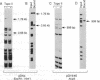
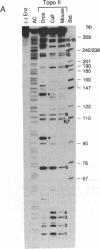
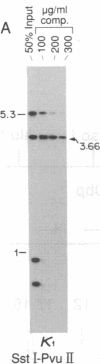
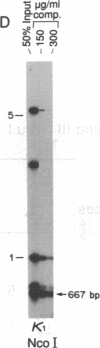
Abstract
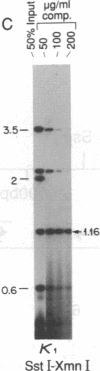
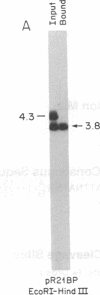
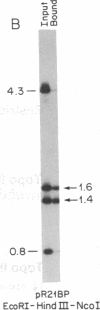
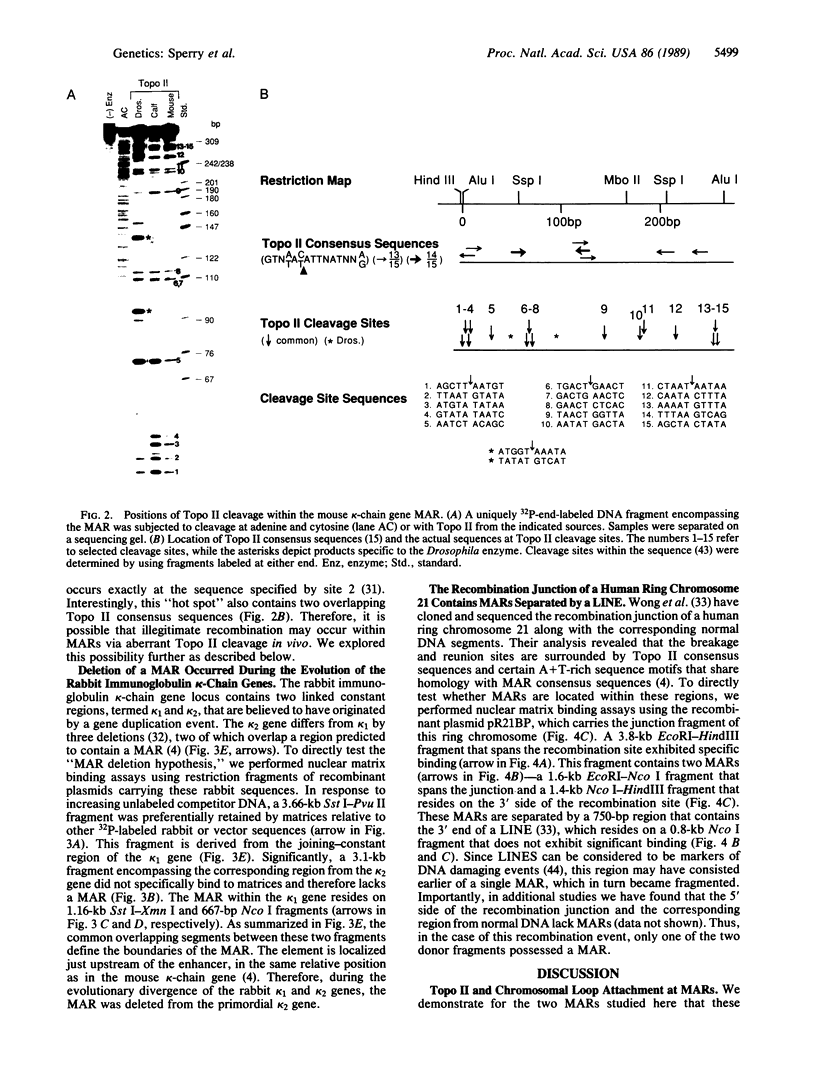
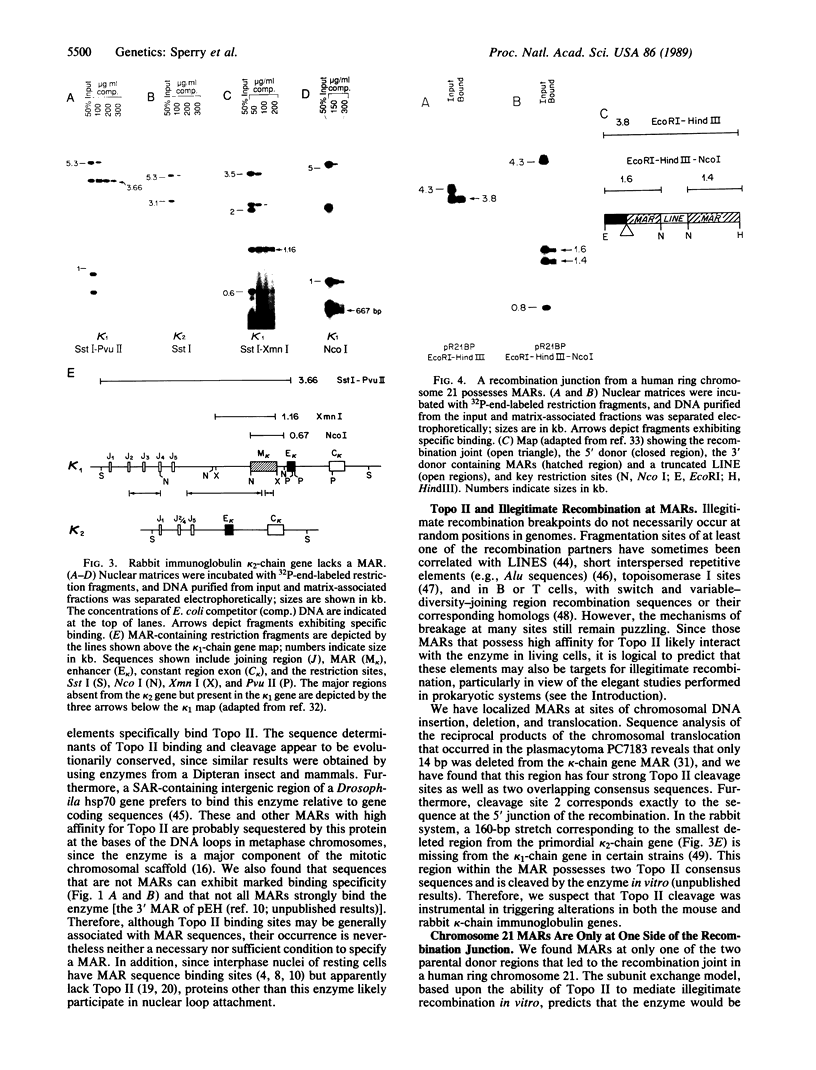
A family of A + T-rich sequences termed MARs ("matrix association regions") mediate chromosomal loop attachment. Here we demonstrate that several MARs both specifically bind and contain multiple sites of cleavage by topoisomerase II, a major protein of the mitotic chromosomal scaffold. Interestingly, "hotspots" of enzyme cutting occur within the MAR of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene at the breakpoint of a previously described chromosomal translocation. Since topoisomerase II can mediate illegitimate recombination in prokaryotes, we explored further the possibility that MARs might be targets for this process in eukaryotes. We found that a MAR had been deleted from one of the two rabbit immunoglobulin kappa-chain genes and that MARs reside next to a long interspersed repetitive element within the recombination junction of a human ring chromosome 21. These results, taken together with other accounts of nonhomologous recombination, lead to the proposal that a dysfunction of MARs is illegitimate recombination.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimenko M. A., Mariamé B., Rougeon F. Evolution of the immunoglobulin kappa light chain locus in the rabbit: evidence for differential gene conversion events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5180–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amati B. B., Gasser S. M. Chromosomal ARS and CEN elements bind specifically to the yeast nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):967–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Vanin E. F. Molecular characterization of a beta zero-thalassemia resulting from a 1.4 kilobase deletion. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae Y. S., Kawasaki I., Ikeda H., Liu L. F. Illegitimate recombination mediated by calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berent S. L., Sevall J. S. Histone H1 binding at the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):2977–2983. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., Sternglanz R. Transcription-dependent DNA supercoiling in yeast DNA topoisomerase mutants. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90203-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Champoux J. J., Botchan M. Association of crossover points with topoisomerase I cleavage sites: a model for nonhomologous recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.2997924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage sites appear to be evolutionarily conserved. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Yuen M. H., Garrard W. T. The enhancer of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus is flanked by presumptive chromosomal loop anchorage elements. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5394–5397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Role of chromosome translocations in human neoplasia. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90552-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Herrera R. E., Vosberg H. P., Nordheim A. DNA topoisomerase II cleaves at specific sites in the 5' flanking region of c-fos proto-oncogenes in vitro. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2257–2265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Matrix attachment regions are positioned near replication initiation sites, genes, and an interamplicon junction in the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5398–5409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L., Max E. E. Structural analysis of a rabbit immunoglobulin kappa 2 J-C locus reveals multiple deletions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8877–8890. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairman R., Brutlag D. L. Expression of the Drosophila type II topoisomerase is developmentally regulated. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):560–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaulden M. E. Hypothesis: some mutagens directly alter specific chromosomal proteins (DNA topoisomerase II and peripheral proteins) to produce chromosome stickiness, which causes chromosome aberrations. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):357–365. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. A hotspot for novel amplification joints in a mosaic of Alu-like repeats and palindromic A + T-rich DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2401–2408. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H. Bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase mediates illegitimate recombination in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):922–926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Kawasaki I., Gellert M. Mechanism of illegitimate recombination: common sites for recombination and cleavage mediated by E. coli DNA gyrase. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):546–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00436208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mirkovitch J., Laemmli U. K. Interaction of DNA with nuclear scaffolds in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):111–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R. Nuclear scaffold attachment sites in the human globin gene complexes. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3337–3344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutation in LDL receptor: Alu-Alu recombination deletes exons encoding transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):140–146. doi: 10.1126/science.3155573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loc P. V., Strätling W. H. The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme gene co-map with the boundaries of the chromatin domain. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):655–664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Liu L. F., Englund P. T. A homogeneous type II DNA topoisomerase from HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9334–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Scaffold attachment of DNA loops in metaphase chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 5;200(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Spierer P., Laemmli U. K. Genes and loops in 320,000 base-pairs of the Drosophila melanogaster chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Spann T. Disassembly of the nucleus in mitotic extracts: membrane vesicularization, lamin disassembly, and chromosome condensation are independent processes. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M. B., Malamy M. H. Mapping of DNA gyrase cleavage sites in vivo oxolinic acid induced cleavages in plasmid pBR322. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 20;181(4):545–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90426-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Fungal recombination. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):33–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.33-58.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Zechiedrich E. L. Calcium-promoted DNA cleavage by eukaryotic topoisomerase II: trapping the covalent enzyme-DNA complex in an active form. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4303–4309. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Klotz J. L., Pravtcheva D., Ruddle F., Hood L. A novel 6:10 chromosomal translocation in the murine plasmacytoma NS-1. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):473–476. doi: 10.1038/307473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley L. S., Dubins J. S., deBoer J. G., DeMarini D. M., Bogerd A. M., Kreuzer K. N. Hotspot sites for acridine-induced frameshift mutations in bacteriophage T4 correspond to sites of action of the T4 type II topoisomerase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):665–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T., Udvardy A., Schedl P. Sequence dependence of Drosophila topoisomerase II in plasmid relaxation and DNA binding. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):219–229. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. A., Weigert M. A complex translocation at the murine kappa light-chain locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4130–4133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Osheroff N., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Purification and physical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9530–9535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask D. K., DiDonato J. A., Muller M. T. Rapid detection and isolation of covalent DNA/protein complexes: application to topoisomerase I and II. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):671–676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Novel partitioning of DNA cleavage sites for Drosophila topoisomerase II. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):933–941. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F., Henthorn P. S., Kioussis D., Grosveld F., Smithies O. Unexpected relationships between four large deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Earnshaw W. C., Van Keuren M. L., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular mechanism in the formation of a human ring chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. On the structure of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):127–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]