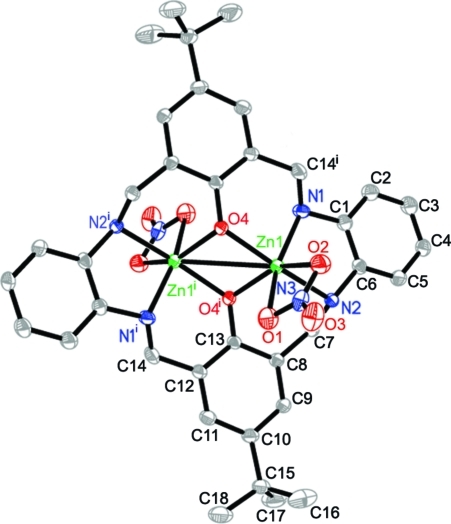
Abstract
In the title centrosymmetric dinuclear zinc(II) complex, [Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(NO3)2], the ZnII atom has a distorted octahedral geometry, defined by two N atoms and two O atoms from the macrocyclic ligand and two O atoms from a chelating nitrate anion and are bridged by two phenolate O atoms, forming a four-membered Zn2O2 ring.
Related literature
For general background to the biochemistry of zinc(II) compounds, see: Bazzicalupi et al. (1997 ▶); Burley et al. (1990 ▶); Lipscomb & Straeter (1996 ▶); Roderick & Mathews (1993 ▶). For related structures, see: Dutta et al. (2005 ▶). For further synthetic details, see: Fan et al. (2009 ▶).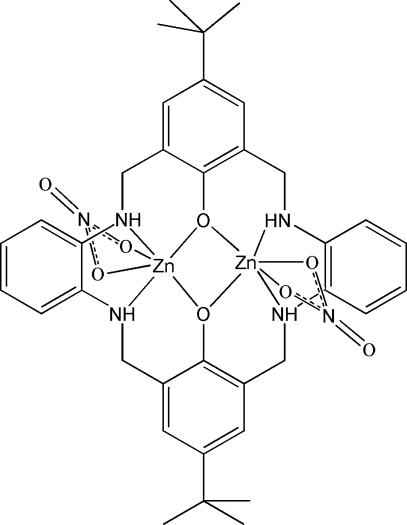
Experimental
Crystal data
[Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(NO3)2]
M r = 817.20
Monoclinic,
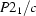
a = 13.7149 (8) Å
b = 18.0691 (10) Å
c = 7.3523 (3) Å
β = 101.110 (5)°
V = 1787.87 (16) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.40 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.661, T max = 0.752
15034 measured reflections
4340 independent reflections
1698 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.099
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.065
S = 0.91
4340 reflections
241 parameters
357 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.66 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809028530/hy2213sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809028530/hy2213Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Zn1—N1 | 2.081 (4) |
| Zn1—N2 | 2.102 (3) |
| Zn1—O1 | 2.264 (3) |
| Zn1—O2 | 2.243 (3) |
| Zn1—O4 | 2.019 (2) |
| Zn1—O4i | 2.043 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) 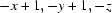 .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 20471014), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Chinese Universities (grant No. NCET-05–0320), the Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Northeast Normal University for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Dinuclear zinc(II) compounds have attracted much interest as a result of their significance in biological systems (Burley et al., 1990; Roderick & Mathews, 1993). In addition, some synthetic dinuclear zinc(II) compounds are found to have functions in dephosphorylation (Bazzicalupi et al., 1997). As part of our studies in this area, the title compound, a new dinuclear zinc(II) compound, has been synthesized and its structure is reported here (Fig. 1).
In the title centrosymmetric dinuclear zinc(II) compound, each of the two ZnII atoms has a distorted octahedral geometry, defined by two N atoms and two O atoms from the macrocyclic (C36H42N4O2) ligand and two O atoms from a chelating nitrate anion. The two Zn atoms are bridged by two phenolate O atoms, forming a four-membered Zn2O2 ring. The Zn—O and Zn—N distances are normal (Table 1) (Dutta et al., 2005).
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by a reaction between the macrocyclic ligand C36H44N4O2 (H2L), which was synthesized according to the published procedure (Fan et al., 2009), and zinc nitrate. A mixture of H2L (0.135 g, 0.25 mmol) and Zn(NO3)2.6H2O (0.149 g, 0.5 mmol) in ethanol (20 ml) was heated with stirring to yield a clear pale yellow solution. Filtration and cooling to room temperature resulted in the formation of a crystalline precipitate. Recrystallization by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution of the compound resulted in well formed yellow blocks of the title compound (yield 52%).
Refinement
N-bonded H atoms were located in a difference map and their coordinates were freely refined, with Uiso fixed. C-bonded H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2(or 1.5 for methyl)Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound. Displaceement ellipsoids are draw at the 30% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(NO3)2] | F(000) = 848 |
| Mr = 817.20 | Dx = 1.518 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2682 reflections |
| a = 13.7149 (8) Å | θ = 1.9–29.2° |
| b = 18.0691 (10) Å | µ = 1.40 mm−1 |
| c = 7.3523 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 101.110 (5)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1787.87 (16) Å3 | 0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra diffractometer | 4340 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1698 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.099 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.3°, θmin = 1.9° |
| ω scans | h = −16→17 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006) | k = −24→24 |
| Tmin = 0.661, Tmax = 0.752 | l = −8→10 |
| 15034 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.065 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.91 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.01P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4340 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 241 parameters | Δρmax = 0.66 e Å−3 |
| 357 restraints | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.2727 (3) | 0.6078 (2) | 0.1435 (5) | 0.0401 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.1724 (3) | 0.6150 (2) | 0.1476 (5) | 0.0486 (12) | |
| H2 | 0.1254 | 0.5897 | 0.0621 | 0.058* | |
| C3 | 0.1424 (3) | 0.6598 (2) | 0.2783 (5) | 0.0506 (12) | |
| H3 | 0.0753 | 0.6651 | 0.2807 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 0.2122 (4) | 0.6965 (2) | 0.4047 (5) | 0.0469 (12) | |
| H4 | 0.1920 | 0.7266 | 0.4931 | 0.056* | |
| C5 | 0.3108 (3) | 0.6893 (2) | 0.4022 (5) | 0.0404 (11) | |
| H5 | 0.3572 | 0.7141 | 0.4900 | 0.048* | |
| C6 | 0.3426 (3) | 0.6460 (2) | 0.2723 (5) | 0.0332 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.5006 (3) | 0.4041 (2) | −0.4386 (4) | 0.0334 (11) | |
| H7A | 0.4997 | 0.3731 | −0.5467 | 0.040* | |
| H7B | 0.5382 | 0.4484 | −0.4537 | 0.040* | |
| C8 | 0.3954 (3) | 0.4258 (2) | −0.4294 (4) | 0.0296 (9) | |
| C9 | 0.3152 (3) | 0.3961 (2) | −0.5486 (5) | 0.0386 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.3268 | 0.3600 | −0.6320 | 0.046* | |
| C10 | 0.2177 (3) | 0.4175 (3) | −0.5504 (5) | 0.0427 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.2043 (3) | 0.4716 (2) | −0.4249 (5) | 0.0464 (11) | |
| H11 | 0.1400 | 0.4879 | −0.4243 | 0.056* | |
| C12 | 0.2823 (3) | 0.5029 (2) | −0.2995 (5) | 0.0375 (11) | |
| C13 | 0.3800 (3) | 0.4796 (2) | −0.3002 (5) | 0.0322 (10) | |
| C14 | 0.2598 (3) | 0.5610 (3) | −0.1703 (5) | 0.0584 (12) | |
| H14A | 0.2707 | 0.6085 | −0.2244 | 0.070* | |
| H14B | 0.1894 | 0.5578 | −0.1684 | 0.070* | |
| C15 | 0.1319 (3) | 0.3808 (3) | −0.6848 (6) | 0.0525 (12) | |
| C16 | 0.1355 (4) | 0.2980 (3) | −0.6507 (6) | 0.0896 (16) | |
| H16A | 0.1987 | 0.2791 | −0.6668 | 0.134* | |
| H16B | 0.0835 | 0.2744 | −0.7372 | 0.134* | |
| H16C | 0.1267 | 0.2882 | −0.5266 | 0.134* | |
| C17 | 0.1414 (3) | 0.3929 (2) | −0.8848 (5) | 0.0749 (14) | |
| H17A | 0.2044 | 0.3745 | −0.9031 | 0.112* | |
| H17B | 0.1367 | 0.4448 | −0.9128 | 0.112* | |
| H17C | 0.0889 | 0.3670 | −0.9653 | 0.112* | |
| C18 | 0.0325 (3) | 0.4077 (3) | −0.6600 (6) | 0.0918 (16) | |
| H18A | 0.0253 | 0.3993 | −0.5344 | 0.138* | |
| H18B | −0.0185 | 0.3813 | −0.7427 | 0.138* | |
| H18C | 0.0268 | 0.4596 | −0.6869 | 0.138* | |
| N1 | 0.3096 (3) | 0.5622 (2) | 0.0108 (5) | 0.0479 (11) | |
| N2 | 0.4476 (3) | 0.63682 (17) | 0.2695 (4) | 0.0315 (9) | |
| N3 | 0.5574 (4) | 0.6847 (2) | −0.1030 (5) | 0.0470 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.6025 (2) | 0.63223 (18) | −0.0177 (4) | 0.0545 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.4639 (3) | 0.68288 (18) | −0.1261 (4) | 0.0575 (10) | |
| O3 | 0.5992 (3) | 0.73463 (18) | −0.1672 (4) | 0.0714 (11) | |
| O4 | 0.4592 (2) | 0.50597 (14) | −0.1821 (3) | 0.0309 (7) | |
| Zn1 | 0.46177 (4) | 0.57671 (3) | 0.03129 (6) | 0.03462 (15) | |
| H1N | 0.296 (3) | 0.5176 (13) | 0.031 (5) | 0.052* | |
| H2N | 0.475 (3) | 0.6800 (13) | 0.282 (5) | 0.052* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.034 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.040 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.017 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C2 | 0.037 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.045 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| C3 | 0.038 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C4 | 0.046 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.045 (2) | 0.011 (3) | 0.014 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C5 | 0.038 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C6 | 0.029 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.032 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.0007 (19) |
| C7 | 0.036 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.026 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0078 (19) | −0.0020 (19) |
| C8 | 0.030 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0254 (19) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0060 (18) | −0.003 (2) |
| C9 | 0.041 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0300 (19) | 0.001 (2) | 0.0052 (19) | −0.0112 (18) |
| C10 | 0.033 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.041 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0022 (18) | −0.013 (2) |
| C11 | 0.031 (2) | 0.063 (3) | 0.043 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C12 | 0.035 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0104 (19) |
| C13 | 0.031 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0019 (19) |
| C14 | 0.043 (3) | 0.078 (3) | 0.051 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.018 (2) |
| C15 | 0.034 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.061 (2) | 0.001 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.019 (2) |
| C16 | 0.083 (3) | 0.087 (3) | 0.088 (3) | −0.027 (3) | −0.011 (3) | −0.007 (3) |
| C17 | 0.064 (3) | 0.089 (3) | 0.062 (3) | −0.011 (3) | −0.013 (2) | −0.013 (3) |
| C18 | 0.048 (3) | 0.120 (4) | 0.101 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.055 (3) |
| N1 | 0.032 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.046 (2) | 0.000 (3) | 0.0058 (19) | −0.017 (3) |
| N2 | 0.037 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0292 (18) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0064 (18) | −0.0054 (17) |
| N3 | 0.071 (4) | 0.031 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.005 (3) | 0.018 (3) | −0.005 (2) |
| O1 | 0.058 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0080 (17) | 0.0188 (18) | 0.0047 (17) |
| O2 | 0.055 (3) | 0.063 (3) | 0.0534 (19) | 0.003 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0025 (17) |
| O3 | 0.098 (3) | 0.038 (2) | 0.090 (2) | −0.012 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0090 (19) |
| O4 | 0.032 (2) | 0.0326 (18) | 0.0283 (15) | 0.0044 (15) | 0.0067 (14) | −0.0065 (13) |
| Zn1 | 0.0343 (3) | 0.0372 (3) | 0.0319 (2) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0052 (2) | −0.0047 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.388 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.393 (5) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C1—N1 | 1.441 (5) | C15—C18 | 1.490 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.378 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.516 (6) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C15—C17 | 1.517 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.363 (5) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.368 (5) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C6—N2 | 1.453 (5) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C7—N2i | 1.502 (4) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.510 (5) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9700 | Zn1—N1 | 2.081 (4) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9700 | N1—H1N | 0.845 (19) |
| C8—C9 | 1.376 (5) | N2—C7i | 1.502 (4) |
| C8—C13 | 1.404 (5) | Zn1—N2 | 2.102 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.390 (5) | N2—H2N | 0.863 (19) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | N3—O3 | 1.212 (4) |
| C10—C11 | 1.380 (5) | N3—O1 | 1.234 (4) |
| C10—C15 | 1.534 (5) | N3—O2 | 1.262 (5) |
| C11—C12 | 1.391 (5) | Zn1—O1 | 2.264 (3) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | Zn1—O2 | 2.243 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.405 (5) | Zn1—O4 | 2.019 (2) |
| C12—C14 | 1.487 (5) | Zn1—O4i | 2.043 (2) |
| C13—O4 | 1.341 (4) | Zn1—Zn1i | 3.0302 (10) |
| C14—N1 | 1.375 (4) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.6 (4) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 123.1 (4) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 117.3 (4) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.0 (4) | C15—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C15—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.0 | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.6 (4) | C15—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.7 (4) | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.9 (4) | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.5 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.2 (4) | C14—N1—C1 | 119.5 (4) |
| C5—C6—N2 | 121.6 (4) | C14—N1—Zn1 | 112.1 (3) |
| C1—C6—N2 | 119.1 (4) | C1—N1—Zn1 | 110.9 (3) |
| N2i—C7—C8 | 113.3 (3) | C14—N1—H1N | 94 (3) |
| N2i—C7—H7A | 108.9 | C1—N1—H1N | 108 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.9 | Zn1—N1—H1N | 111 (3) |
| N2i—C7—H7B | 108.9 | C6—N2—C7i | 110.9 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.9 | C6—N2—Zn1 | 108.8 (2) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 | C7i—N2—Zn1 | 109.3 (2) |
| C9—C8—C13 | 119.6 (4) | C6—N2—H2N | 108 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.6 (4) | C7i—N2—H2N | 103 (3) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 118.7 (4) | Zn1—N2—H2N | 116 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 123.2 (4) | O3—N3—O1 | 122.8 (5) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 118.4 | O3—N3—O2 | 120.7 (5) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 118.4 | O1—N3—O2 | 116.4 (5) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 116.3 (4) | N3—O1—Zn1 | 93.6 (3) |
| C11—C10—C15 | 123.5 (4) | N3—O2—Zn1 | 93.8 (3) |
| C9—C10—C15 | 120.2 (4) | C13—O4—Zn1 | 128.2 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 123.1 (4) | C13—O4—Zn1i | 111.8 (2) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 118.5 | Zn1—O4—Zn1i | 96.50 (9) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 118.5 | O4—Zn1—O4i | 83.50 (9) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.2 (4) | O4—Zn1—N1 | 89.82 (13) |
| C11—C12—C14 | 118.9 (4) | O4i—Zn1—N1 | 111.54 (13) |
| C13—C12—C14 | 121.9 (4) | O4—Zn1—N2 | 169.86 (13) |
| O4—C13—C12 | 123.1 (4) | O4i—Zn1—N2 | 92.88 (11) |
| O4—C13—C8 | 118.4 (4) | N1—Zn1—N2 | 82.68 (14) |
| C12—C13—C8 | 118.6 (4) | O4—Zn1—O2 | 98.08 (11) |
| N1—C14—C12 | 120.3 (4) | O4i—Zn1—O2 | 147.90 (13) |
| N1—C14—H14A | 107.2 | N1—Zn1—O2 | 100.54 (14) |
| C12—C14—H14A | 107.2 | N2—Zn1—O2 | 90.02 (12) |
| N1—C14—H14B | 107.2 | O4—Zn1—O1 | 92.56 (11) |
| C12—C14—H14B | 107.2 | O4i—Zn1—O1 | 91.78 (11) |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 106.9 | N1—Zn1—O1 | 156.68 (13) |
| C18—C15—C16 | 107.6 (4) | N2—Zn1—O1 | 97.03 (12) |
| C18—C15—C17 | 108.8 (4) | O2—Zn1—O1 | 56.16 (11) |
| C16—C15—C17 | 107.2 (4) | O4—Zn1—Zn1i | 42.06 (7) |
| C18—C15—C10 | 112.8 (4) | O4i—Zn1—Zn1i | 41.45 (6) |
| C16—C15—C10 | 108.9 (4) | N1—Zn1—Zn1i | 104.20 (11) |
| C17—C15—C10 | 111.4 (4) | N2—Zn1—Zn1i | 133.61 (9) |
| C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 | O2—Zn1—Zn1i | 131.67 (9) |
| C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 | O1—Zn1—Zn1i | 92.91 (9) |
| H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (6) | C12—C13—O4—Zn1 | 4.7 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.9 (4) | C8—C13—O4—Zn1 | −174.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (6) | C12—C13—O4—Zn1i | 122.7 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (7) | C8—C13—O4—Zn1i | −56.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.8 (7) | C13—O4—Zn1—O4i | 124.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.2 (6) | Zn1i—O4—Zn1—O4i | 0.0 |
| C4—C5—C6—N2 | −179.0 (4) | C13—O4—Zn1—N1 | 12.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.8 (6) | Zn1i—O4—Zn1—N1 | −111.71 (13) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.2 (4) | C13—O4—Zn1—N2 | 54.8 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—N2 | 178.7 (4) | Zn1i—O4—Zn1—N2 | −69.6 (7) |
| N1—C1—C6—N2 | −1.4 (6) | C13—O4—Zn1—O2 | −87.9 (3) |
| N2i—C7—C8—C9 | −114.2 (4) | Zn1i—O4—Zn1—O2 | 147.67 (13) |
| N2i—C7—C8—C13 | 68.2 (5) | C13—O4—Zn1—O1 | −144.1 (3) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.9 (6) | Zn1i—O4—Zn1—O1 | 91.50 (12) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −176.7 (4) | C13—O4—Zn1—Zn1i | 124.4 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.4 (6) | C14—N1—Zn1—O4 | −41.6 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C15 | −178.8 (4) | C1—N1—Zn1—O4 | −177.9 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.3 (6) | C14—N1—Zn1—O4i | −124.5 (3) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | 177.8 (4) | C1—N1—Zn1—O4i | 99.2 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.9 (6) | C14—N1—Zn1—N2 | 145.2 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C14 | 179.8 (4) | C1—N1—Zn1—N2 | 8.9 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—O4 | −178.9 (3) | C14—N1—Zn1—O2 | 56.6 (3) |
| C14—C12—C13—O4 | 2.2 (6) | C1—N1—Zn1—O2 | −79.7 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.5 (6) | C14—N1—Zn1—O1 | 54.5 (5) |
| C14—C12—C13—C8 | −178.4 (4) | C1—N1—Zn1—O1 | −81.8 (4) |
| C9—C8—C13—O4 | 178.1 (3) | C14—N1—Zn1—Zn1i | −81.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—C13—O4 | −4.3 (5) | C1—N1—Zn1—Zn1i | 142.2 (2) |
| C9—C8—C13—C12 | −1.3 (6) | C6—N2—Zn1—O4 | −51.9 (8) |
| C7—C8—C13—C12 | 176.3 (3) | C7i—N2—Zn1—O4 | 69.3 (8) |
| C11—C12—C14—N1 | 140.1 (4) | C6—N2—Zn1—O4i | −120.7 (2) |
| C13—C12—C14—N1 | −40.9 (7) | C7i—N2—Zn1—O4i | 0.5 (2) |
| C11—C10—C15—C18 | −2.3 (6) | C6—N2—Zn1—N1 | −9.4 (2) |
| C9—C10—C15—C18 | 176.8 (4) | C7i—N2—Zn1—N1 | 111.8 (3) |
| C11—C10—C15—C16 | −121.6 (5) | C6—N2—Zn1—O2 | 91.3 (3) |
| C9—C10—C15—C16 | 57.5 (5) | C7i—N2—Zn1—O2 | −147.6 (2) |
| C11—C10—C15—C17 | 120.4 (4) | C6—N2—Zn1—O1 | 147.1 (2) |
| C9—C10—C15—C17 | −60.5 (6) | C7i—N2—Zn1—O1 | −91.7 (2) |
| C12—C14—N1—C1 | −166.4 (4) | C6—N2—Zn1—Zn1i | −112.0 (2) |
| C12—C14—N1—Zn1 | 61.4 (5) | C7i—N2—Zn1—Zn1i | 9.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—N1—C14 | 40.4 (6) | N3—O2—Zn1—O4 | −88.6 (2) |
| C6—C1—N1—C14 | −139.5 (4) | N3—O2—Zn1—O4i | 2.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—N1—Zn1 | 173.0 (3) | N3—O2—Zn1—N1 | −180.0 (2) |
| C6—C1—N1—Zn1 | −6.9 (5) | N3—O2—Zn1—N2 | 97.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—N2—C7i | 66.3 (5) | N3—O2—Zn1—O1 | −1.0 (2) |
| C1—C6—N2—C7i | −111.5 (4) | N3—O2—Zn1—Zn1i | −60.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—N2—Zn1 | −173.5 (3) | N3—O1—Zn1—O4 | 99.0 (2) |
| C1—C6—N2—Zn1 | 8.7 (4) | N3—O1—Zn1—O4i | −177.4 (2) |
| O3—N3—O1—Zn1 | −179.5 (4) | N3—O1—Zn1—N1 | 3.5 (5) |
| O2—N3—O1—Zn1 | −1.7 (4) | N3—O1—Zn1—N2 | −84.3 (2) |
| O3—N3—O2—Zn1 | 179.5 (3) | N3—O1—Zn1—O2 | 1.0 (2) |
| O1—N3—O2—Zn1 | 1.7 (4) | N3—O1—Zn1—Zn1i | 141.1 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HY2213).
References
- Bazzicalupi, C., Bencini, A., Bianchi, A., Fusi, V., Giorgi, C., Paoletti, P., Valtancoli, B. & Zanchi, D. (1997). Inorg. Chem 36, 2784–2790. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Burley, S. K., David, P. R., Taylor, A. & Lipscomb, W. N. (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 6878–6882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dutta, B., Bag, P., Flörke, U. & Nag, K. (2005). Inorg. Chem 44,147–157. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.-J., Ma, J.-F. & Liu, J. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m777–m778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, W. N. & Straeter, N. (1996). Chem. Rev 96, 2375–2434. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2006). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Roderick, S. & Mathews, B. W. (1993). Biochemistry, 32, 3907–3912. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809028530/hy2213sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809028530/hy2213Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report