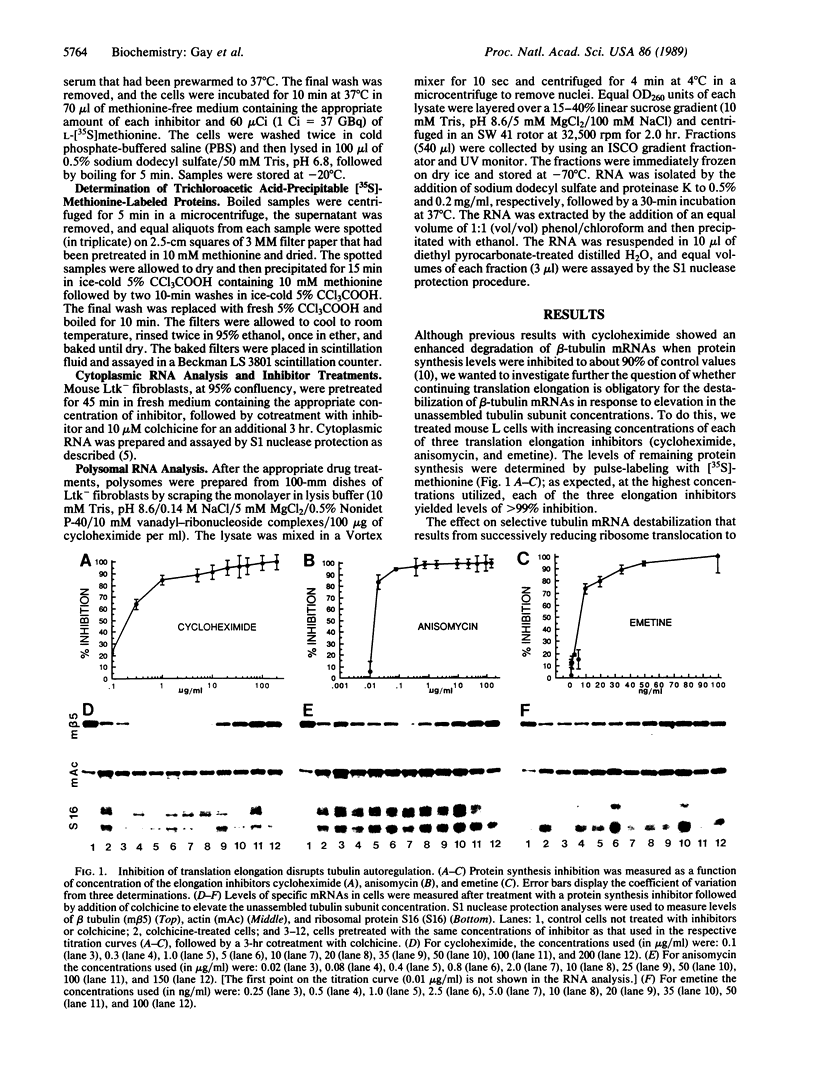
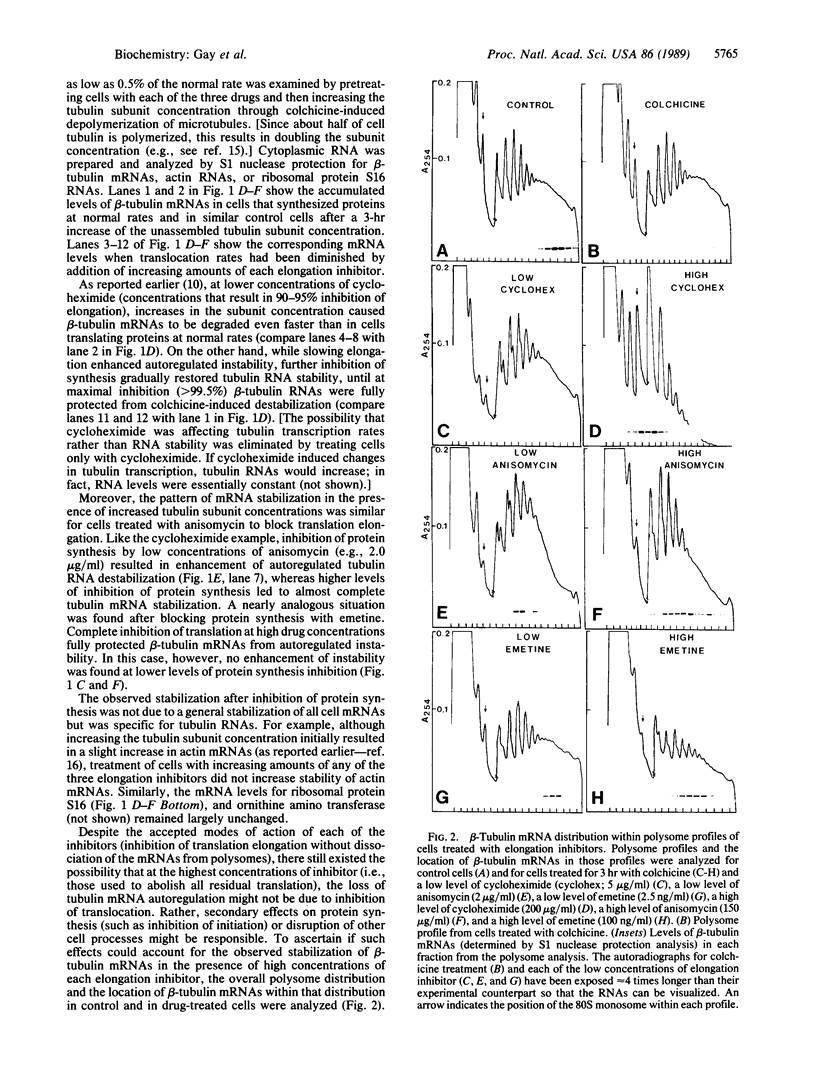
Abstract
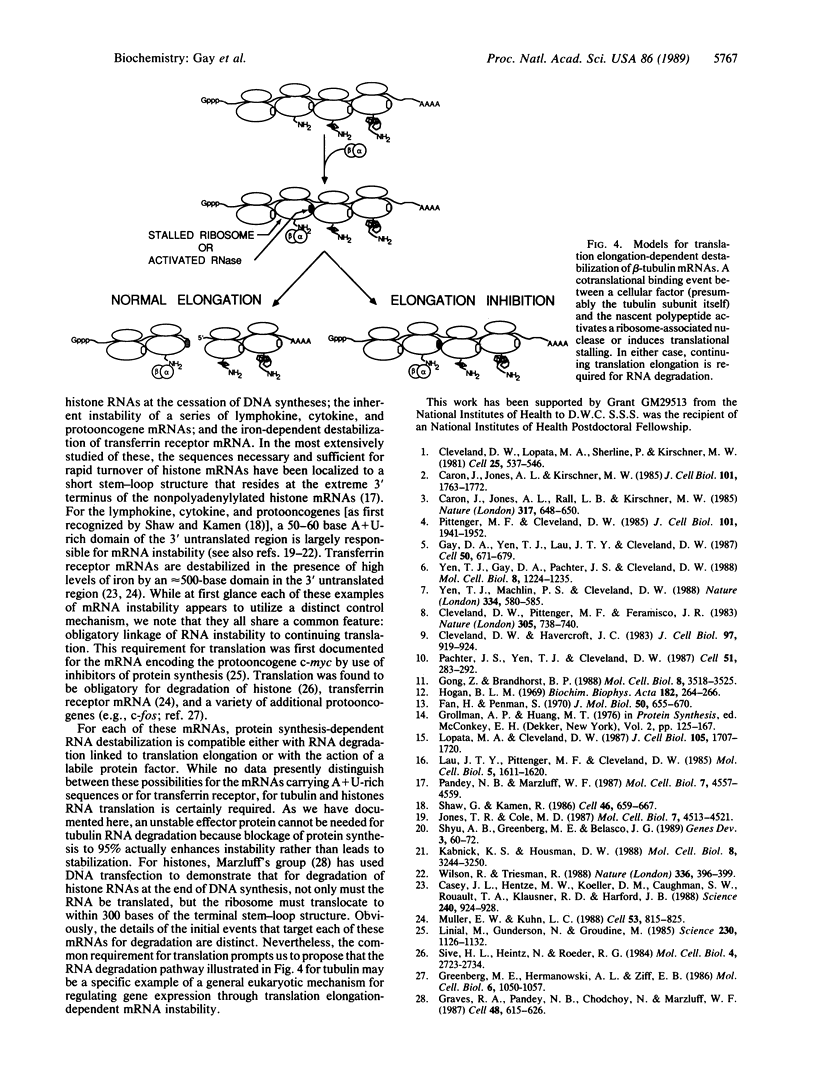
Tubulin synthesis in animal cells is controlled in part by an autoregulatory mechanism that modulates the stability of ribosome-bound tubulin mRNAs. For beta tubulin, the initial recognition event for this selective RNA instability has previously been shown to be a cotranslational binding (presumably by tubulin itself) to the nascent amino-terminal beta-tubulin tetrapeptide just after it emerges from the ribosome. Although this "autoregulation" of tubulin expression is thus obligatorily linked to the translation process, the mechanism of how a cotranslational protein-protein binding event ultimately triggers RNA degradation is unknown. Using protein synthesis inhibitors to slow and ultimately to block translation elongation, we now show that the mRNA destabilization pathway requires ongoing ribosome translocation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caron J. M., Jones A. L., Kirschner M. W. Autoregulation of tubulin synthesis in hepatocytes and fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1763–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron J. M., Jones A. L., Rall L. B., Kirschner M. W. Autoregulation of tubulin synthesis in enucleated cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):648–651. doi: 10.1038/317648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Havercroft J. C. Is apparent autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis nontranscriptionally regulated? J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):919–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., Sherline P., Kirschner M. W. Unpolymerized tubulin modulates the level of tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Pittenger M. F., Feramisco J. R. Elevation of tubulin levels by microinjection suppresses new tubulin synthesis. Nature. 1983 Oct 20;305(5936):738–740. doi: 10.1038/305738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Yen T. J., Lau J. T., Cleveland D. W. Sequences that confer beta-tubulin autoregulation through modulated mRNA stability reside within exon 1 of a beta-tubulin mRNA. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Z. Y., Brandhorst B. P. Stabilization of tubulin mRNA by inhibition of protein synthesis in sea urchin embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3518–3525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L. he effect of inhibitors of protein synthesis on the level of ribosomal subunits in ascites cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):264–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90546-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabnick K. S., Housman D. E. Determinants that contribute to cytoplasmic stability of human c-fos and beta-globin mRNAs are located at several sites in each mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3244–3250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. T., Pittenger M. F., Cleveland D. W. Reconstruction of appropriate tubulin and actin gene regulation after transient transfection of cloned beta-tubulin and beta-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1611–1620. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W. In vivo microtubules are copolymers of available beta-tubulin isotypes: localization of each of six vertebrate beta-tubulin isotypes using polyclonal antibodies elicited by synthetic peptide antigens. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1707–1720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittenger M. F., Cleveland D. W. Retention of autoregulatory control of tubulin synthesis in cytoplasts: demonstration of a cytoplasmic mechanism that regulates the level of tubulin expression. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1941–1952. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression during the HeLa cell cycle requires protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2723–2734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Gay D. A., Pachter J. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated changes in stability of polyribosome-bound beta-tubulin mRNAs are specified by the first 13 translated nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1224–1235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Machlin P. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated instability of beta-tubulin mRNAs by recognition of the nascent amino terminus of beta-tubulin. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):580–585. doi: 10.1038/334580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]