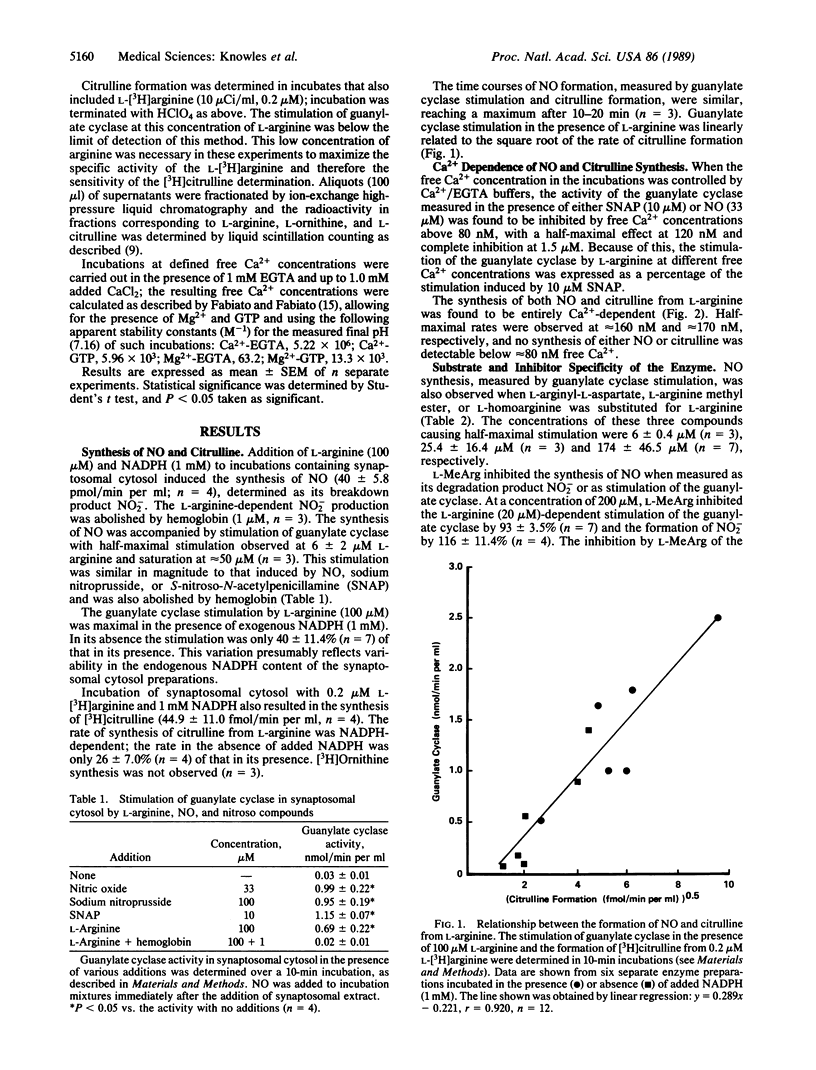
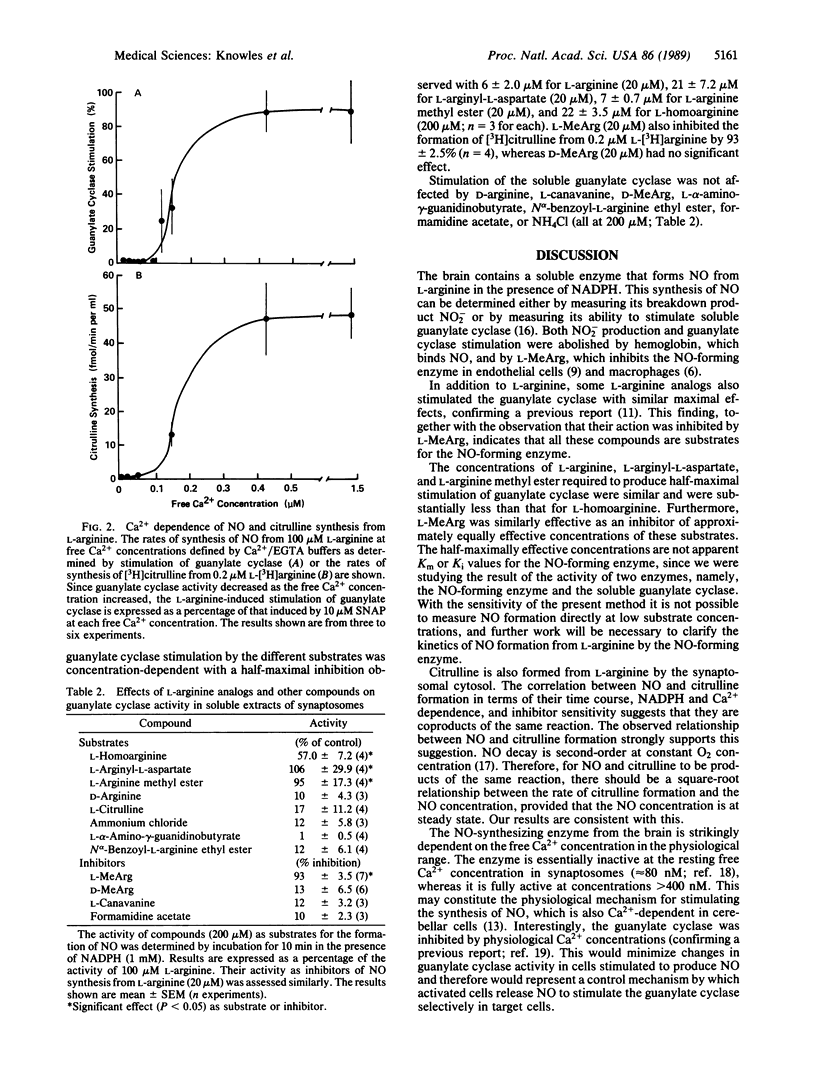
Abstract
A soluble enzyme obtained from rat forebrain catalyzes the NADPH-dependent formation of nitric oxide (NO) and citrulline from L-arginine. The NO formed stimulates the soluble guanylate cyclase and this stimulation is abolished by low concentrations of hemoglobin. The synthesis of NO and citrulline is dependent on the presence of physiological concentrations of free Ca2+ and is inhibited by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine, but not by its enantiomer NG-monomethyl-D-arginine or by L-canavanine. L-Homoarginine, L-arginyl-L-aspartate, or L-arginine methyl ester can replace L-arginine as substrates for the enzyme. These results indicate that NO is formed from L-arginine in the brain through an enzymic reaction similar to that in vascular endothelial cells, neutrophils, and macrophages, adding support to our hypothesis that the formation of NO from L-arginine is a widespread transduction mechanism for the stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley R. H., Brammer M. J., Marchbanks R. Measurement of intrasynaptosomal free calcium by using the fluorescent indicator quin-2. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 1;219(1):149–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2190149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T. Endogenous activating factor for guanylate cyclase in synaptosomal-soluble fraction of rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7617–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Yoshioka M. L-Arginine identified as an endogenous activator for soluble guanylate cyclase from neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10147–10151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Macrophage synthesis of nitrite, nitrate, and N-nitrosamines: precursors and role of the respiratory burst. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6369–6373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Kawabe Y., Kuriyama K. Activation of cerebral guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):851–856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91460-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Identification as nitric oxide and role in the control of vascular tone and platelet function. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2495–2501. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. R., Kon C., Breckenridge B. M. Calcium ion effects on guanylate cyclase of brain. Life Sci. 1976 May 1;18(9):935–940. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Moncada S. A novel citrulline-forming enzyme implicated in the formation of nitric oxide by vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):348–352. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy A., Bajusz S., Patthy L. Preparation and characterization of Ng-mono-, di- and trimethylated arginines. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1977;12(3):191–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara H., Oikawa Y., Sugawara K. Purification and characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):1945–1953. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickmann J. L., Himmel M. E., Smith D. W., Fahrney D. E. Arginine deiminase: demonstration of two active sites and possible half-of-the-sites reactivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jul 14;83(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


