Abstract
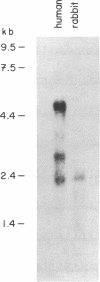
Cotransport proteins are responsible for the active accumulation of organic substrates in cells. Na+ gradients provide the driving force for uptake of most substrates into eukaryotes and for a few substrates in some prokaryotes. We report here the cloning and sequencing of the human intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) and compare its structure with other cloned transporters. At the DNA level and the predicted amino acid and secondary structure levels, close homology is evident between the human and rabbit intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporters, and a significant homology is found between these and the Escherichia coli Na+/proline cotransporter (putP). No homology is detectible with other known proteins. We infer from these results that the mammalian Na+/glucose and prokaryote Na+/proline cotransporters share a common ancestral gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen C. C., Tsuchiya T., Yamane Y., Wood J. M., Wilson T. H. Na+ (Li+)-proline cotransport in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1985;84(2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01872213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Wilson T. H. Solubilization and functional reconstitution of the proline transport system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2599–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada K., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Purification and reconstitution of Escherichia coli proline carrier using a site specifically cleavable fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7181–7185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Active transport in Escherichia coli: passage to permease. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:279–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M. I. Los Alamos sequence analysis package for nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):183–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiden M. C., Davis E. O., Baldwin S. A., Moore D. C., Henderson P. J. Mammalian and bacterial sugar transport proteins are homologous. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):641–643. doi: 10.1038/325641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Nucleotide sequence of putP, the proline carrier gene of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):70–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00330424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa M., Mogi T., Yamamoto H., Yamato I., Anraku Y. Proline carrier mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 with altered cation sensitivity of substrate-binding activity: cloning, biochemical characterization, and identification of the mutation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5185–5191. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5185-5191.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerce B. E., Wright E. M. Evidence for tyrosyl residues at the Na+ site on the intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6026–6031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerce B. E., Wright E. M. Sodium-induced conformational changes in the glucose transporter of intestinal brush borders. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14105–14112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Peerce B. E. Identification and conformational changes of the intestinal proline carrier. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):14993–14996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazyu H., Shiota-Niiya S., Shimamoto T., Kanazawa H., Futai M., Tsuchiya T. Nucleotide sequence of the melB gene and characteristics of deduced amino acid sequence of the melibiose carrier in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4320–4326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]