Abstract
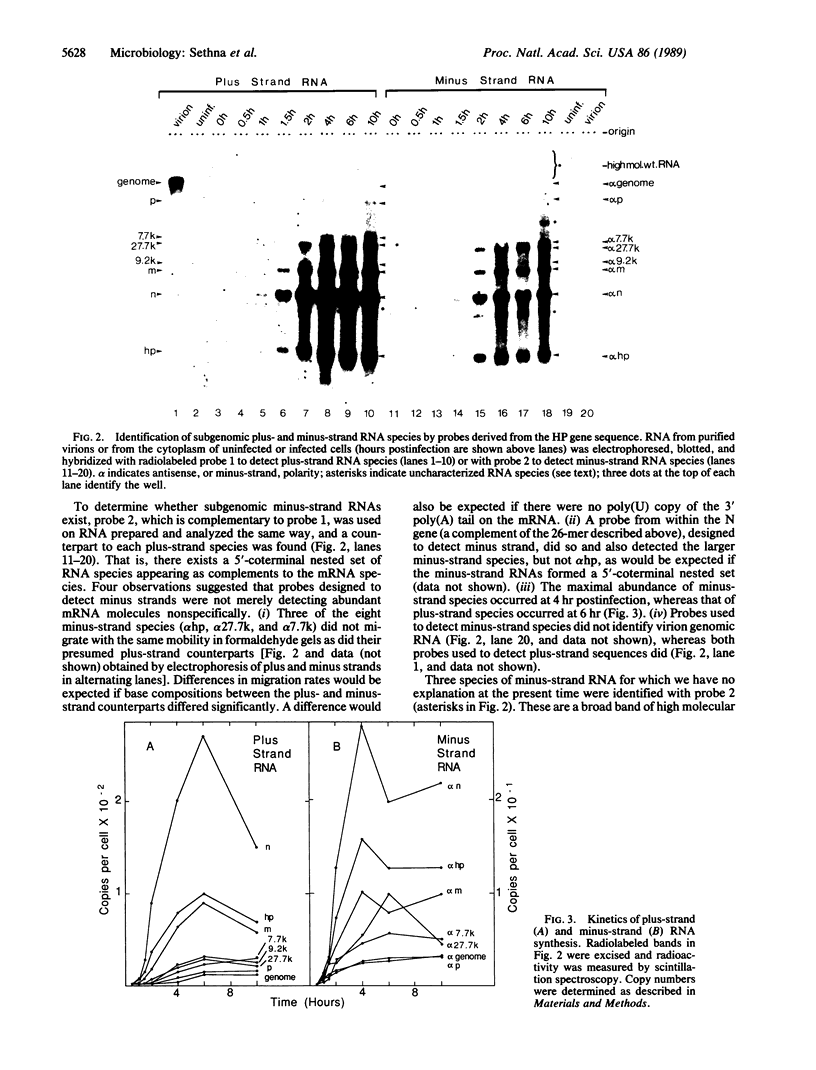
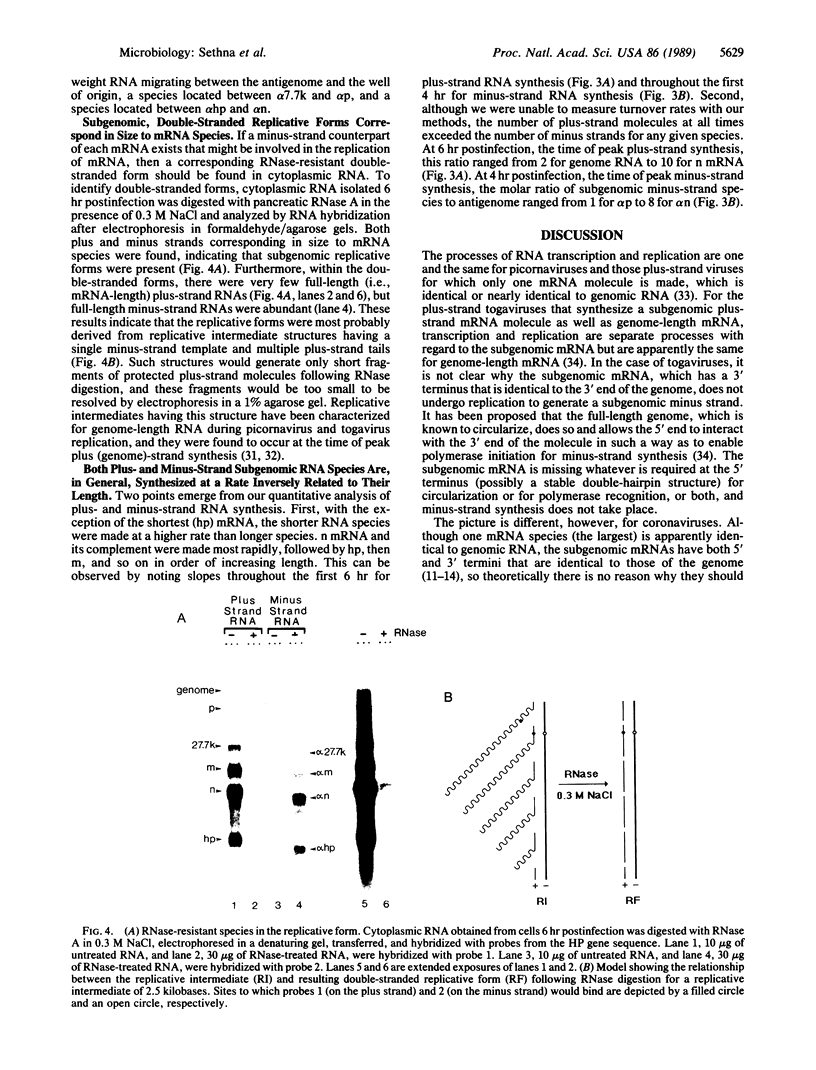
The genome of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus is a plus-strand, polyadenylylated, infectious RNA molecule of approximately 20 kilobases. During virus replication, seven subgenomic mRNAs are generated by what is thought to be a leader-priming mechanism to form a 3'-coterminal nested set. By using radiolabeled, strand-specific, synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes in RNA blot hybridization analyses, we have found a minus-strand counterpart for the genome and for each subgenomic mRNA species in the cytoplasm of infected cells. Subgenomic minus strands were found to be components of double-stranded replicative forms and in numbers that surpass full-length antigenome. We propose that subgenomic mRNA replication, in addition to leader-primed transcription, is a significant mechanism of mRNA synthesis and that it functions to amplify mRNAs. It is a mechanism of amplification that has not been described for any other group of RNA viruses. Subgenomic replicons may also function in a manner similar to genomes of defective interfering viruses to lead to the establishment of persistent infections, a universal property of coronaviruses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Characterization of replicative intermediate RNA of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of leader RNA sequences on nascent chains. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.633-640.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell M. E., Brown T. D., Foulds I. J., Green P. F., Tomley F. M., Binns M. M. Completion of the sequence of the genome of the coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):57–77. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian D. A., Dennis D. E., Guy J. S. Genome of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.410-415.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M. A leader sequence is present on mRNA A of avian infectious bronchitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1437–1442. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Tomley F. M. Cloning and sequencing of 5' terminal sequences from avian infectious bronchitis virus genomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):221–228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzilowicz C. J., Weiss S. R. In vitro synthesis of two polypeptides from a nonstructural gene of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):509–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90293-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzilowicz C. J., Wilczynski S. P., Weiss S. R. Three intergenic regions of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 genome RNA contain a common nucleotide sequence that is homologous to the 3' end of the viral mRNA leader sequence. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):834–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.834-840.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M., Perlman S. Identification of putative polymerase gene product in cells infected with murine coronavirus A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90303-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis D. E., Brian D. A. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity in coronavirus- infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):153–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.153-164.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., de Groot R., van der Zeijst B. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. The nucleotide sequence of the peplomer gene of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV): comparison with the sequence of the peplomer protein of feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV). Virus Res. 1987 Nov;8(4):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90008-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., van der Zeijst B. A., Horzinek M. C. Characterization and translation of transmissible gastroenteritis virus mRNAs. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1010–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1010-1015.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapke P. A., Brian D. A. Sequence analysis of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus nucleocapsid protein gene. Virology. 1986 May;151(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90102-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapke P. A., Tung F. Y., Brian D. A. Nucleotide sequence between the peplomer and matrix protein genes of the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus identifies three large open reading frames. Virus Genes. 1989 May;2(3):293–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00125345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapke P. A., Tung F. Y., Hogue B. G., Brian D. A., Woods R. D., Wesley R. The amino-terminal signal peptide on the porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus matrix protein is not an absolute requirement for membrane translocation and glycosylation. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90581-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W. UV crosslinking of RNA to nylon membrane enhances hybridization signals. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00364822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of leader RNA sequences on the virion and mRNAs of mouse hepatitis virus, a cytoplasmic RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3626–3630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Brayton P. R., Armen R. C., Patton C. D., Pugh C., Stohlman S. A. Mouse hepatitis virus A59: mRNA structure and genetic localization of the sequence divergence from hepatotropic strain MHV-3. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.823-834.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Makino S., Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Keck J. G., Fleming J. O. Coronavirus: a jumping RNA transcription. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:359–365. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Replication of mouse hepatitis virus: negative-stranded RNA and replicative form RNA are of genome length. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.487-492.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laude H., Rasschaert D., Huet J. C. Sequence and N-terminal processing of the transmembrane protein E1 of the coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1687–1693. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Perlman S., Weinstock G., DeVries J. R., Budzilowicz C., Weissemann J. M., Weiss S. R. Detection of a murine coronavirus nonstructural protein encoded in a downstream open reading frame. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):156–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90631-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Weiss S. R., Paavola E., Bond C. W. Cell-free translation of murine coronavirus RNA. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.905-913.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J. Origin and replication of defective interfering particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:151–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasschaert D., Laude H. The predicted primary structure of the peplomer protein E2 of the porcine coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1883–1890. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Stevens R. H., Simpson R. W. Presence of infectious polyadenylated RNA in coronavirus avian bronchitis virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):772–782. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Makino S., Chang M. F., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. The 5'-end sequence of the murine coronavirus genome: implications for multiple fusion sites in leader-primed transcription. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. II. Multiple forms of double-stranded RNA isolated from infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):615–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species 1, 3, 6, and 7 of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):432–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.432-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. II. Mapping the avian infectious bronchitis virus intracellular RNA species to the genome. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.440-449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Replication strategies of the single stranded RNA viruses of eukaryotes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:1–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Müller A., ter Meulen V. Genomic RNA of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):217–227. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]