Abstract
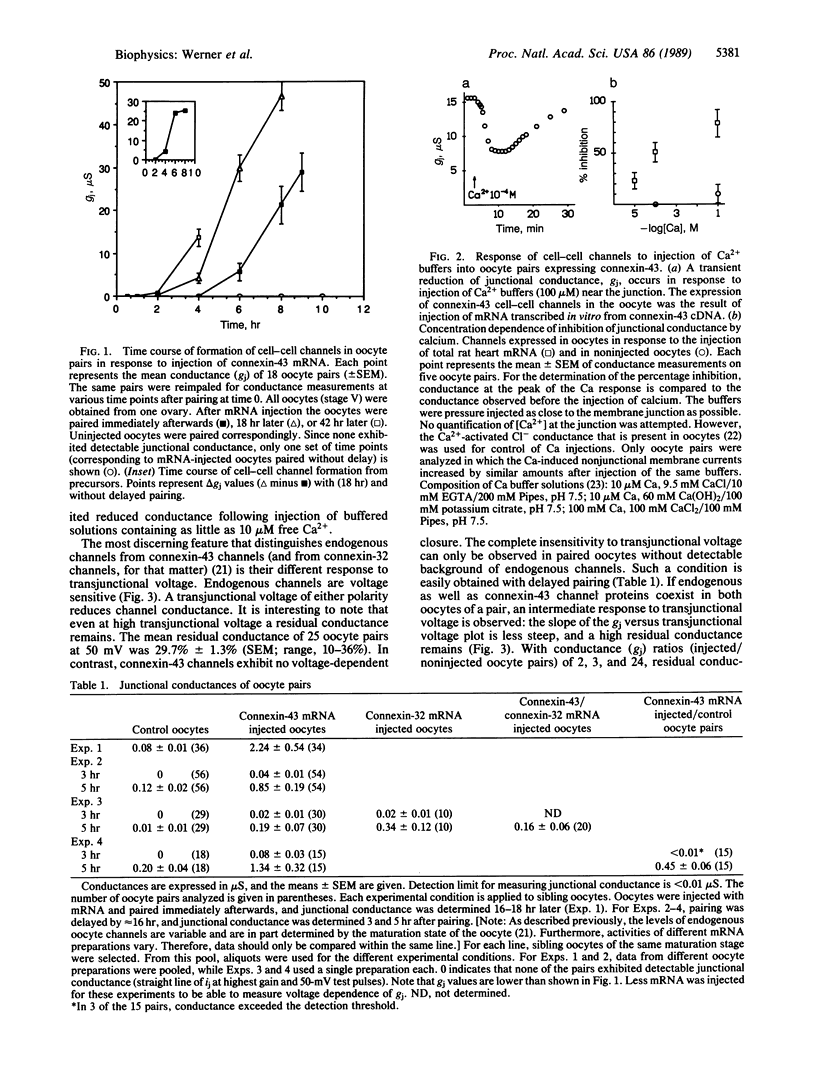
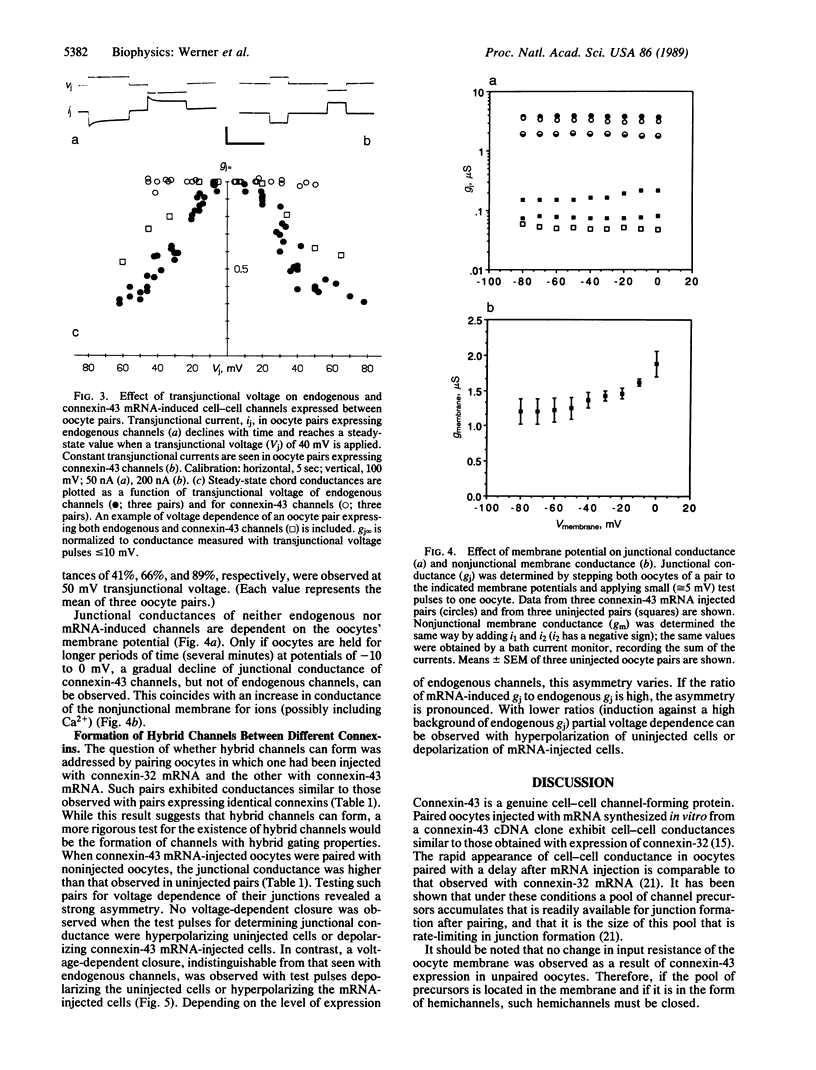
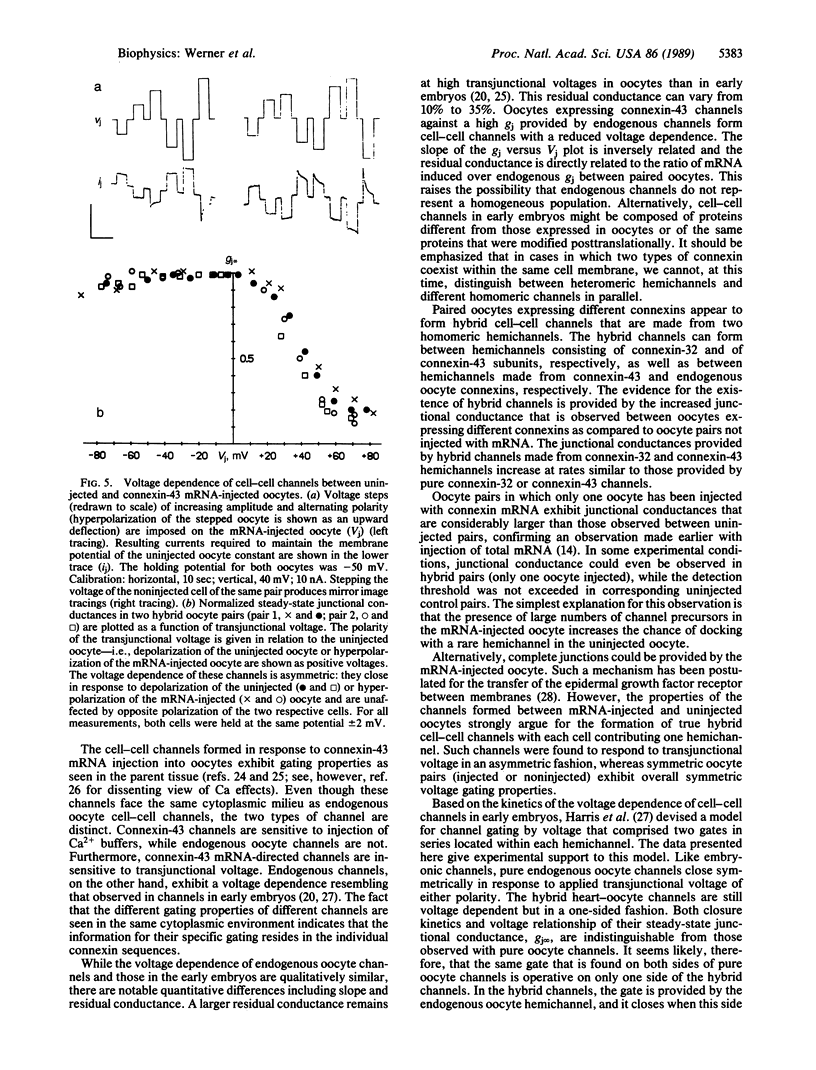
The oocyte cell-cell channel assay was used to demonstrate that connexin-43 is a cell-cell channel-forming protein as previously shown for connexin-32. Expression of connexin-32 in one and connexin-43 in the other oocyte of a pair results in the formation of junctional conductances at rates similar to those observed when only one or the other connexin is expressed in both oocytes of a pair. This suggests that hybrid cell-cell channels form in the oocyte system. Hybrid channels also form when a connexin-43 mRNA-injected oocyte is paired with a noninjected oocyte expressing endogenous connexin. The latter hybrids have properties apparently contributed by both types of hemichannels. Pure connexin-43 channels are not voltage gated, whereas pure oocyte channels are voltage dependent; hybrids of these channels rectify.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A. A., Bennett M. V. A rectifying electrotonic synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):211–237. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin43: a protein from rat heart homologous to a gap junction protein from liver. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2621–2629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Isenberg G. Decoupling of heart muscle cells: correlation with increased cytoplasmic calcium activity and with changes of nexus ultrastructure. J Membr Biol. 1980 Mar 31;53(1):63–75. doi: 10.1007/BF01871173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Miller T., Paul D., Voellmy R., Werner R. Expression of functional cell-cell channels from cloned rat liver gap junction complementary DNA. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1290–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.3035715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Feinman J., Pittenger M., Michael H., Bishayee S. Spontaneous transfer of exogenous epidermal growth factor receptors into receptor-negative mutant cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:555–561. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. L., Gilula N. B. A study of communication specificity between cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):769–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURSHPAN E. J., POTTER D. D. Transmission at the giant motor synapses of the crayfish. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):289–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna R. B., Keeter J. S., Pappas G. D. The fine structure of a rectifying electrotonic synapse. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):764–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Spray D. C., Bennett M. V. Kinetic properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):95–117. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Skibbens R. V. A protein homologous to the 27,000 dalton liver gap junction protein is present in a wide variety of species and tissues. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde A., Blondel B., Matter A., Cheneval J. P., Filloux B., Girardier L. Homo- and heterocellular junctions in cell cultures: an electrophysiological and morphological study. Prog Brain Res. 1969;31:283–311. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaslove S. W., Brink P. R. The mechanism of rectification at the electrotonic motor giant synapse of the crayfish. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):63–65. doi: 10.1038/323063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M. Electrical coupling between ventricular paired cells isolated from guinea-pig heart. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:345–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler J., Christie D., Bullivant S. Homologies between gap junction proteins in lens, heart and liver. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):721–723. doi: 10.1038/331721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Cloning and characterization of human and rat liver cDNAs coding for a gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):767–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalke W., Loewenstein W. R. Communication between cells of different type. Nature. 1971 Jul 9;232(5306):121–122. doi: 10.1038/232121b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T., Dahl G., Werner R. Structure of a gap junction gene: rat connexin-32. Biosci Rep. 1988 Oct;8(5):455–464. doi: 10.1007/BF01121644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller K. J., Scott S. A. Transmission at a 'direct' electrical connexion mediated by an interneurone in the leech. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson B., Dermietzel R., Teplow D., Traub O., Willecke K., Revel J. P. Two homologous protein components of hepatic gap junctions. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):732–734. doi: 10.1038/329732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preus D., Johnson R., Sheridan J. Gap junctions between Novikoff hepatoma cells following dissociation and recovery in the absence of cell contact. J Ultrastruct Res. 1981 Dec;77(3):248–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(81)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel J. P., Nicholson B. J., Yancey S. B. Molecular organization of gap junctions. Fed Proc. 1984 Sep;43(12):2672–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Rick R. Intracellular pH, intracellular free Ca, and junctional cell-cell coupling. J Membr Biol. 1978 Dec 29;44(3-4):377–415. doi: 10.1007/BF01944230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spray D. C., Harris A. L., Bennett M. V. Equilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jan;77(1):77–93. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. E., Guthrie S. C., Gilula N. B. Antibodies to gap-junctional protein selectively disrupt junctional communication in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):127–131. doi: 10.1038/311127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner R., Miller T., Azarnia R., Dahl G. Translation and functional expression of cell-cell channel mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):253–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01871226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Spray D. C., Campos de Carvalho A. C., Wittenberg B. A., Bennett M. V. Some electrical and pharmacological properties of gap junctions between adult ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):C447–C455. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.5.C447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer D. B., Green C. R., Evans W. H., Gilula N. B. Topological analysis of the major protein in isolated intact rat liver gap junctions and gap junction-derived single membrane structures. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7751–7763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



