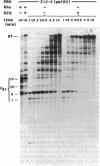
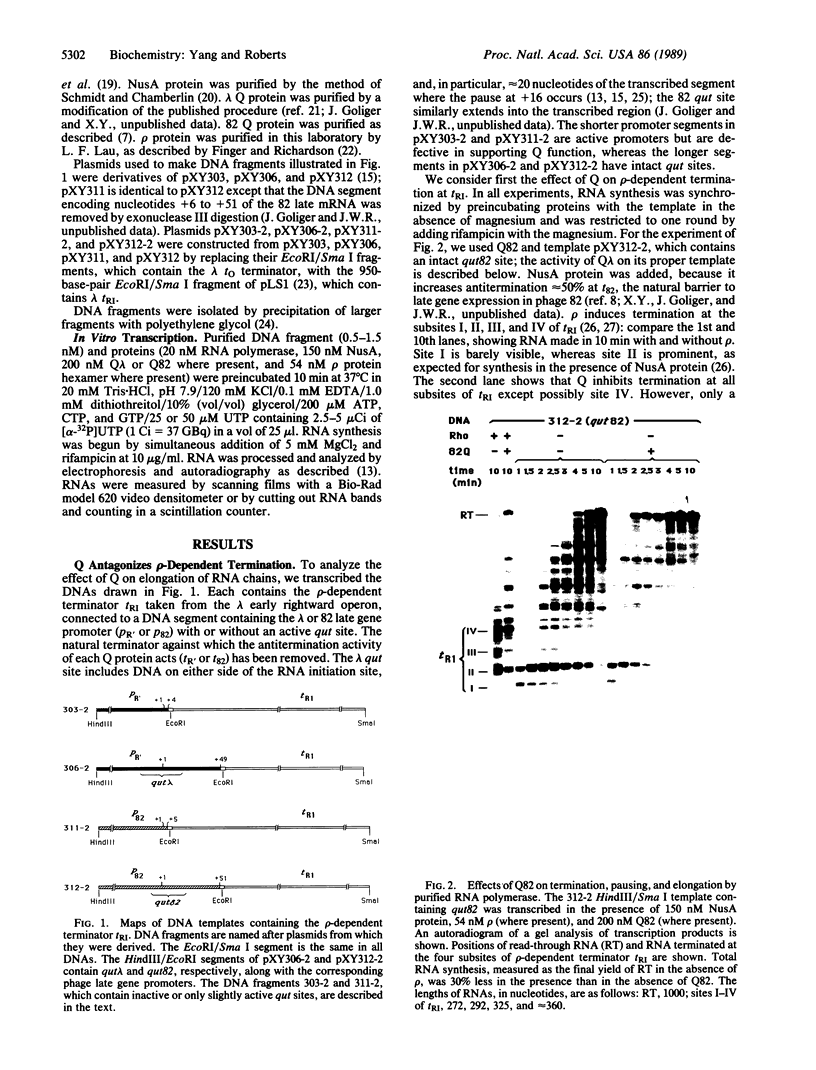
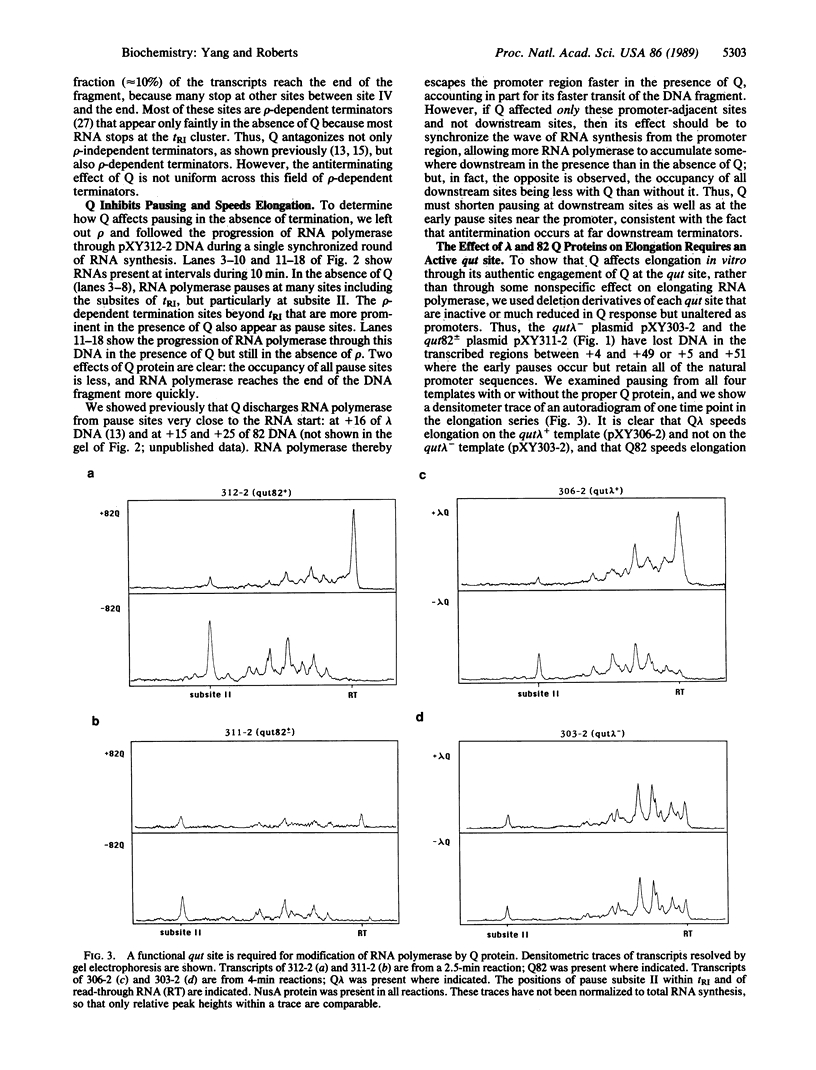
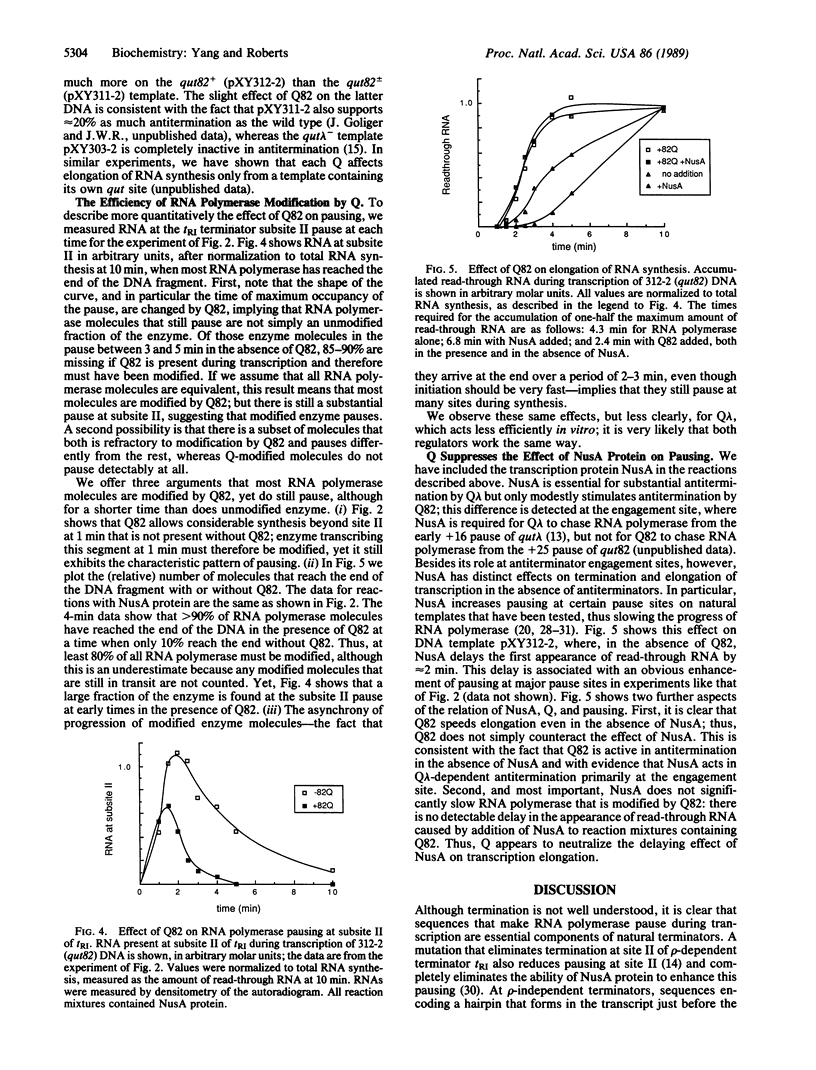
Abstract
The Q genes of phages lambda and 82 encode transcription antiterminators that are active in vitro in a purified transcription system. Transcription termination is thought to involve two distinct steps: pausing of the transcription complex at the terminator and release of enzyme and RNA; either or both steps might be inhibited by Q protein. We show that Q-modified RNA polymerase pauses much less efficiently than does unmodified enzyme at the natural pause sites of a rho-dependent terminator as well as at other pause sites. This changed behavior can account for the termination properties of Q-modified RNA polymerase and reflects a fundamental alteration of the elongation properties of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barik S., Ghosh B., Whalen W., Lazinski D., Das A. An antitermination protein engages the elongating transcription apparatus at a promoter-proximal recognition site. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):885–899. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Greenblatt J., Platt T. Effects of NusA protein on transcription termination in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):945–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger L. R., Richardson J. P. Procedure for purification of Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid synthesis termination protein rho. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1640–1645. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Yanofsky C. Mutations of the beta subunit of RNA polymerase alter both transcription pausing and transcription termination in the trp operon leader region in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8146–8150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D., Herskowitz I. Polarity suppression by the Q gene product of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 5;160(4):549–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goliger J. A., Roberts J. W. Bacteriophage 82 gene Q and Q protein. Sequence, overproduction, and activity as a transcription antiterminator in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11721–11725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack E. J., Roberts J. W. The phage lambda Q gene product: activity of a transcription antiterminator in vitro. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayhack E. J., Yang X. J., Lau L. F., Roberts J. W. Phage lambda gene Q antiterminator recognizes RNA polymerase near the promoter and accelerates it through a pause site. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):259–269. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz R. J., Li J., Greenblatt J. An elongation control particle containing the N gene transcriptional antitermination protein of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and termination of transcription within the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Carey J., Yanofsky C. Detection of transcription-pausing in vivo in the trp operon leader region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landick R., Yanofsky C. Stability of an RNA secondary structure affects in vitro transcription pausing in the trp operon leader region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11550–11555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Roberts J. W. Rho-dependent transcription termination at lambda R1 requires upstream sequences. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):574–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Roberts J. W., Wu R. RNA polymerase pausing and transcript release at the lambda tR1 terminator in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9391–9397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Roberts J. W., Wu R. Transcription terminates at lambda tR1 in three clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6171–6175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T. Fractionation of DNA fragments by polyethylene glycol induced precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery-Goldhammer C., Richardson J. P. An RNA-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (ATPase) associated with rho termination factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2003–2007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Rho-dependent termination of transcription. I. Identification and characterization of termination sites for transcription from the bacteriophage lambda PR promoter. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9553–9564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P., Grimley C., Lowery C. Transcription termination factor rho activity is altered in Escherichia coli with suA gene mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1725–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Phage lambda and the regulation of transcription termination. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90523-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Chamberlin M. J. Amplification and isolation of Escherichia coli nusA protein and studies of its effects on in vitro RNA chain elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):197–203. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar G., Szybalski W. Mapping of the Q-utilization site (qut) required for antitermination of late transcription in bacteriophage lambda. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Masukata H. Factor-independent termination of transcription in a stretch of deoxyadenosine residues in the template DNA. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen W., Ghosh B., Das A. NusA protein is necessary and sufficient in vitro for phage lambda N gene product to suppress a rho-independent terminator placed downstream of nutL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2494–2498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. J., Hart C. M., Grayhack E. J., Roberts J. W. Transcription antitermination by phage lambda gene Q protein requires a DNA segment spanning the RNA start site. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):217–226. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]