Abstract
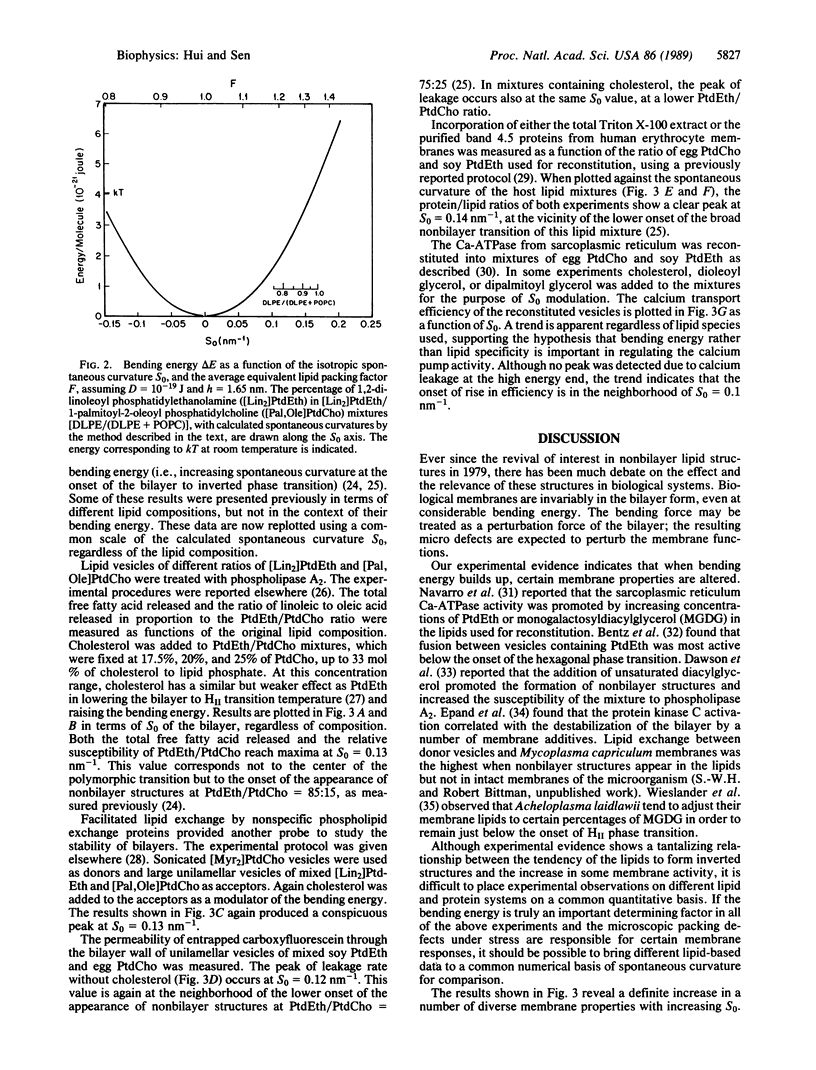
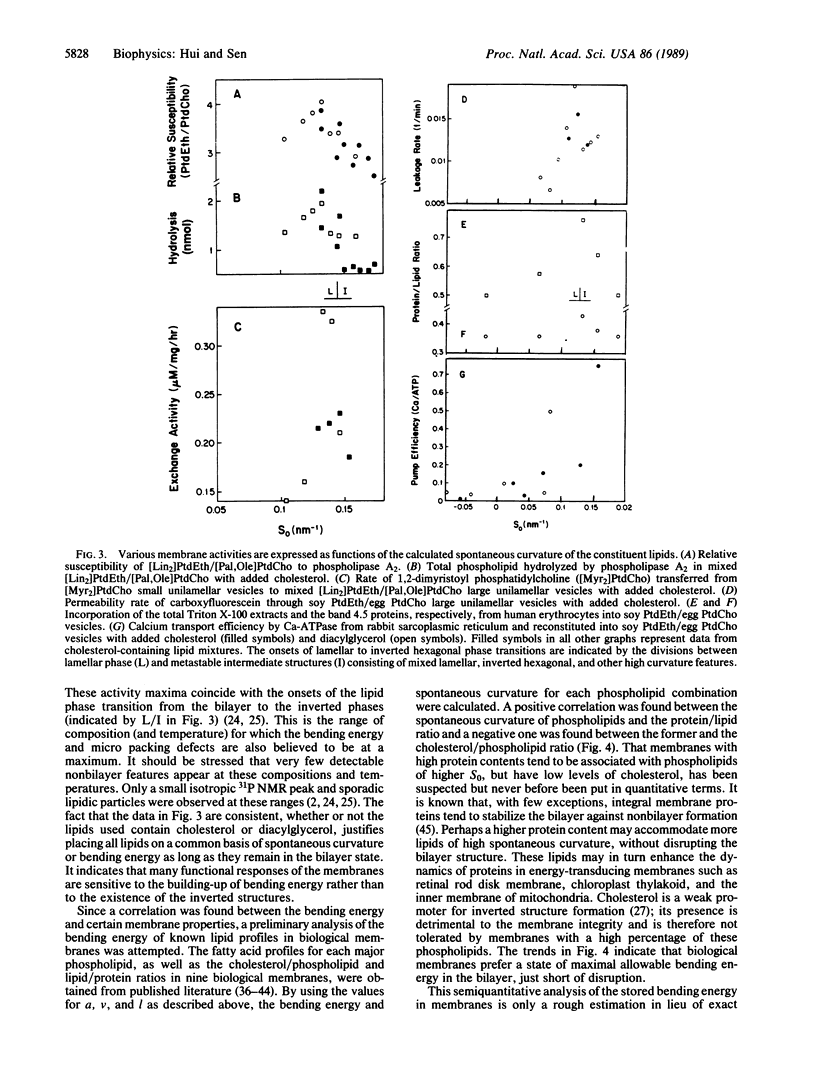
The self assembly of phospholipid molecules in the bilayer form was considered in terms of equivalent molecular shapes representing intermolecular forces. The equivalent size of each phospholipid headgroup was approximated by the net atomic volume plus the volume of the associated water molecules, which was derived from water/hydrocarbon partitioning experiments. The equivalent lengths of unsaturated acyl chains were derived from the retention time data from chromatographic measurements. The spontaneous curvature of various phospholipid monolayers was calculated from their equivalent molecular shapes, and the energy required to flatten them to the bilayer plane was calculated, using the known bending modulus. With increasing bending energy, the mixtures showed increasing susceptibility to phospholipase A2, facilitated lipid transfer rate by phospholipid exchange proteins, permeability to carboxyfluorescein, incorporation of human erythrocyte proteins, and calcium transport by Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum in reconstituted vesicles. When the calculation was applied to known lipid compositions of nine cellular membranes, the protein/lipid ratio and phospholipid/cholesterol ratio were found to have a positive and a negative correlation, respectively, with the latent bending energy of the phospholipids. The energy expense in conforming to a bilayer phase may be an important physical parameter regarding the activity and the biogenesis of membranes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. E., Maude M. B. Phospholipids of bovine outer segments. Biochemistry. 1970 Sep 1;9(18):3624–3628. doi: 10.1021/bi00820a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentz J., Ellens H., Lai M. Z., Szoka F. C., Jr On the correlation between HII phase and the contact-induced destabilization of phosphatidylethanolamine-containing membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5742–5745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boni L. T., Hui S. W. Polymorphic phase behaviour of dilinoleoylphosphatidylethanolamine and palmitoyloleoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures. Structural changes between hexagonal, cubic and bilayer phases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 10;731(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnie S., Israelachvili J. N., Pailthorpe B. A. Lipid packing and transbilayer asymmetries of mixed lipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):340–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90375-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. H., Lepock J. R., Hui S. W., Yeagle P. L. The role of cholesterol in the activity of reconstituted Ca-ATPase vesicles containing unsaturated phosphatidylethanolamine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5081–5087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):1–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Irvine R. F., Bray J., Quinn P. J. Long-chain unsaturated diacylglycerols cause a perturbation in the structure of phospholipid bilayers rendering them susceptible to phospholipase attack. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):836–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijck P. W., Zoelen E. J., Seldenrijk R., Deenen L. L., Gier J. Calorimetric behaviour of individual phospholipid classes from human and bovine erythrocyte membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1976 Oct;17(2-3):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(76)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Bottega R. Modulation of the phase transition behavior of phosphatidylethanolamine by cholesterol and oxysterols. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1820–1825. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Stafford A. R., Cheetham J. J., Bottega R., Ball E. H. The relationship between the bilayer to hexagonal phase transition temperature in membranes and protein kinase C activity. Biosci Rep. 1988 Feb;8(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01128971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84319-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M. Intrinsic curvature hypothesis for biomembrane lipid composition: a role for nonbilayer lipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruner S. M., Parsegian V. A., Rand R. P. Directly measured deformation energy of phospholipid HII hexagonal phases. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc. 1986;(81):29–37. doi: 10.1039/dc9868100029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hah J. S., Hui S. W., Jung C. Y. Effects of physical states of phospholipids on the incorporation and cytochalasin B binding activity of human erythrocyte membrane proteins in reconstituted vesicles. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4763–4769. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Pascher I., Pearson R. H., Sundell S. Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 16;650(1):21–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Lévy M., Pascaud M. Spécificité de constitution en acides gras des phospholipides des membranes mitochondriales. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Boni L. T. The nature of lipidic particles and their roles in polymorphic transitions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1983 Aug;33(2):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(83)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui S. W., Stewart T. P., Yeagle P. L., Albert A. D. Bilayer to non-bilayer transition in mixtures of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine: implications for membrane properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili J. N., Marcelja S., Horn R. G. Physical principles of membrane organization. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 May;13(2):121–200. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis L. J., McAlister M., Fuller N., Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Interactions between neutral phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):657–665. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh T. J., Simon S. A. Area per molecule and distribution of water in fully hydrated dilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4948–4952. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Toivio-Kinnucan M., Racker E. Effect of lipid composition on the calcium/adenosine 5'-triphosphate coupling ratio of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):130–135. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. C., Huang C. Structural studies on phophatidylcholine-cholesterol mixed vesicles. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 29;14(15):3363–3370. doi: 10.1021/bi00686a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Sampson E. L. Lipid composition of the normal human brain: gray matter, white matter, and myelin. J Lipid Res. 1965 Oct;6(4):537–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann E., Duwe H. P., Engelhardt H. Membrane bending elasticity and its role for shape fluctuations and shape transformations of cells and vesicles. Faraday Discuss Chem Soc. 1986;(81):281–290. doi: 10.1039/dc9868100281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. B., Jenkins J. T., Webb W. W. Thermal fluctuations of large cylindrical phospholipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):891–899. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84235-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Hui S. W. Direct measurement of headgroup hydration of polar lipids in inverted micelles. Chem Phys Lipids. 1988 Dec;49(3):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(88)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamsunder E., Gruner S. M., Tate M. W., Turner D. C., So P. T., Tilcock C. P. Observation of inverted cubic phase in hydrated dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2332–2336. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Jungalwala F. B. Reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography of phosphatidylcholine: a simple method for determining relative hydrophobic interaction of various molecular species. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):697–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi A. Lipid composition of sarcoplasmic reticulum of human skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 5;248(1):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoeven R. P., Emmelot P., Krol J. H., Oomen-Meulemans E. P. Studies on plasma membranes. XXII. Fatty acid profiles of lipid classes in plasma membranes of rat and mouse livers and hepatomas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J. Lipidic intramembranous particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 27;779(1):43–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh R. E., Hochmuth R. M. Mechanical equilibrium of thick, hollow, liquid membrane cylinders. Biophys J. 1987 Sep;52(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83227-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander A., Rilfors L., Lindblom G. Metabolic changes of membrane lipid composition in Acholeplasma laidlawii by hydrocarbons, alcohols, and detergents: arguments for effects on lipid packing. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7511–7517. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoeven R. P., Emmelot P. Studies on plasma membranes. 18. Lipid class composition of plasma membranes isolated from rat and mouse liver and hepatomas. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(2):105–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



