Abstract
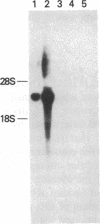
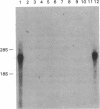
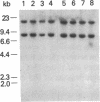
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is an intermediate-filament (IF) protein that is highly specific for cells of astroglial lineage, although its tissue-specific role is speculative. Determination of the primary structure of this protein should be of importance for understanding the functional role it plays in astroglia. Therefore, we isolated a cDNA clone encoding this protein and determined its nucleotide sequence. The predicted amino acid sequence indicates that GFAP shares structural similarities--particularly in the central rod domain and to a lesser degree in the carboxyl-terminal domain--with other IF proteins found in nonepithelial cell types. Considerable sequence divergence in the amino-terminal region of GFAP suggests that the tissue-specific functions of this IF protein might be mediated through this region of the molecule. In contrast, conservation of structural characteristics and a moderate degree of sequence conservation in the carboxyl-terminal region suggest functional similarities. Blot hybridization analysis using the GFAP cDNA as a probe failed to detect GFAP mRNA in both normal and neoplastic human tissues in which IF proteins other than GFAP are known to be expressed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarek J. M., Cowan N. J. Structure of the mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein gene: implications for the evolution of the intermediate filament multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5527–5543. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D., Bigner S. H., Pontén J., Westermark B., Mahaley M. S., Ruoslahti E., Herschman H., Eng L. F., Wikstrand C. J. Heterogeneity of Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of fifteen permanent cell lines derived from human gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):201–229. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock E. Nervous system specific proteins. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carden M. J., Schlaepfer W. W., Lee V. M. The structure, biochemical properties, and immunogenicity of neurofilament peripheral regions are determined by phosphorylation state. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9805–9817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crewther W. G., Inglis A. S., McKern N. M. Amino acid sequences of alpha-helical segments from S-carboxymethylkerateine-A. Complete sequence of a type-II segment. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):365–371. doi: 10.1042/bj1730365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Fajardo M., Naughton S. A., Eng L. F. Degradation of glial fibrillary acidic protein by a calcium dependent proteinase: an electroblot study. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Battini R., Kaczmarek L., Rittling S., Calabretta B., de Riel J. K., Philiponis V., Wei J. F., Baserga R. Coding sequence and growth regulation of the human vimentin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3614–3620. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann U., Amann E., Zettlmeissl G., Küpper H. A. Characterization of cDNA coding for human factor XIIIa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8024–8028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helman L. J., Thiele C. J., Linehan W. M., Nelkin B. D., Baylin S. B., Israel M. A. Molecular markers of neuroendocrine development and evidence of environmental regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2336–2339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. Multiple phosphorylation sites in mammalian neurofilament polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10467–10470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. The distribution of phosphorylation sites among identified proteolytic fragments of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4019–4025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Brown J. A., Lawrence J., Korsmeyer S. J., Morton C. C. Translocations that highlight chromosomal regions of differentiated activity. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1985 Oct;18(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(85)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Remarkable conservation of structure among intermediate filament genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):491–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pixley S. K., de Vellis J. Transition between immature radial glia and mature astrocytes studied with a monoclonal antibody to vimentin. Brain Res. 1984 Aug;317(2):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(84)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rataboul P., Faucon Biguet N., Vernier P., De Vitry F., Boularand S., Privat A., Mallet J. Identification of a human glial fibrillary acidic protein cDNA: a tool for the molecular analysis of reactive gliosis in the mammalian central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 1988;20(2):165–175. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490200204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutka J. T., Giblin J. R., Dougherty D. Y., Liu H. C., McCulloch J. R., Bell C. W., Stern R. S., Wilson C. B., Rosenblum M. L. Establishment and characterization of five cell lines derived from human malignant gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(1):92–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00686798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salim M., Rehman S., Sajdel-Sulkowska E. M., Chou W. G., Majocha R. E., Marotta C. A., Zain S. B. Preparation of a recombinant cDNA library from poly(A+) RNA of the Alzheimer brain. Identification and characterization of a cDNA copy encoding a glial-specific protein. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Mar-Apr;9(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Zimmerman U. P. Calcium-mediated breakdown of glial filaments and neurofilaments in rat optic nerve and spinal cord. Neurochem Res. 1981 Mar;6(3):243–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00964040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G., Osborn M., Weber K. Occurrence of two different intermediate filament proteins in the same filament in situ within a human glioma cell line. An immunoelectron microscopical study. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90227-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer A., de Tribolet N., Diserens A. C., Gaide A. C., Matthieu J. M., Carrel S., Stavrou D. Characterization of four human malignant glioma cell lines. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;66(3):208–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00688585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Moulding C., Battey J., Murphy W., Vasicek T., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. Activation and somatic mutation of the translocated c-myc gene in burkitt lymphoma cells. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Cairncross J. G., Liem R. K. Identification of glial filament protein and vimentin in the same intermediate filament system in human glioma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2102–2106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filaments: structural conservation and divergence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Fields K. L. Antibodies to neurofilament, glial filament, and fibroblast intermediate filament proteins bind to different cell types of the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):115–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]