Abstract
Intrinsic excitability is a key feature dictating neuronal response to synaptic input. Here we investigate the recent observation that dentate granule neurons exhibit a more depolarized voltage threshold for action potential initiation than CA3 pyramidal neurons. We find no evidence that tonic GABA currents, leak or voltage-gated potassium conductances, or the expression of sodium channel isoform differences can explain this depolarized threshold. Axonal initial segment voltage-gated sodium channels, which are dominated by the NaV1.6 isoform in both cell types, distribute more proximally and exhibit lower overall density in granule neurons than in CA3 neurons. To test possible contributions of sodium channel distributions to voltage threshold and to test whether morphological differences participate, we performed simulations of dentate granule neurons and of CA3 pyramidal neurons. These simulations revealed that cell morphology and sodium channel distribution combine to yield the characteristic granule neuron action potential upswing and voltage threshold. Proximal axon sodium channel distribution strongly contributes to the higher voltage threshold of dentate granule neurons for two reasons. First, action potential initiation closer to the somatodendritic current sink causes the threshold of the initiating axon compartment to rise. Second, the proximity of the action potential initiation site to the recording site causes somatic recordings to more faithfully reflect the depolarized threshold of the axon than in cells like CA3 neurons, with distally initiating action potentials. Our results suggest that the proximal location of axon sodium channel in dentate granule neurons contributes to the intrinsic excitability differences between DG and CA3 neurons and may participate in the low-pass filtering function of dentate granule neurons.
Keywords: seizures, hippocampus, excitability, potassium channel, principal cell
Introduction
The factors contributing to neuronal intrinsic excitability are incompletely understood and yet are vital to the normal function of the nervous system. Intrinsic excitability influences neuronal input-output characteristics, the temporal precision of action potential generation, and behavior (Desbordes et al., 2008; Fairhall et al., 2001; Zhurov and Brezina, 2006). Intrinsic excitability is also important to many nervous system dysfunctions, including epilepsy. Different constellations, distributions and gating properties of voltage-gated channels influence intrinsic excitability (Bean, 2007; Kress and Mennerick, 2009; Vacher et al., 2008). Typically, these factors affect the voltage threshold for action potential initiation, one measure of excitability. On the other hand, passive membrane properties strongly influence a second primary measure of excitability, the rheobase, or current threshold for action potential initiation.
We examined excitability differences by comparing two hippocampal principal cell types, dentate granule (DG) neurons and CA3 pyramidal neurons. We recently described excitability differences between these cells (Kress et al., 2008), and they are key regulators of physiological and pathophysiological information flow through the hippocampus. DG neurons perform a low-pass filtering function, which includes prevention of seizure propagation into the hippocampus (Hsu, 2007). Although network properties, including inhibitory circuitry, may help govern the relative inexcitability of granule neurons (Coulter and Carlson, 2007), DG intrinsic excitability could also participate. By contrast, CA3 neurons, a major synaptic target of granule neurons, appear to be quite seizure prone (Lazarewicz et al., 2002; Meeks et al., 2005; Schwartzkroin and Prince, 1978).
Consideration of the excitability of these two cell types yields a paradox. DG neurons are morphologically compact (Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2007) and therefore have a lower rheobase than CA3 neurons. On the other hand, action potential voltage threshold of DG neurons is significantly more depolarized than in CA3 pyramidal neurons (Kress et al., 2008). Here we explored several candidate mechanisms that could contribute to the elevated action potential voltage threshold of DG neurons. These include tonic GABA currents, which might shunt depolarizing currents that dictate voltage threshold (Semyanov et al., 2004). We also considered differences resulting from voltage-gated potassium currents (Kvs) (Bekkers and Delaney, 2001) and from voltage-gated sodium currents (Navs) (Royeck et al., 2008), an important influence on action potential voltage threshold because of Nav gating properties and distribution at the site of action potential initiation (Lai and Jan, 2006).
We found cell type differences primarily in the distribution of Navs. To assess the contribution of these differences, we constructed simulations of granule neurons and CA3 pyramidal neurons. Simulations revealed that a strong contributor to the shape and voltage threshold of action potentials is the restricted proximal distribution of Navs at the DG axonal initiation site. Proximal axon initial segment (AIS) channel distribution in DG neurons had two effects on action potential threshold. First, the voltage threshold increased (depolarized) in the proximal axon initiation site because of the nearby somatodendritic current sink. Secondly, the somatic voltage threshold tracked more closely with the AIS voltage threshold because of the shorter distance between recording site and initiation site. Thus, the location of the action potential initiation site relative to the soma plays an important role in cell type excitability differences.
Materials and Methods
Slice preparation
Experiments were performed on hippocampal slices from postnatal day 19 (P19) to P23 Sprague Dawley rats as previously described (Kress et al., 2008). In accordance with Washington University Animal Studies Committee, rats were anesthetized with isoflurane and decapitated. The brain was removed and glued onto a Vibratome 1000 specimen holder (Vibratome, St. Louis, MO). Transverse (300 μm) slices were cut in ice-cold, modified artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) (in mM: 125 NaCl, 25 Glucose, 25 NaHCO3, 2.5 KCl, 1.25 NaH2PO4), equilibrated with 95% oxygen, 5% CO2 plus 0.5 mM CaCl2, 3 mM MgCl2, and 2 mM kynurenic acid. Slices were then incubated at 32-34° C for 30 min in aCSF containing 2 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM MgCl2 and subsequently stored at room temperature. Except when noted, drugs were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). All Alexa Fluor reagents were from Invitrogen/Molecular Probes (Carlsbad, CA).
Electrophysiology
Slices were perfused at 2-4 mL min-1 with oxygenated aCSF containing 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, and 2 mM kynurenic acid at 25 ± 1°C. DG cells and CA3 pyramidal neurons were identified using infrared differential interference contrast on an upright Nikon Eclipse E600FN microscope and a cooled digital camera (Roper Scientific, Tucson, AZ) controlled with MetaMorph software (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Somatic whole-cell recordings were made with borosilicate patch pipettes (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL; Sutter Instruments, Novato, CA), having open tip resistance of 3-7 MΩ.
To determine if altering intracellular chloride concentration affects action potential properties either a potassium gluconate (chloride reversal potential, ECl=-50 mV) or potassium chloride (ECl = 0 mV) intracellular pipette solution was utilized. The composition of potassium based internal solutions was as follows (in mM) 115 potassium gluconate or KCl, 20 KCl, 10 HEPES, 2 EGTA, 2 MgATP, 0.3 Na2GTP, 10 sodium phosphocreatine, and 100-200 μM Alexa Fluor 488. pH was adjusted with KOH to pH 7.35. In some experiments Alexa Fluor 568 hydrazide and/or 5 mg/mL biocytin were used for axon visualization instead of Alexa Fluor 488. To determine if potassium channels contribute to action potential properties, a tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA-Cl) intracellular pipette solution was utilized with the following composition (in mM): 135 TEA-Cl, 10 HEPES, 2 EGTA, 2 MgATP, 0.3 Na2GTP, 10 sodium phosphocreatine, and 100-200 μM Alexa Fluor 488. pH was adjusted with CsOH to pH 7.35. After a somatic recording was established, cells were allowed to fill with the intracellular solution for approximately 10 minutes. Fluorescent dye excitation with a metal halide lamp was used to visualize the attached axon with limited light exposure. Only somatic whole-cell data from neurons with axons 100 μm or longer were utilized.
Nucleated out-side-out patches were used to record somatic sodium currents from both DG and CA3 pyramidal neurons. To isolate nucleated patches, after a somatic whole-cell recording was established, negative pressure (70-200 mbar) was applied and the patch pipette was withdrawn slowly, a small negative pressure (10-30 mbar) was maintained during the recording. The resulting nucleated patch was visualized under infrared differential interference contrast microscopy to be spherical and under fluorescence to lack connectivity to the neuron’s processes. A cesium chloride intracellular pipette solution was utilized, composed of (in mM): 125 CsCl, 10 HEPES, 10 EGTA, 2MgCl2, 0.3 Na2GTP, 10 sodium phosphocreatine, and 100-200 μM Alexa Fluor 488. pH was adjusted with CsOH to pH 7.35. 20 mM TEA-Cl was bath applied to further block potassium channels. Leakage and capacitive currents were subtracted on-line using the pipette capacitance compensation circuit of the amplifier and a P/-4 protocol. Voltage-clamp commands were similar to previous work (Martina and Jonas, 1997). Nucleated patches were held at -90 mV throughout the experiment. Before each test pulse, a 50 ms pulse to -120 mV was applied to obtain complete recovery from fast inactivation. Test pulses were applied every 5 s. Traces shown in the figures represent single sweeps.
All recordings were obtained using a MultiClamp 700B amplifier (Molecular Devices) and pClamp 9.2 software (Molecular Devices). Somatic bridge balance and pipette capacitance were adjusted using MultiClamp 700B Commander software. Whole-cell data were acquired at 100 kHz, filtered at 10 kHz using an 8-pole Bessel filter and digitized using a DigiData 1322A 16-bit A/D converter (Molecular Devices). Somatic sodium currents were sampled at 20 kHz or 40 kHz. Whole-cell somatic access resistance was monitored continuously, and cells with unstable access resistance (>20% change) or with values > 20 MΩ were excluded from analysis. When necessary, a small bias current was injected to maintain a similar baseline membrane potential (near -84 mV in both cell types) before depolarizing current injections. Reported values of the membrane potential and action potential thresholds have been corrected for the liquid junction potential of +14 mV with potassium gluconate, +4.4 mV with potassium chloride, +2.8 mV with CsCl, and -1.7 mV with TEA-Cl estimated from Igor XOP Patcher’s Calculator (Wavemetrics, Oswego, OR). All DG neurons studied exhibited electrophysiological and morphological properties of mature granule neurons (Liu et al., 2000; Liu et al., 1996; Overstreet et al., 2004).
Electrophysiology Data Analysis
Analysis was performed with custom written programs in Igor Pro 6.0 (Wavemetrics). Data were imported and filtered with Igor Filter Design Laboratory lowpass Bessel 8-pole at 5 kHz. First order derivatives (dV/dt) of the somatic membrane potential were calculated using a central differences algorithm. Phase plots were constructed from the first derivative of the somatic membrane potential (dV/dt) versus the somatic membrane potential. Action potential voltage threshold was calculated by using the first inflection point of phase plots. The membrane potential at which phase plot slope reached 10 mV ms-1 (Kress et al., 2008; Naundorf et al., 2006; Shu et al., 2007) was denoted voltage threshold. We also examined the slope of phase plots at action potential threshold (Naundorf et al., 2006; Yu et al., 2008). Slopes of the phase plot at the three data points bracketing spike threshold at 10 mV ms-1 were calculated using linear regression. For calculation of voltage threshold and slope from phase plots, the baseline dV/dt value resulting from the passive membrane response to current injection was subtracted.
Imaging and Immunocytochemistry
For studies of Nav localization, slices were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate buffered saline for 30-35 min, permeabilized and blocked with 6% goat serum, 5% bovine serum albumin, 0.3% tritonX-100, 3 mM sodium azide for 2 hrs at 25° C. Primary antibody incubation included the above solution plus 4 μg/mL of monoclonal anti-sodium channel antibody, clone K58/35 (PanNaV antibody, Sigma-Aldrich), for 32-34 hrs at room temperature. Secondary antibody incubation was with a goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488, goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 555 for 2 hr at 25°C or with Zenon mouse IgG1 Alexa Fluor 555 applied according to kit instructions (Invitrogen/Molecular Probes). Slices were then incubated with 10 μM Hoechst 33342 for 20 min at 25° C, washed with phosphate buffered saline, and mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade Reagent (Invitrogen/Molecular Probes) onto microscope slides. To identify Nav isoforms, anti-NaV1.2 (monoclonal, clone K69/3, NeuroMabs, Davis, CA; 1:100) and anti-NaV1.6 (polyclonal anti-NaV1.6, Chemicon International/Millipore, Billerica, MA; 1:500) antibodies were utilized.
To quantify the intensity, area, and density of Nav immunoreactivity within the dentate gyrus and CA3 pyramidal subfield, three-dimensional images were acquired using a Nikon C1 laser scanning confocal system. Using Metamorph, a three-dimensional mask of the PanNaV positive AIS trajectory was plotted. The Metamorph kymograph function was used to measure the average PanNaV fluorescence intensity, area, and integrated intensity were quantified. In our case, the kymograph function of Metamorph was used to create a 2-dimensional image with the x-axis representing the combined “x” and “y” dimensions of the traced axon within the confocal stack and the y-axis representing the course of the traced axon in the “z” dimension from a confocal x-y-z stack. Similar analysis parameters have been described (Kress et al., 2008). To quantify NaV1.2 and NaV1.6 immunoreactivity, a PanNaV mask was transferred onto the NaV1.2 or NaV1.6 kymograph, and the PanNaV positive region was used to quantify NaV1.2 and NaV1.6 average intensity and integrated intensity. Data from 5-6 axons DG and 5-6 CA3 axons in each acute hippocampal slice were pooled and expressed as a percent difference on DG and CA3 axons. Data were collected from at least 3 independent experiments.
Multi-compartment Modeling
All simulations were implemented and run with NEURON version 6.2 (Hines and Carnevale, 2001). We added a multi-compartment axon to a previously published CA3 pyramidal cell model (Lazarewicz et al., 2002)(obtained from http://senselab.med.yale.edu/modeldb/ShowModel.asp?model=20007). The model used essentially similar somatodendritic ion channel distribution as the previously published model (Lazarewicz et al., 2002). The only change was a decrease in hyperpolarization-activated H current to better account for passive membrane responses of our experimental recordings. This was decreased to 10% in the soma and 50% in the dendrites of our CA3 model and to 0.001% of the published CA3 value (Lazarewicz et al., 2002) in the soma and dendrites of our DG model.
CA3 axon morphology was based on previous measurements (Kress et al., 2008), with an initial diameter of 2.5 μm and a taper to 1 μm by 100 μm from the soma, extending to a final length of 190 μm (resulting in 189 segments). The axonal NaV distribution was based on previous immunostaining of fluorescently filled CA3 neurons (Meeks and Mennerick, 2007) with NaV distribution extending from the soma to 80 μm. The peak axonal NaV density (of 0.5 Scm-2) was 20 times greater than the somatic NaV density (0.025 Scm-2). In both types, modeled somatic NaV biophysical properties were identical to those used previously (Lazarewicz et al., 2002) and similar to data obtained from nucleated outside-out patches of DG and CA3 neurons, shown in Figure 6B. To account for more hyperpolarized activation of AIS Navs (Colbert and Pan, 2002; Kole and Stuart, 2008), simulated AIS Navs had a half-activation voltage 5 mV more hyperpolarized than the simulated somatic Nav channels. In some simulations we did not employ the hyperpolarized Nav activation shift in the AIS; these results are given in Supplemental Figure 2. For potassium currents, we used axonal ID and IA densities identical to previously published dendritic values (Lazarewicz et al., 2002).
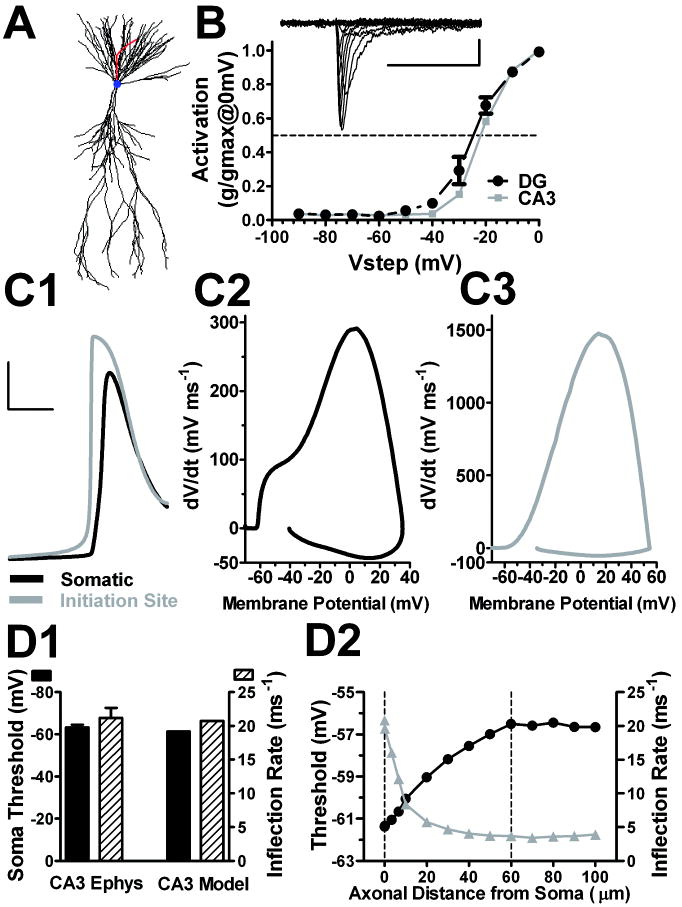
Figure 6.
Action potential properties of a CA3 multi-compartment model. A. CA3 reconstruction was imported into NEURON, resulting in 821 segments (morphology adapted from (Ishizuka et al., 1990); compartment model from (Lazarewicz et al., 2002)) with an axon added based on our previous measurements (Kress et al., 2008), of an AIS initial diameter of 2.5 μm that tapered to a final diameter of 1 μm. The axonal Nav distribution was based on previous immunohistochemistry measures from our lab with Nav distribution extending to the distal axon 80 μm from the soma (Meeks and Mennerick, 2007). Somatic and dendritic channel distributions were from existing models (Lazarewicz et al., 2002). B. Conductance/voltage profile of Nav currents in nucleated patches from DG (black circles) and CA3 neurons (gray squares) (n = 5). The inset shows sample traces evoked in a DG patch by voltage pulses from -90 mV to +30 mV, the protocol used to generate the summary. Somatic and axonal Nav biophysical properties were consistent with this activation profile, with a half-activation voltage of -30 mV. C1-C3. Somatic (black) and AIS (gray) action potentials (C1) with their corresponding phase plots (C2-3). The action potential was elicited with a just-suprathreshold current injection of approximately 134 pA. Calibration bars for the action potential traces are 25 mV and 2 ms. D1. CA3 model action potential threshold and inflection rate were similar to experimentally derived CA3 neuron responses (n = 9 CA3 pyramidal neurons)(Kress et al., 2008). D2. CA3 model action potential voltage threshold and inflection rate as a function of the axonal distance from soma. Dashed line at 60 μm is the site of action potential initiation; dashed line at 0 μm is the soma compartment.
All compartments had a specific intracellular resistivity (Ra) of 200 Ωcm. The somatic and axonal compartments had a specific membrane resistivity (Rm) and membrane capacitance (Cm) set to 60000 Ωcm2 and 1 μF/cm2, respectively. The dendritic membrane values for Rm and Cm were set to 30000 Ωcm2 and 2 μF/cm2, respectively to account for passive properties of dendritic spines. Resting membrane potential was set to -70 mV. More negative resting potentials up to -84 mV did not change threshold or phase plot inflection. Passive properties of the two cell types were reasonably reproduced by the two models. The CA3 action potential simulation protocol consisted of a short (20ms) pulse of minimal somatic current injection to elicit an action potential 15-16 ms after current onset, generating an action potential threshold and phase plot inflection rate similar to the experimentally derived CA3 neuron responses (Kress et al., 2008).
Simulations of DG neurons were performed on morphology imported from a previous DG model (Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2007)(obtained from http://senselab.med.yale.edu/modeldb/ShowModel.asp?model=95960), with the same constellation of channels and channels densities utilized in the above CA3 model except for Nav variations (Figure 8). The axon of the DG neuron was composed of 189 segments. It began with a diameter of 1.4 μm and tapered to final diameter of 0.5 μm by 100 μm from the soma, extending to a final length of 190 μm. The DG action potential simulation protocol was a short (20ms) pulse of minimal somatic current injection to elicit an action potential between 15-16 ms after current onset. All simulations modeled conditions at 25° C.
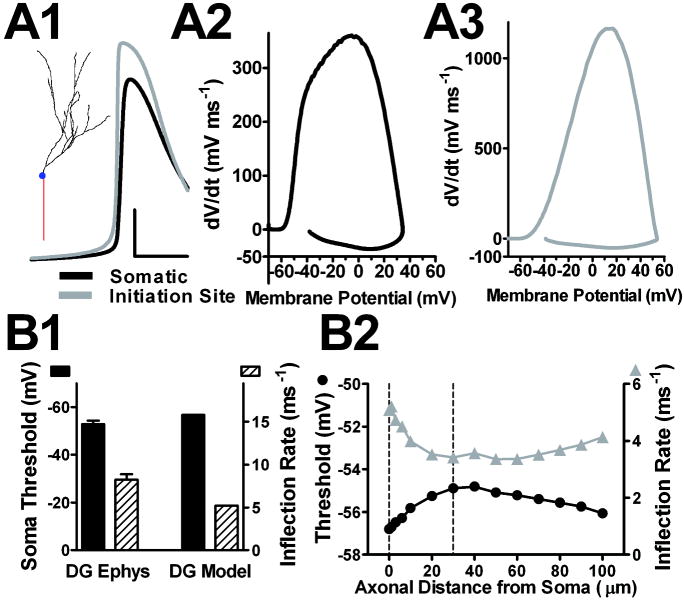
Figure 8.
Detailed action potential properties of a DG multi-compartment model. The DG model shown here in detail is Figure 7, simulation #7. A1. The inset shows the DG morphology adapted from Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2007, resulting in 253 segments. The trace is the simulated action potential waveform generated with a just-suprathreshold current injection (35 pA). The initiation site action potential precedes the somatic action potential and has a shallower inflection rate. Calibration: 25 mV and 2 ms A2. The model DG somatic phase plot resembled the experimentally obtained DG somatic phase plot (Figure 1A), with similar maximum dV/dt values. A3. Initiation site phase plot. The initiation site was 30 μm from the soma. B1. DG model action potential voltage threshold and inflection rate are similar to the experimentally derived (DG Ephys) DG neuron responses (n = 11 DG neurons)(Kress et al., 2008). B2. DG model action potential voltage threshold and inflection rate axonal compartments of varying distance from soma. Dotted line at 30 μm indicates the site of action potential initiation; dotted line at 0 μm represents soma.
Analysis and statistics
Graphs were constructed with Sigma Plot 10.0 (Systat, San Jose, CA), Prism 5.0 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA), or Wavemetrics Igor 6.0 (Wavemetrics). Variability is indicated in the text and figures as standard error of the mean. Unless otherwise indicated, statistical comparisons were made using two-tailed Student’s t-test.
Results
Chloride and potassium conductances do not influence DG voltage threshold
We previously found that DG neurons have a more depolarized threshold than pyramidal neurons. DG neurons appear to be the outlier cell type; voltage threshold in our CA3 measurements (Kress et al., 2008), is similar to others’ measures of other pyramidal cell types (Shu et al., 2007). Therefore, we concentrated on factors that could be responsible for the high threshold of granule neurons. DG neurons are known for their strong tonic GABA current, mediated by ambient GABA acting at high-affinity, extrasynaptic GABAARs (Farrant and Nusser, 2005; Glykys et al., 2008; Stell and Mody, 2002). Although pyramidal neurons also possess tonic currents (Glykys et al., 2008), we hypothesized that the tonic current in DG cells may play a more prominent role in shunting action potential initiation and raising threshold. To test whether this current could impose a chloride mediated shunting influence on DG excitability, we performed two experiments (Figure 1). Our primary measures of excitability were taken from phase plots (Figure 1A, B)(Bean, 2007), plots of the membrane potential slope (dV/dt) versus the membrane potential. We used a primary criterion of the membrane potential at a phase plot slope of 10 mV ms-1 to estimate DG action potential threshold (Figure 1B, 1C).
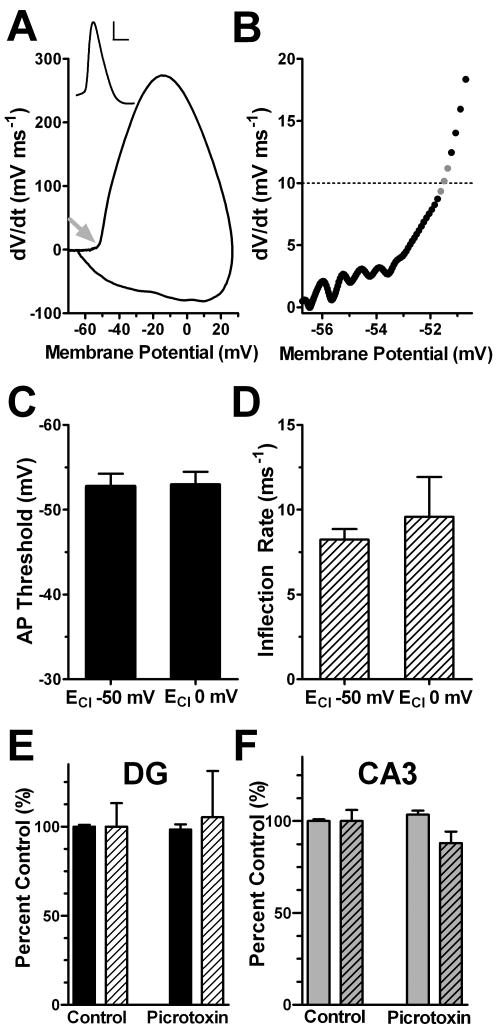
Figure 1.
Altered intracellular chloride concentration and GABA receptor antagonists do not influence DG action potential voltage threshold or inflection rate. DG action potentials were elicited with a brief (20 ms) minimal current injection in the presence of either a potassium gluconate (ECl -50 mV) or a potassium chloride (ECl 0 mV) internal solution. A. Phase plot, the slope of the somatic membrane potential (dV/dt) versus the somatic membrane potential, of a DG neuron filled with potassium gluconate. The arrow points to the action potential voltage threshold. Inset shows the somatic membrane potential record of an action potential used to generate the phase plot (scale bar 20 mV, 1 ms). The membrane potential and action potential thresholds have been corrected for the liquid junction potentials. B. The membrane potential at which phase plot slope reached 10 mV ms-1 (dashed line) was denoted threshold. The slope of the phase plot at the three data points bracketing spike threshold at 10 mV ms-1 (gray data points) were calculated using linear regression and denoted as an inflection rate (ms-1). Phase plot analysis yields a voltage threshold at -51.49 mV and an inflection rate of 7.25 ms-1. C and D. Neither action potential threshold nor inflection rate was influenced with altered intracellular chloride concentration (n =7-11 p>0.05). (E) and (F) GABA receptor antagonist, picrotoxin (100 μM) does not influence DG (E) or CA3 (F) voltage threshold or inflection rate. Action potentials were elicited with a brief (20 ms) minimal current injection in the presence of either a bath solution or 100 μM picrotoxin (with potassium gluconate pipette solution). Solid bars represent the action potential voltage threshold, while hashed bars represent the inflection rate (n=3-9 p<0.05).
Under DG cell somatic current clamp, we elicited action potentials with just-suprathreshold current stimulation with one of two pipette solutions designed to alter the driving force for chloride (Figure 1C, D). With symmetrical chloride concentrations inside and outside the cell, the chloride reversal potential (ECl) was set to near 0 mV. We reasoned that a chloride conductance (GABAA receptor mediated or otherwise) might have an excitatory influence and lower action potential voltage threshold compared with our standard low intracellular chloride solution (ECl at -50 mV). We found that symmetrical chloride did not significantly influence the DG action potential voltage threshold (Figure 1C). We also examined the action potential phase plot inflection rate, which is shallower in DG neurons than in pyramidal neurons (Kress et al., 2008). The inflection rate of phase plots has been variably associated with unusual gating kinetics of Navs responsible for action potential initiation (Naundorf et al., 2006) or with the electrotonic separation between the axonal initiation site and the soma (Yu et al., 2008). We found that the inflection was unaffected by changes in ECl. (Figure 1D). These observations indicate that tonic GABA currents are unlikely to shape the action potential voltage threshold or the inflection rate in DG neurons under our experimental conditions and therefore are not responsible for the depolarized DG action potential threshold.
As an additional test, we bathed hippocampal slices in a GABAAR antagonist (100 μM picrotoxin) while eliciting action potentials in either DG or CA3 neurons (Figure 1E and F, respectively). A standard potassium gluconate pipette solution was used for this experiment. Action potential voltage thresholds and phase plot inflection rates did not significantly change in the presence of picrotoxin (Figure 1, solid and hashed bars, respectively). These data suggest that under our experimental conditions, the network is sufficiently quiescent that GABA accumulation does not affect the excitability of DG neurons or CA3 neurons, defined by voltage threshold. Thus, chloride conductances, including any located on the axon, do not influence action potential voltage threshold under our conditions in either DG or CA3 neurons.
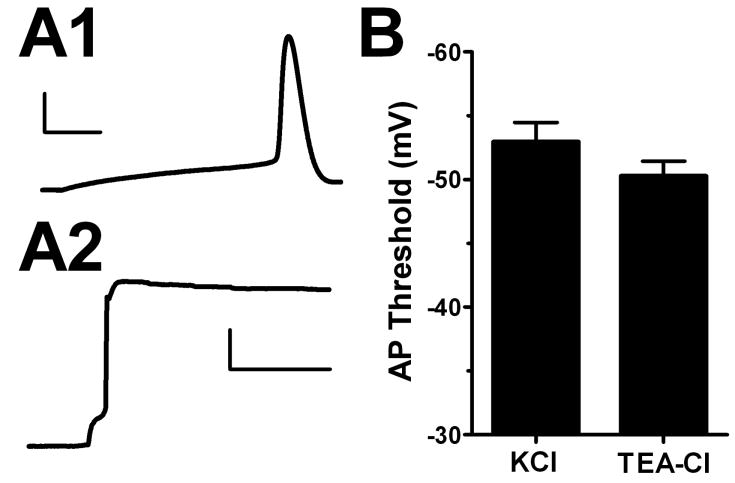
It is possible that subthreshold potassium currents, especially those on the axon, might participate in setting voltage threshold (Bekkers and Delaney, 2001; Shah et al., 2008). Differential density and/or distribution of potassium channels on DG and CA3 neurons could contribute to the observed threshold and phase plot inflection rate differences. To test this, we filled neurons with 135 mM TEA-Cl to block most potassium channels and to alter EK in remaining unblocked channels. Our approach is therefore expected to affect all leak and Kv contributions. Although TEA-filled cells showed strongly depolarized resting potentials, we compensated this using a bias current to maintain a negative resting membrane potential. To our surprise, DG action potentials elicited under these conditions with minimal depolarization showed no significant difference in either action potential voltage threshold or phase plot inflection rate (Figure 2 B). These results indicate that DG neuron potassium conductances do not significantly contribute to the cells’ depolarized action potential threshold.
Figure 2.
Blocking potassium channels does not change DG voltage threshold. Action potentials were elicited with a brief depolarization from -70 mV with KCl (A1) (scale bar 25 mV, 3 ms) or TEA-Cl (A2) (scale bar 25 mV, 150 ms) intracellular pipette solution. The traces represent different cells. B. Summary. DG action potential (AP) voltage threshold was not significantly changed when potassium channels were blocked (n=6-9 p>0.05).
Expression of NaVs on DG and CA3 axons
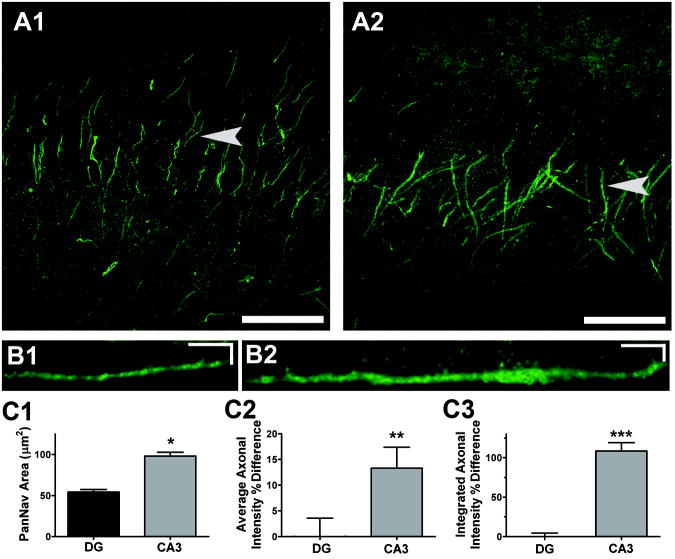
NaVs participate critically in setting action potential voltage threshold (Hodgkin and Huxley, 1952). NaV axonal density, kinetics, and isoform have all been suggested to participate in setting initial neuronal excitability (Colbert and Pan, 2002; Kole et al., 2008; Royeck et al., 2008). Although NaV distribution is more proximal on DG axons than CA3 axons (Kress et al., 2008; Meeks and Mennerick, 2007), it is unclear if CA3 and DG axons differ in the isoform and/or density of NaVs in the axon initial segment. Overall axonal DG and CA3 NaV density was estimated using immunostaining with a pan-sodium channel (PanNaV) antibody, directed against the alpha subunit (intracellular III-IV loop) of all vertebrate NaVs (Figure 3). Representative confocal images of PanNaV staining on DG (Figure 3A1) and CA3 (Figure 3A2) axon initial segments show high density of axonal NaVs. We previously confirmed that the PanNav distribution under these conditions is located on the axon initial segment by combining fluorescent dye fills with PanNaV immunolabeling, and by co-localization of PanNaV staining with ankyrin G staining (Kress et al., 2008; Meeks and Mennerick, 2007). Figures 3A1 and 3A2 are confocal projections, from which individual fiber staining is difficult to discern. However, the example in Figure 3B1 is magnified and rotated, as described in the Methods, to highlight a single PanNaV positive axon (arrow in Figure 3A1). Quantitative analysis of florescence intensity along the axon was used to calculate the average axonal area (Figure 3C1), average intensity (Figure 3C2) and the integrated intensity (Figure 3C3) of PanNaV immunoreactivity on both DG and CA3 axons. This analysis revealed a higher density (~15%) and larger area (~2 fold) of PanNaV immunostaining in the axon initial segment of CA3 neurons compared with DG neurons (Figure 3C). Although we cannot confirm that immunostaining of permeabilized cells represents functional membrane channels, these results suggest that differences in distribution of channels could participate in shaping CA3 action potentials.
Figure 3.
The CA3 pyramidal axons have a greater area and density of Nav alpha-subunit immunoreactivity than DG axons. A. PanNav immunoreactivity within DG (A1) and CA3 (A2) regions shown by three dimensional confocal reconstructions. Scale bars are 50 μm. B1-2. Stretched side views (created with Metamorph kymograph function), of PanNav staining from a representative DG axon (B1) and CA3 axon (B2) indicated by arrows in A. Scale bars are 5 μm and 5 μm. C1-3. The axonal area (C1), density (C2), and total sum (C3) of PanNav staining on DG (n=32) and CA3 (n=32) axons. Density and total sum are expressed as a percent difference on DG and CA3 axons. *, P<0.00001; **,P<0.02; ***, P<0.0001.
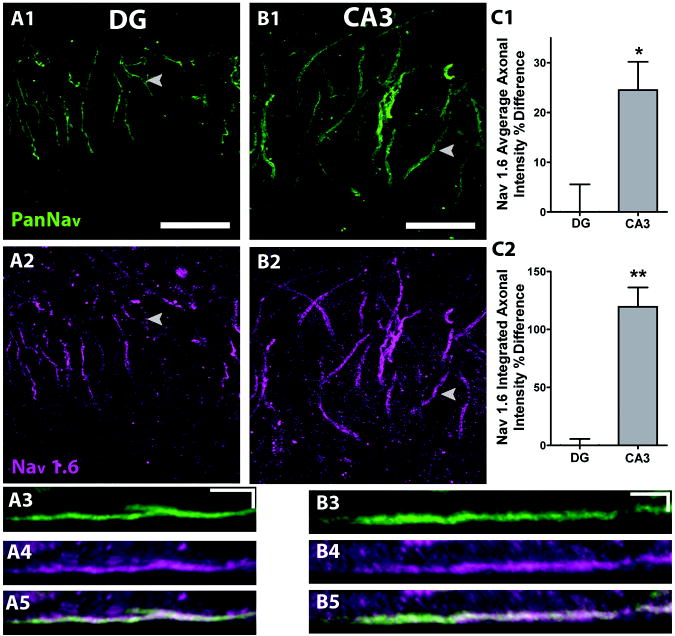
Additionally, differences in action potential voltage threshold could be caused by the expression of kinetically distinct NaV isoforms (Royeck et al., 2008). In order to test for differential NaV isoform expression, we performed quantitative fluorescence analysis of NaV1.6 and NaV1.2 immunoreactivity, thought to be the major axonal isoforms (Van Wart and Matthews, 2006; Van Wart et al., 2007). In each case, PanNaV staining was used as a guide in double immunofluorescence assays. Using the PanNaV antibody (Figure 4A1, 4B1) with the NaV1.6-specific antibody (Figure 4A2, 4B2), we found that NaV1.6 immunoreactivity was confined to the PanNaV positive area on DG (Figure 4A5) and CA3 axons (Figure 4B5). As observed with PanNaV staining, there was a higher density and larger area of NaV1.6 immunostaining in the axon initial segment of CA3 neurons compared with DG neurons (Figure 4C). These data lend further support to the hypothesis that different NaV distributions on axons might influence the shape of action potentials in the two cell types.
Figure 4.
CA3 axons have a greater area and density of Nav1.6 than DG axons. Immunoreactivity for Nav1.6 co-localizes with PanNav on DG (A1-2) and CA3 (B1-2) axons (scale bars 25 μm). A3-5. Kymographs of a representative DG axon for PanNav (A3), Nav1.6 (A4) and overlay (A5) (scale bars 5 μm, 5 μm). B3-5. Kymographs of a representative CA3 axon for PanNav (B3), Nav1.6 (B4) and overlay (B5) (scale bars 5 μm, 5 μm). C1-2. Quantification of the density (C1) and total sum (C2) of Nav1.6 axonal immunoreactivity expressed as a percent difference on DG and CA3 axons. N=22. *, P<0.004;**, P<0.0001.
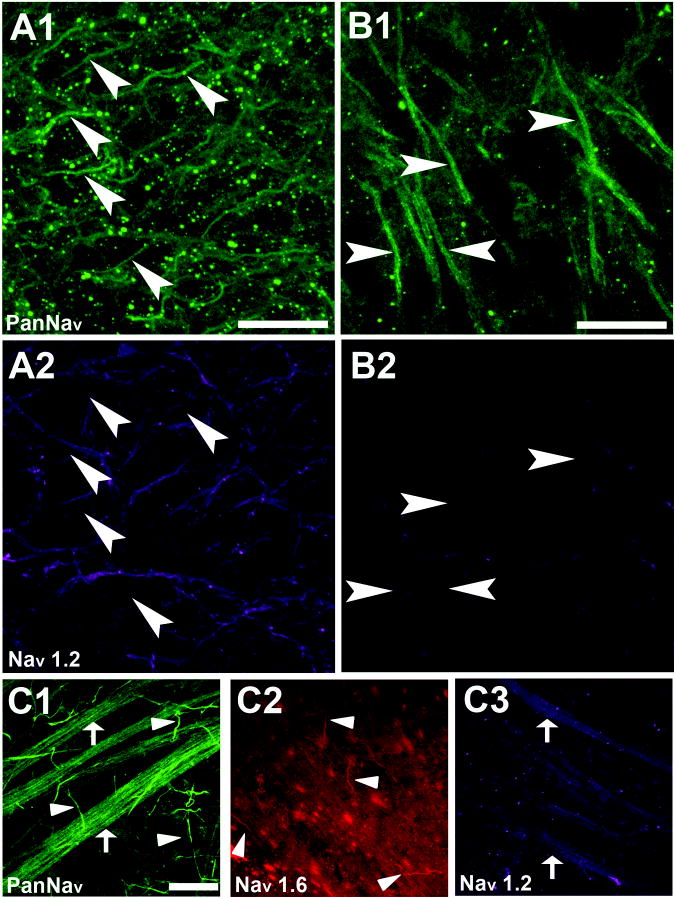
In contrast to NaV1.6 staining, NaV1.2 immunoreactivity was not detectable in either DG or CA3 axons in regions of high PanNaV staining (Figure 5A, B, arrowheads), although we observed staining of unclear origins within the hilus (Figure 5A2). The lack of axonal initial segment NaV1.2 immunoreactivity calls antibody sensitivity into question under our experimental conditions. In order to test the sensitivity of the NaV1.2 antibody, we stained retinal tissue with similar fixation and permeabilization conditions to those used in hippocampal slices. We used retina as a positive control because of the well-characterized NaV1.2 and NaV1.6 isoform expression from previous studies (Boiko et al., 2003; Van Wart and Matthews, 2006; Van Wart et al., 2007). Both NaV1.6 and NaV1.2 immunoreactivity was co-localized within regions of PanNaV positive staining of rat retinal whole-mounts: PanNaV (Figure 5C1) and NaV1.6 (Figure 5C2) (arrowheads) co-localized on the ganglion cell axon initial segments, and the nerve fiber layer was immunoreactive for both PanNav (Figure 5C1) and NaV1.2 (Figure 5C3) (arrows). These results are in agreement with previous work (Van Wart and Matthews, 2006; Van Wart et al., 2007) and validate the sensitivity of the NaV1.2 antibody in our experiments. We therefore conclude that NaV1.2 is unlikely to play a strong role at the site of action potential initiation in either DG neurons or CA3 neurons and that NaV1.6 is the major axonal initial segment isoform in juvenile rat hippocampus.
Figure 5.
Immunoreactivity for Nav1.2 does not co-localize with PanNav on DG and CA3 axons but is found on the rat retinal nerve fiber layer. A1-2. DG immunoreactivity for PanNav (A1) and Nav1.2 (A2). Although there is hilar staining with the Nav1.2 antibody, it does not co-localize with the PanNav antibody staining (arrows) and therefore is not associated with DG AIS (scale bar 25 μm). B1-2. CA3 immunoreactivity for PanNav (B1) and Nav1.2 (B2). Again there is no detectable co-localization. C1-C3. Whole-mount rat retina positive control for antibody sensitivity. Immunoreactivity was detected with PanNav (C1) and Nav1.6 (C2) on ganglion cell AIS. Immunoreactivity was detected with Nav1.2 (C3) in the nerve fiber layer (scale bar 25 μm). These patterns are as previously published (Boiko et al., 2003; Van Wart and Matthews, 2006; Van Wart et al., 2007).
CA3 and DG multi-compartment modeling
To probe whether geometrical differences and/or the above differences in NaV distribution could contribute to the depolarized threshold and slower inflection rate of DG neurons compared to CA3 neurons, we performed in silico experiments. The strategy was to employ a previously published CA3 multi-compartment model (Lazarewicz et al., 2002)(Figure 6A), adapted to include a 100 μm long axon, and to adjust Nav density to recapitulate important features of an experimentally derived CA3 neuron action potential. We gave particular attention to the following CA3 action potential features from our previously published work (Kress et al., 2008; Meeks and Mennerick, 2007): action potential initiation within the axon initial segment; action potential voltage threshold of -63.3 ± 1.3 mV (membrane potential at a dV/dt of 10 mV ms-1); phase plot inflection rate at threshold of 21.2 ± 1.3 ms-1; somatic maximum dV/dt amplitude of 311 ± 17.5 mV ms-1; 2 inflection points on the CA3 neuron phase plot (Kress et al., 2008). Details of the CA3 model are given in the Methods. The axonal architecture was based on previous measurements (Kress et al., 2008), with an AIS initial diameter of 2.5 μm (Figure 6A). The axonal NaV distribution profile was similar to that used by other groups (Kole and Stuart, 2008; Mainen et al., 1995; Yu et al., 2008). NaV density was 20-fold greater in the AIS than in the soma and extended from the hillock to 80 μm distal from the soma. The higher axonal density was warranted by immunostaining results, previous literature (Kole et al., 2008), and by previous simulations (Kole and Stuart, 2008; Mainen et al., 1995; Shu et al., 2007). Through tests in pilot simulations, we chose a 20-fold higher density in the axon based on the overall phase plot appearance (peak amplitude of dV/dt, inflection rate, voltage threshold, and the overall shape; see Figure 6C2).
To determine appropriate NaV activation kinetics, we measured the NaV activation curves from DG and CA3 nucleated-outside out patches (Figure 6B). We found no difference in the activation of currents from these two cell types, so we modeled somatic Nav channels with a half-maximum activation voltage of -30 mV (Figure 6B). These Nav kinetics are in agreement with previously published studies (Chen et al., 2008; Martina and Jonas, 1997; Rush et al., 2005). Previous studies show that AIS Nav activation is more hyperpolarized than somatic Navs (Colbert and Pan, 2002; Kole and Stuart, 2008), including DG axonal channels (Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2008b). We therefore incorporated this difference into our models.
To determine if the CA3 model produced action potentials with features similar to the experimentally derived CA3 action potentials, a short somatic current injection was implemented to evoke a simulated action potential. The resulting CA3 model action potential shared salient features with our experimental data. The action potential initiated in the modeled axon compartment as indicated by the timing between the somatic and AIS action potentials (Figure 6C1). As the action potential developed proximally from the site of initiation to the soma, the large current supplied by the axonally derived spike preceded and overlapped with the current supplied by somatic compartment, resulting in a characteristic double-hump in the somatic phase plot (Figure 6C2). The action potential voltage threshold, phase plot inflection rate, and peak dV/dt of the simulated CA3 neuron were similar to the experimentally derived CA3 neuron responses (Fig. 6D1). These results confirm that the modeled CA3 action potential shows hallmarks similar to experimentally generated CA3 action potentials (Kress et al., 2008).
Consistent with other recent findings (Kole and Stuart, 2008), our simulations showed that the voltage threshold of the axonal initiating compartment is actually more depolarized than the voltage threshold of the action potential measured at the cell body (Figure 6D2), despite the hyperpolarized activation voltages of AIS versus soma Navs. As the action potential developed and propagated toward the soma from the initiation site (60 μm from the soma), the voltage threshold, defined by the phase plot slope of 10 mV ms-1 in the relevant compartment, became more hyperpolarized, and the phase plot inflection rate increased (Figure 6D2). The difference in action potential threshold between the soma and initiation site (dotted lines Figure 6D2) was approximately 4.5 mV. This can also be appreciated by examining either raw action potential waveforms from the two compartments (Figure 6C1) or by comparing phase plots derived from the two compartments (Figure 6C2 and C3).
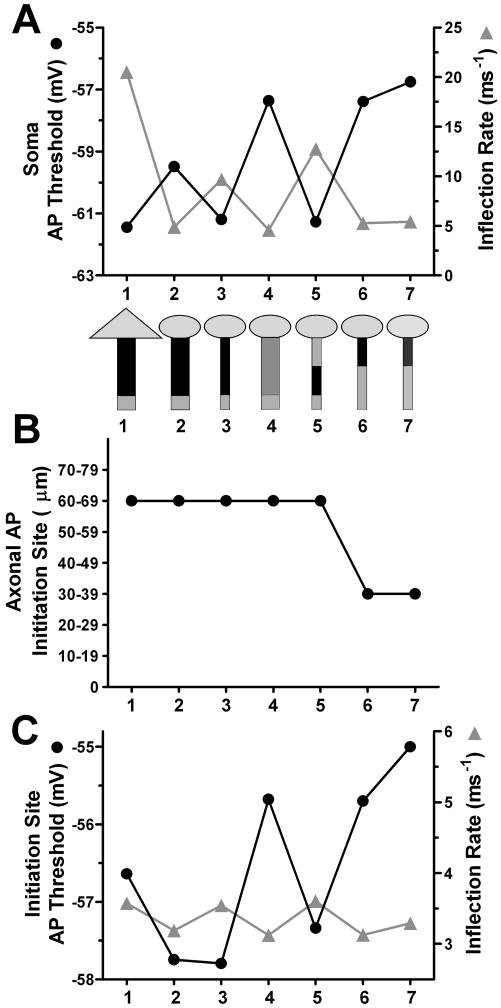
These observations suggest one reason for an apparently depolarized threshold in DG neurons. Because of electrotonic proximity of somatic recordings to initiation in DG neurons (Kress et al., 2008), DG somatic recordings may reflect a voltage threshold closer to that of the initiating axonal compartment’s depolarized threshold. To explore this idea and other potential contributors, we systematically altered morphology and Nav distribution to match observations made in DG neurons. First, we placed the same constellation of channels and channel densities used in the above CA3 model onto a DG somatodendritic morphology, which was adapted from previous studies (Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2007). Our first iteration of the DG model used an axon identical in geometry and channel distribution to the CA3 model (Figure 7, simulation #2). A short somatic current injection was simulated to elicit a DG action potential. The somatic voltage threshold and inflection rate were measured and compared with the CA3 model action potential (Figure 7A, simulation #1 versus #2). We also examined the site of action potential initiation (the first axonal location to reach the action potential peak) (Figure 7B) and the action potential voltage threshold and inflection rate in this initiating compartment (Figure 7C). The change in somatodendritic morphology alone (simulations #1 and #2) resulted in a dramatic decrease of phase plot inflection rate that nearly matched the inflection rate of an experimentally derived DG action potential (Figure 1A). Action potential voltage threshold depolarized by ~2 mV with the morphology change. Therefore, somatodendritic morphology can strongly influence the phase plot inflection and can influence voltage threshold more subtly.
Figure 7.
Constructing a model with DG action potential characteristics from the CA3 model. A1. Cartoons depict the sequential changes made to the CA3 model (simulation #1) to produce a simulated DG neuron and to test contributions to the depolarized threshold and altered action potential shape. Triangle depicts the CA3 soma, circle represents DG soma. The rectangle represents a 100 μm long axon, with either a CA3-like initial diameter (2.5 μm) and AIS taper (taper not represented) or a DG-like diameter (1.4 μm) and AIS taper. Gray shading represents both the location and relative density of Nav channels. Simulation #7 includes a cell-wide decrease in channel density of 20% to match experimental observations and to simulate experimentally observed phase plot shape. The constellation of channels and the channel densities were the same among all simulations, except for the indicated changes in Nav location and density. The graph shows the somatic action potential threshold (filled circles, solid line) and inflection rate (gray triangles and line) with model modifications. Numbers indicate simulation number for reference. B. The axonal initiation site (first to peak) from the indicated simulations. C. Initiation site action potential voltage threshold and inflection rate corresponding to the indicated simulations. The model most fully recapitulating DG action potential characteristics is simulation #7.
However, both the inflection rate and the voltage threshold reverted partially back toward CA3 values when the diameter of the axon was adjusted to match realistic DG neuron measurements (compare Figure 7A, simulations #2 versus #3). We considered the possibility that the lower overall number of NaVs in the two models accounted for the rather dramatic changes in apparent excitability. The change in Nav axonal density by 50% in a CA3-like (wider) axon depolarized the threshold and slowed the inflection rate, but the initiation site remained at 60 μm from the soma (Figures 7A and 7B, simulation #4). Similarly, in a model with full CA3 morphology, a decrease in Nav density by 50% significantly depolarized threshold and decreased the somatic phase plot inflection rate, but did not alter the site of initiation (Supplemental Figure 1). Thus, the overall change in number of Navs is important for the voltage threshold and inflection rate, and reductions of at least 50% in AIS Nav density did not influence the location of action potential initiation. The site of initiation over this range of AIS Nav density appears preferentially to occur near the distal end of dense Nav localization (Figure 7B and Supplemental Figure 1). So far our simulations have shown that the somatodendritic morphology greatly influences the inflection rate, and density of Navs influences action potential voltage threshold.
To test the impact of NaV AIS distribution in the context of DG-like geometry, we distributed the high density of axonal Nav channels either 0-40 μm (Figure 7A, simulation #6) or 40-80 μm (Figure 7A, simulation #5) along the axon. The results show that the restricted, proximal AIS NaV distribution depolarized the action potential voltage threshold, slowed the phase plot inflection rate, and moved the action potential initiation site closer to the soma (Figures 7A and 7B) compared with a similar density of channels distributed distally. This closer electrotonic distance caused the soma to more faithfully reflect the threshold voltage in the initiating compartment (-57.4 vs. -55.7 mV; Figure 7A versus 7C, simulation #6) than in the distal distribution model (-61.3 vs. -57.3 mV; Figure 7A versus 7C, simulation #5). Furthermore, in the proximal distribution model (Figure 7C, simulation #6), the nearby somatodendritic current sink caused the voltage threshold in the initiating segment (proximal axon) to increase by nearly 2 mV compared with the distal distribution model (Figure 7C, simulation #5). Taken together, the proximal axon profile of Nav distribution observed in DGs represents an important component of the depolarized voltage threshold observed in these cells.
As a final simulation to account for all of our experimental observations, we simulated a 20% reduction in DG neuron NaV channel density (Figure 3C2, 4C1). This modification resulted in a more positive DG action potential voltage threshold in both the proximal axon and somatodendritic compartments (Figures 7C and 7A, simulation #7). These results demonstrate that a reduction of AIS NaVs of a magnitude similar to that detected in immunostaining could have a significant influence on voltage threshold.
Figure 8 shows additional details of the final output of a simulated DG neuron with geometrical and NaV distribution (the same model as in Figure 7, simulation #7) similar to those observed experimentally. Figure 8A shows the granule cell morphology (inset) and the simulated membrane voltage at the soma and at the initiating site, 30 μm from the soma. In addition to voltage threshold and action potential inflection, the simulated DG action potential recapitulated other salient features of experimentally derived DG action potentials. The AIS action potential temporally preceded the somatic action potential and had a shallower inflection rate (Figure 8A1, 8A3). The model DG somatic phase plot resembled the experimentally obtained DG somatic phase plot in maximum dV/dt value, and the action potential initiation site occurred proximally on the axon, similar to electrophysiological estimates (Kress et al., 2008; Schmidt-Hieber et al., 2008a)(Figure 8A2 and Figure 1A). As the action potential developed from the initiation site, the threshold became more hyperpolarized and the inflection rate increased (Figure 8B2). The difference in action potential voltage threshold between the soma and initiation site (dotted lines Figure 8B2) was approximately 2 mV. All of these changes as the action potential developed with distance from initiation were less pronounced than in the CA3 model (compare Figure 8B2 with Figure 6D2).
Taken together, these findings demonstrate that both the geometrical differences and differences in NaV distribution combine to explain a depolarized threshold of DG neurons compared to CA3 neurons. DG somatic recordings more faithfully reflect the axonal voltage threshold because of proximal initiation. In addition, proximal axonal initiation requires that a larger somatodendric load be overcome by subthreshold axonal sodium currents; this depolarizes voltage threshold in the initiating proximal axon.
Discussion
In this study we investigated mechanisms influencing the intrinsic excitability difference responsible for the depolarized action potential threshold of DG neurons. DG neurons receive weak excitation (~0.1-0.5 mV peak EPSPs) from individual presynaptic inputs (McNaughton et al., 1981). Therefore at face value, the 5-10 mV more depolarized voltage threshold of DG cells could require the recruitment of 10-100 additional presynaptic inputs to trigger an action potential than if DG neurons had a more pyramidal cell-like threshold. We also examined cell type differences in the initial slope of phase plots, which have recently been variably attributed to NaV kinetics (Naundorf et al., 2006) or to remote action potential initiation (Yu et al., 2008). By systematically testing candidate mechanisms and through complementary simulations, we have concluded that neuronal geometry and distribution of NaVs culminate to contribute to the depolarized DG action potential voltage threshold and decreased phase plot inflection rate. We cannot fully exclude contributions from other differences between the cells. However, our simulations suggest little need to postulate large contributions from other potential sources.
Resting inhibitory conductances and voltage threshold
Previous studies have shown that neuronal excitability is influenced by a tonic chloride conductance. This change in neuronal excitability has most often been measured as a change in the current threshold, or rheobase, primarily attributed to changes in the cell input resistance (Eisenman et al., 2006; Mitchell and Silver, 2003; Semyanov et al., 2003). We found no involvement of chloride conductances in modulating action potential voltage threshold or inflection rate under our conditions. Most studies of tonic current in brain slices augment the tonic current by adding exogenous GABA, inhibiting GABA uptake, or inhibiting GABA degradation (Caraiscos et al., 2004; Glykys et al., 2008). These manipulations are thought to achieve ambient GABA levels present in vivo. We performed none of these manipulations and thus likely had comparatively small tonic conductances. Accordingly, we cannot comment on the likely effect of tonic conductances on voltage threshold under in vivo conditions; our experiments suggest only that tonic currents do not contribute to the depolarized DG voltage threshold under the present conditions. Our results are also consistent with layer 5 cortical cells, where no effect of exogenous GABA on voltage threshold was found (Palmer and Stuart, 2006).
Blocking DG neuron KVs with intracellular TEA depolarized the resting membrane potential and altered rheobase but did not alter action potential voltage threshold. This is consistent with the idea that rheobase could be a more sensitive indicator of intrinsic excitability. On the other hand, several studies have suggested that voltage threshold is altered by blocking KVs that are active near resting membrane potential (Bekkers and Delaney, 2001; Shah et al., 2008). Our results may differ from previous work because we used a relatively hyperpolarized baseline resting potential and examined only single, minimally evoked action potentials.
Functional implications of axonal NaV expression
Our immunohistochemistry showed a slightly higher density and larger extent of NaV immunoreactivity in the axon initial segment of CA3 neurons compared to DG neurons. We found no evidence for strong NaV1.2 isoform expression on DG and CA3 axon initial segments, although NaV1.2 has been shown to be expressed on unmyelinated axons within the retina (Boiko et al., 2003; Van Wart and Matthews, 2006; Van Wart et al., 2007). Instead, NaV1.6 appears to be the predominant initial segment channel in pyramidal and granule axons, a conclusion supported by a recent study using NaV1.6 mutant mice (Royeck et al., 2008). Although we found no evidence for AIS NaV1.2 staining, we cannot exclude a contribution of this channel that might fall below our immunostaining detection threshold. It was tempting to speculate that cell type isoform differences might contribute to the differing voltage thresholds since some studies suggest biophysical differences based on isoform (Royeck et al., 2008; Rush et al., 2005) but see (Chen et al., 2008). However, neither our staining nor nucleated patch recordings suggested a cell type differences in NaV isoform or kinetics. Furthermore, our simulations suggest that Nav biophysical differences are not needed to explain most of the voltage threshold and action potential shape differences between CA3 and DG neurons.
Several recent papers have suggested that AIS NaVs, including those of DG neurons, may exhibit hyperpolarized gating kinetics relative to somatic channels (Colbert and Pan, 2002; Kole and Stuart, 2008). To our knowledge there is no evidence for cell-type dependent differences in this phenomenon. Therefore, we used NaVs with slightly more hyperpolarized activation properties on the axon (5 mV) compared with the soma. Supplemental Figure 2 shows that the essential conclusions of our study were not affected by using uniform (somatodendritic-like) Nav activation. Similarly a 5 mV hyperpolarizing shift in the half-voltage of inactivation had no effect on results (data not shown). As expected, voltage thresholds of both cell types were uniformly shifted to more depolarized values.
Implications for cellular excitability
Our simulations suggest that the somatodendritic geometry and localization of axonal NaVs affect the apparent voltage threshold measured at the soma. Counterintuitively, although the axon is recruited first to spike (lowest rheobase), the voltage threshold at the axon initiation site is higher than that measured in the soma (Figure 6D2 for CA3 model and Figure 8B2 for DG model). Our conclusions are supported by recent data from direct axonal recordings and simulations of layer 5 neocortical neurons that show the axon initiation site has a depolarized voltage threshold relative to the soma (Kole and Stuart, 2008; Shu et al., 2007). Here we show that the location of the depolarized voltage threshold at a neuron’s initiation site plays an important role in cell type differences in apparent excitability. Proximal distribution of axonal NaVs in DG neurons moved the site of initiation toward the soma. In turn the soma more faithfully reflected the depolarized axonal membrane potential at the time of initiation. However, proximal Nav distribution and associated proximal initiation also directly depolarized threshold at the site of initiation. Therefore, proximal Nav distribution has two distinct effects to raise the somatically measured action potential voltage threshold.
The first effect suggests that caution is warranted in the use of voltage threshold to define neuronal excitability. Voltage threshold, unless it is measured at the site of initiation, can be influenced by the remoteness of initiation from the site of recording. In this context, the depolarized threshold of DG neurons does not necessarily indicate weak excitability or play a strong role in the “filtering” function of DG neurons (Hsu, 2007). The effect also implies that direct axonal recordings may be necessary to measure true voltage threshold (Kole and Stuart, 2008).
The second effect suggests a way in which passive membrane properties, particularly of the somatodendritic compartment, can influence voltage threshold in the axon. This effect might be considered to be a truer excitability difference than the first effect. If the somatodendritic compartment is electrotonically nearby, the large current sink raises threshold by shunting sodium current that would otherwise go toward the upswing of the action potential. The depolarization needed to fuel the regenerative upstroke is therefore greater. This mechanism of decreased excitability could play a significant role in the postulated low-pass filtering function of DG neurons (Hsu, 2007). Additionally, structural modification such as the formation of DG neuron basal dendrites after status epilepticus could significantly modify their excitability by increasing the current sink of the somatodendritic compartment (Shapiro et al., 2008; Thind et al., 2008). Finally, we note that our analysis was limited to a tightly defined set of experimental conditions: single action potentials elicited with minimal current stimulation. It is possible that in the context of repetitive firing or natural patterns of activity, other aspects of intrinsic excitability of DG neurons could more strongly participate, along with network properties, in their gatekeeper function.
In summary, our results exclude important roles for chloride, potassium, and Nav isoform differences in the depolarized action potential threshold difference of DG neurons compared with pyramidal neurons. Instead, we propose the apparent weaker excitability is the somewhat counterintuitive result of proximal axon Nav distribution near the soma.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank lab members for support and discussion and Drs. Aaron DiAntonio, Jim Huettner, Yukitoshi Izumi, Peter Lukasiewicz, Joe Henry Steinbach and Chuck Zorumski for advice on experiments. MD was supported by an HHMI SURF award to Washington University.
Grant sponsor: NIH: NINDS and NIMH
Grant numbers. NS54174 and MH78823
References
- Bean BP. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(6):451–65. doi: 10.1038/nrn2148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers JM, Delaney AJ. Modulation of excitability by alpha-dendrotoxin-sensitive potassium channels in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2001;21(17):6553–60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-17-06553.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiko T, Van Wart A, Caldwell JH, Levinson SR, Trimmer JS, Matthews G. Functional specialization of the axon initial segment by isoform-specific sodium channel targeting. J Neurosci. 2003;23(6):2306–13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02306.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caraiscos VB, Elliott EM, You-Ten KE, Cheng VY, Belelli D, Newell JG, Jackson MF, Lambert JJ, Rosahl TW, Wafford KA. Tonic inhibition in mouse hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons is mediated by a5 subunit-containing g-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(10):3662–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307231101. and others. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Yu FH, Sharp EM, Beacham D, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. Functional properties and differential neuromodulation of Nav1.6 channels. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;38(4):607–15. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert CM, Pan E. Ion channel properties underlying axonal action potential initiation in pyramidal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5(6):533–8. doi: 10.1038/nn0602-857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter DA, Carlson GC. Functional regulation of the dentate gyrus by GABA-mediated inhibition. Progr Brain Res. 2007;163:235–43. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbordes G, Jin J, Weng C, Lesica NA, Stanley GB, Alonso JM. Timing precision in population coding of natural scenes in the early visual system. PLoS Biol. 2008;6(12):e324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman LN, Kress G, Zorumski CF, Mennerick S. A spontaneous tonic chloride conductance in solitary glutamatergic hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 2006;1118(1):66–74. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhall AL, Lewen GD, Bialek W, de Ruyter Van Steveninck RR. Efficiency and ambiguity in an adaptive neural code. Nature. 2001;412(6849):787–92. doi: 10.1038/35090500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrant M, Nusser Z. Variations on an inhibitory theme: phasic and tonic activation of GABAA receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(3):215–29. doi: 10.1038/nrn1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glykys J, Mann EO, Mody I. Which GABAA receptor subunits are necessary for tonic inhibition in the hippocampus? J Neurosci. 2008;28(6):1421–6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4751-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines ML, Carnevale NT. NEURON: a tool for neuroscientists. Neuroscientist. 2001;7(2):123–35. doi: 10.1177/107385840100700207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol (Lond) 1952;117:500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D. The dentate gyrus as a filter or gate: a look back and a look ahead. Prog Brain Res. 2007;163:601–13. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)63032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka N, Weber J, Amaral DG. Organization of intrahippocampal projections originating from CA3 pyramidal cells in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990;295:580–623. doi: 10.1002/cne.902950407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole MH, Ilschner SU, Kampa BM, Williams SR, Ruben PC, Stuart GJ. Action potential generation requires a high sodium channel density in the axon initial segment. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(2):178–86. doi: 10.1038/nn2040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole MH, Stuart GJ. Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Nat Neurosci. 2008;11(11):1253–5. doi: 10.1038/nn.2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress GJ, Dowling MJ, Meeks JP, Mennerick S. High threshold, proximal initiation, and slow conduction velocity of action potentials in dentate granule neuron mossy fibers. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100(1):281–91. doi: 10.1152/jn.90295.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress GJ, Mennerick S. Action potential initiation and propagation: upstream influences on neurotransmission. Neuroscience. 2009;158(1):211–22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai HC, Jan LY. The distribution and targeting of neuronal voltage-gated ion channels. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(7):548–62. doi: 10.1038/nrn1938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarewicz MT, Migliore M, Ascoli GA. A new bursting model of CA3 pyramidal cell physiology suggests multiple locations for spike initiation. Biosystems. 2002;67(1-3):129–37. doi: 10.1016/s0303-2647(02)00071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Tilwalli S, Ye G, Lio PA, Pasternak JF, Trommer BL. Morphologic and electrophysiologic maturation in developing dentate gyrus granule cells. Brain Res. 2000;856(1-2):202–12. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu YB, Lio PA, Pasternak JF, Trommer BL. Developmental changes in membrane properties and postsynaptic currents of granule cells in rat dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76(2):1074–1088. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.2.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainen ZF, Joerges J, Huguenard JR, Sejnowski TJ. A model of spike initiation in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron. 1995;15(6):1427–39. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martina M, Jonas P. Functional differences in Na+ channel gating between fast-spiking interneurones and principal neurones of rat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 1997;505(Pt 3):593–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.593ba.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton BL, Barnes CA, Andersen P. Synaptic efficacy and EPSP summation in granule cells of rat fascia dentata studied in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1981;46(5):952–66. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.5.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks JP, Jiang X, Mennerick S. Action potential fidelity during normal and epileptiform activity in paired soma/axon recordings from rat hippocampus. J Physiol (London) 2005;566:425–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks JP, Mennerick S. Action potential initiation and propagation in CA3 pyramidal axons. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97(5):3460–72. doi: 10.1152/jn.01288.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell SJ, Silver RA. Shunting inhibition modulates neuronal gain during synaptic excitation. Neuron. 2003;38(3):433–45. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naundorf B, Wolf F, Volgushev M. Unique features of action potential initiation in cortical neurons. Nature. 2006;440(7087):1060–3. doi: 10.1038/nature04610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overstreet LS, Hentges ST, Bumaschny VF, de Souza FSJ, Smart JL, Santangelo AM, Low MJ, Westbrook GL, Rubinstein M. A transgenic marker for newly born granule cells in dentate gyrus. J Neurosci. 2004;24(13):3251–3259. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5173-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer LM, Stuart GJ. Site of action potential initiation in layer 5 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 2006;26(6):1854–63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4812-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royeck M, Horstmann MT, Remy S, Reitze M, Yaari Y, Beck H. Role of axonal NaV1. 6 sodium channels in action potential initiation of CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2008;100(4):2361–80. doi: 10.1152/jn.90332.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush AM, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. Electrophysiological properties of two axonal sodium channels, Nav1. 2 and Nav1.6, expressed in mouse spinal sensory neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 2005;564(Pt 3):803–15. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.083089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J. Subthreshold dendritic signal processing and coincidence detection in dentate gyrus granule cells. J Neurosci. 2007;27(31):8430–8441. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1787-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J. Action potential initiation and propagation in hippocampal mossy fibre axons. J Physiol. 2008a;586(7):1849–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.150151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Hieber C, Jonas P, Bischofberger J. Differential sodium channel gating in soma and axon of hippocampal granule cells Neuroscience Meeting Planner 535.2. Washington, D.C.: Society for Neuroscience; 2008b. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzkroin PA, Prince DA. Cellular and field potential properties of epileptogenic hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1978;147(1):117–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90776-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM. GABA uptake regulates cortical excitability via cell type-specific tonic inhibition. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6(5):484–90. doi: 10.1038/nn1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semyanov A, Walker MC, Kullmann DM, Silver RA. Tonically active GABAA receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27(5):262–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah MM, Migliore M, Valencia I, Cooper EC, Brown DA. Functional significance of axonal Kv7 channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(22):7869–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802805105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro LA, Ribak CE, Jessberger S. Structural changes for adult-born dentate granule cells after status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2008;49(Suppl 5):13–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu Y, Duque A, Yu Y, Haider B, McCormick DA. Properties of action potential initiation in neocortical pyramidal cells: evidence from whole cell axon recordings. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:746–760. doi: 10.1152/jn.00922.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell BM, Mody I. Receptors with different affinities mediate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 2002;22(10):RC223. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-10-j0003.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thind KK, Ribak CE, Buckmaster PS. Synaptic input to dentate granule cell basal dendrites in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Comp Neurol. 2008;509(2):190–202. doi: 10.1002/cne.21745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacher H, Mohapatra DP, Trimmer JS. Localization and targeting of voltage-dependent ion channels in mammalian central neurons. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(4):1407–47. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00002.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wart A, Matthews G. Expression of sodium channels Nav1. 2 and Nav1.6 during postnatal development of the retina. Neurosci Lett. 2006;403(3):315–7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.05.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wart A, Trimmer JS, Matthews G. Polarized distribution of ion channels within microdomains of the axon initial segment. J Comp Neurol. 2007;500(2):339–52. doi: 10.1002/cne.21173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y, Shu Y, McCormick DA. Cortical action potential backpropagation explains spike threshold variability and rapid-onset kinetics. J Neurosci. 2008;28(29):7260–72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1613-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhurov Y, Brezina V. Variability of motor neuron spike timing maintains and shapes contractions of the accessory radula closer muscle of Aplysia. J Neurosci. 2006;26(26):7056–70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5277-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.