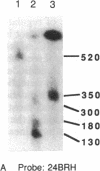
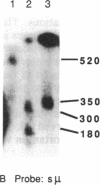
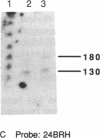
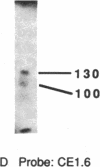
Abstract
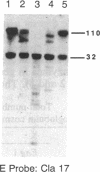
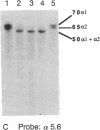
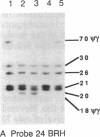
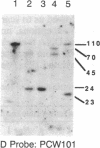
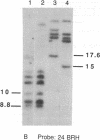
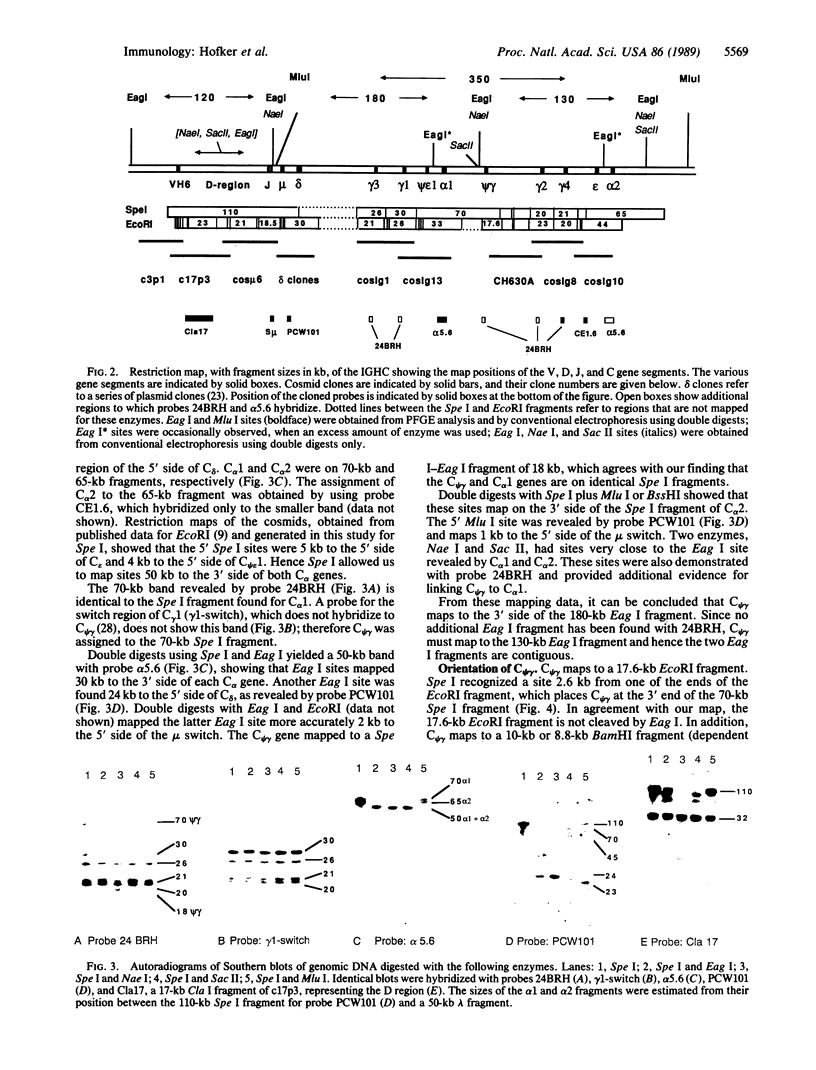
We have found by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis that the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region gene complex maps entirely to a 350-kilobase (kb) Mlu I fragment. The enzyme Eag I was used with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis alone and in double digests with Spe I to map the region. C gamma 3, of the C gamma 3-C gamma 1-C psi epsilon 1-C alpha 1 cluster, maps 60 kb to the 3' side of C delta; C gamma 2 of the C gamma 2-C gamma 4-C epsilon-C alpha 2 cluster maps 80 kb to the 3' side of C alpha 1, where C gamma 3 encodes the constant region of the immunoglobulin gamma 3 chain, C gamma 1 encodes the constant region of the immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain, etc. C psi gamma maps 35 kb to the 3' side of C alpha 1 and is in the same transcriptional orientation as the other genes. Although in the cloned DNA many CpG-containing restriction sites were identified, most of these were methylated in peripheral blood leukocytes. The sites that were not methylated were predominantly found in three clusters, or Hpa I tiny fragment islands. One was found on the 5' side of C mu; the other two lie 30 kb to the 3' side of each of the C alpha genes and could indicate the presence of regulatory sequences or genes. A region showing strong linkage disequilibrium between all C gamma genes spans at least 160 kb. The 70-kb C mu-C gamma 3 region, however, shows no linkage disequilibrium, possibly indicating a recombination hot spot. The immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region has been almost entirely cloned and mapped, and thus most rearrangements occurring in this region should be detectable.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Wei J. F., Wei F. S., Hsu Y. C., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: the H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3441–3449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Cox D. W. Duplication of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain gamma 2 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;38(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensmana M., Huck S., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. The human immunoglobulin pseudo-gamma IGHGP gene shows no major structural defect. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3108–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. E., Mellis S. J., Pollock R., Smith C. L., Suh H., Heinke B., Kowal C., Surti U., Chess L., Cantor C. R. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):727–738. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi N. O., Peltomäki P., Bianchi M. S., Knuutila S., de la Chapelle A. The pattern of methylation in rearranged and germ-line human immunoglobulin constant mu genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 25;909(3):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaabani H., Bech-Hansen N. T., Cox D. W. A multigene deletion within the immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1164–1171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Markovic V. D., Teshima I. E. Genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains and for alpha 1-antitrypsin are localized to specific regions of chromosome 14q. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):428–430. doi: 10.1038/297428a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J., Buxbaum J., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin C gamma 4 gene. DNA. 1981;1(1):11–18. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Rabbitts T. H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing gamma, epsilon and alpha genes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):709–713. doi: 10.1038/300709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. M., Watt S. M., Furley A. J., Molgaard H. V., Greaves M. F. Cell lineage specificity of chromatin configuration around the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2393–2399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Bakker E., Burmeister M., Pearson P. L. Development of additional RFLP probes near the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by cosmid cloning of the DXS84 (754) locus. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):270–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00282547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T. Immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinska E. C., Dunckley H., Propert D. N., Gatenby P. A., Serjeantson S. W. Gm typing by immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene RFLP analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;43(2):175–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. J., de Lange G., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Ig gamma restriction fragment length polymorphisms indicate an ancient separation of Caucasian haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 May;38(5):617–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Matsuda F., Kinashi T., Kodaira M., Honjo T. A novel family of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):761–768. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Helal A. N., de Lange G., Chaabani H., van Loghem E., Lefranc G. Gene conversion in human immunoglobulin gamma locus shown by unusual location of IgG allotypes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Feb 3;196(1):96–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G., Rabbitts T. H. Inherited deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes in normal human individuals. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):760–762. doi: 10.1038/300760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefranc M. P., Lefranc G., de Lange G., Out T. A., van den Broek P. J., van Nieuwkoop J., Radl J., Helal A. N., Chaabani H., van Loghem E. Instability of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region locus indicated by different inherited chromosomal deletions. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Sep;1(2):207–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman J. W., Taghert P. H. Developmental neurobiology. Trophic factor theory matures. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):336–336. doi: 10.1038/326336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda F., Lee K. H., Nakai S., Sato T., Kodaira M., Zong S. Q., Ohno H., Fukuhara S., Honjo T. Dispersed localization of D segments in the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1047–1051. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Battey J., Ney R., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Duplication and deletion in the human immunoglobulin epsilon genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., Oliviero S., de Lange G., Delacroix D. L., Boschis D., Altruda F., Silengo L., DeMarchi M., Carbonara A. O. Multiple gene deletions within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5811–5815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migone N., de Lange G., Piazza A., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Genetic analysis of eight linked polymorphisms within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Nov;37(6):1146–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Forster A., Baer R., Hamlyn P. H. Transcription enhancer identified near the human C mu immunoglobulin heavy chain gene is unavailable to the translocated c-myc gene in a Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):806–809. doi: 10.1038/306806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kirsch I. R., Leder P. Evolutionary approach to the question of immunoglobulin heavy chain switching: evidence from cloned human and mouse genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6734–6738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Walter M. A., Hofker M. H., Ebens A., Willems van Dijk K., Liao L. C., Cox D. W., Milner E. C., Perlmutter R. M. Physical linkage of a human immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene segment to diversity and joining region elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8196–8200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Takahashi N., Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Organization of the constant-region gene family of the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Ravetch J. V., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin D segments encoded in tandem multigenic families. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):631–635. doi: 10.1038/294631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Ueda S., Obata M., Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Structure of human immunoglobulin gamma genes: implications for evolution of a gene family. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. B., Shen A. L., Word C. J., Tucker P. W., Blattner F. R. Human immunoglobulin D: genomic sequence of the delta heavy chain. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):733–737. doi: 10.1126/science.3922054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Desiderio S. V., Paskind M., Kearney J. F., Baltimore D., Alt F. W. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal VH gene segments in pre-B-cell lines. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):727–733. doi: 10.1038/311727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]