Abstract
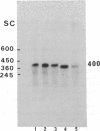
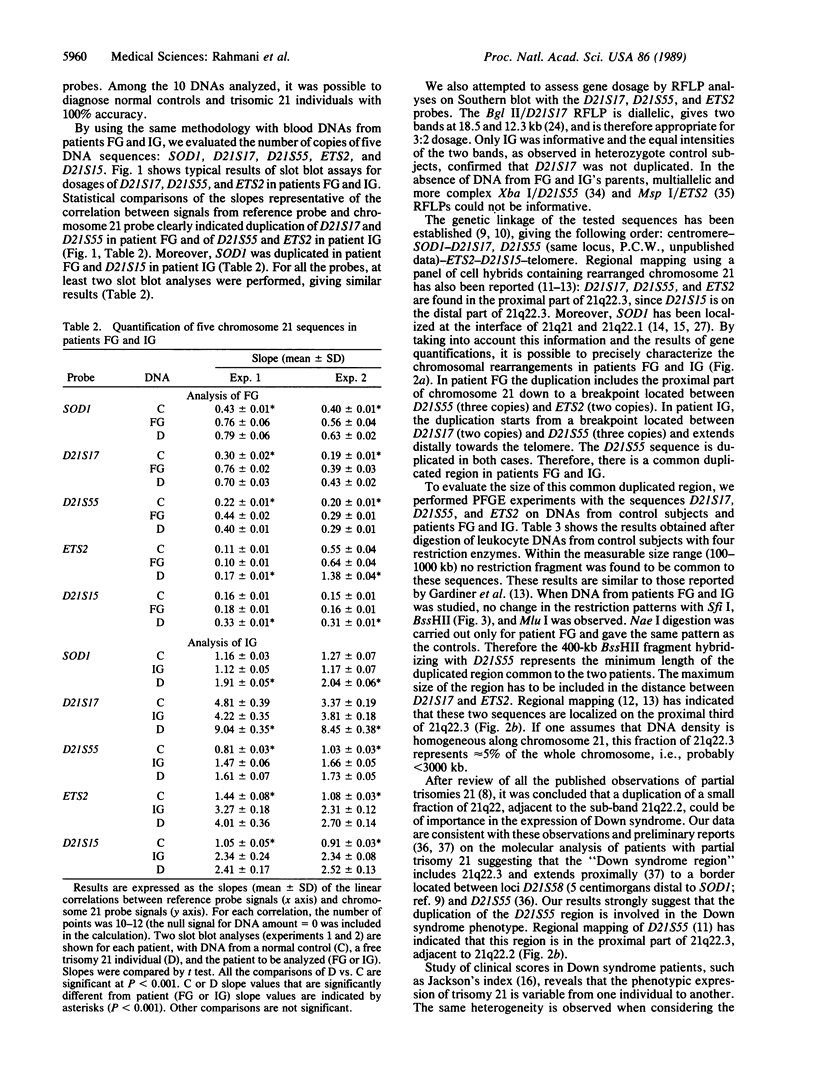
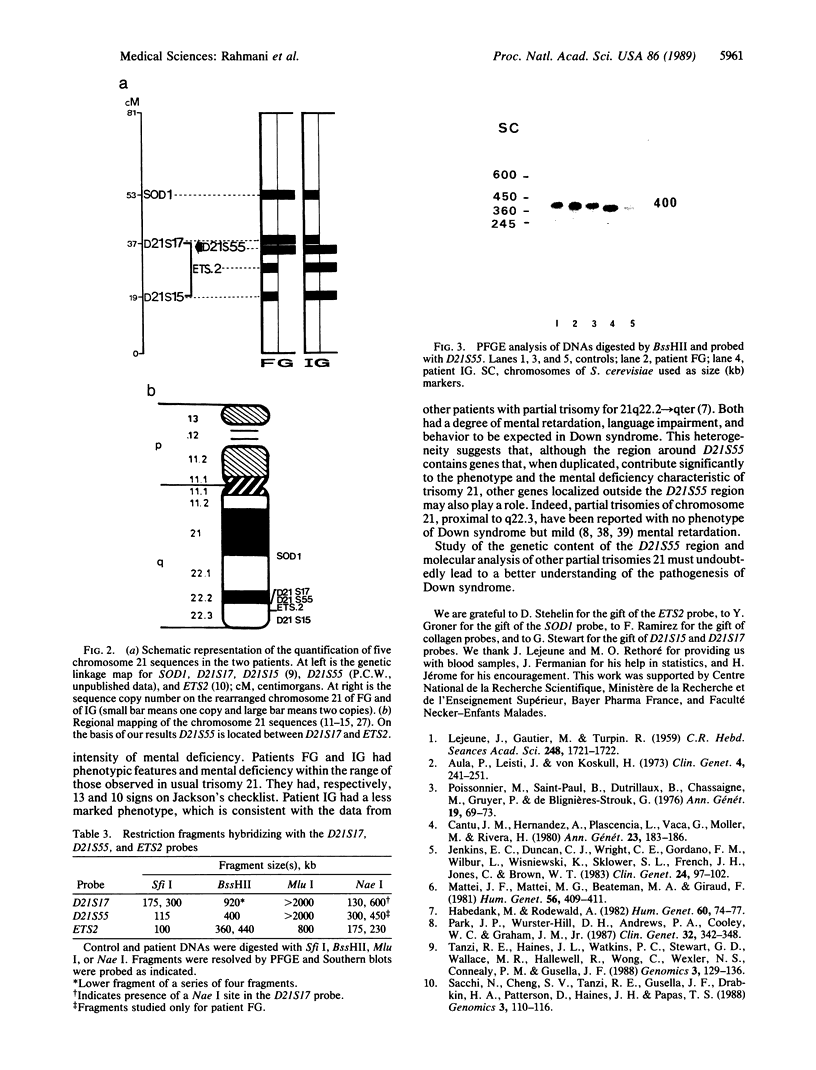
The duplication of a specific region of chromosome 21 could be responsible for the main features of Down syndrome. To define and localize this region, we analyzed at the molecular level the DNA of two patients with partial duplication of chromosome 21. These patients belong to two groups of Down syndrome patients characterized by different partial trisomies 21: (i) duplication of the long arm, proximal to 21q22.2, and (ii) duplication of the end of the chromosome, distal to 21q22.2 We assessed the copy number of five chromosome 21 sequences (SOD1, D21S17, D21S55, ETS2, and D21S15) and found that D21S55 was duplicated in both cases. By means of pulsed-field gel analysis and with the knowledge of regional mapping of the probes D21S17, D21S55 and ETS2, we estimated the size of the common duplicated region to be between 400 and 3000 kilobases. This region, localized on the proximal part of 21q22.3, is suspected to contain genes the overexpression of which is crucial in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aula P., Leisti J., von Koskull H. Partial trisomy 21. Clin Genet. 1973;4(3):241–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulukos K. E., Pognonec P., Begue A., Galibert F., Gesquière J. C., Stéhelin D., Ghysdael J. Identification in chickens of an evolutionarily conserved cellular ets-2 gene (c-ets-2) encoding nuclear proteins related to the products of the c-ets proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):697–705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantu J. M., Hernandez A., Plascencia L., Vaca G., Moller M., Rivera H. Partial trisomy and monosomy 21 in an infant with an unusual de novo 21/21 translocation. Ann Genet. 1980;23(3):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Créau-Goldberg N., Gegonne A., Delabar J., Cochet C., Cabanis M. O., Stehelin D., Turleau C., de Grouchy J. Maternal origin of a de novo balanced t(21q21q) identified by ets-2 polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;76(4):396–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00272452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Goldgaber D., Lamour Y., Nicole A., Huret J. L., de Grouchy J., Brown P., Gajdusek D. C., Sinet P. M. Beta amyloid gene duplication in Alzheimer's disease and karyotypically normal Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2950593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Lamour Y., Gegonne A., Davous P., Roudier M., Nicole A., Ceballos I., Amouyel P., Stehelin D., Sinet P. M. Rearrangement of chromosome 21 in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Genet. 1986;29(4):226–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Sinet P. M., Chadefaux B., Nicole A., Gegonne A., Stehelin D., Fridlansky F., Créau-Goldberg N., Turleau C., de Grouchy J. Submicroscopic duplication of chromosome 21 and trisomy 21 phenotype (Down syndrome). Hum Genet. 1987 Jul;76(3):225–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00283612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habedank M., Rodewald A. Moderate Down's syndrome in three siblings having partial trisomy 21q22.2 to qter and therefore no SOD-1 excess. Hum Genet. 1982;60(1):74–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00281269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Smit E. M. Partial trisomy 21. Further evidence that trisomy of band 21q22 is essential for Down's phenotype. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00295803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Uzan G., Weil D., Nicolas H., Kaplan J. C., Marguerie C., Kahn A., Junien C. The genes coding for A alpha-, B beta-, and gamma-chains of fibrinogen map to 4q2. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):760–768. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huret J. L., Delabar J. M., Marlhens F., Aurias A., Nicole A., Berthier M., Tanzer J., Sinet P. M. Down syndrome with duplication of a region of chromosome 21 containing the CuZn superoxide dismutase gene without detectable karyotypic abnormality. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00281069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. F., North E. R., 3rd, Thomas J. G. Clinical diagnosis of Down's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1976 May;9(5):483–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. C., Duncan C. J., Wright C. E., Giordano F. M., Wilbur L., Wisniewski K., Sklower S. L., French J. H., Jones C., Brown W. T. Atypical Down syndrome and partial trisomy 21. Clin Genet. 1983 Aug;24(2):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb02219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Lavie V., Groner Y. Human cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase cDNA clone: a probe for studying the molecular biology of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2808–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G., Baeteman M. A., Giraud F. Trisomy 21 for the region 21q223: identification by high-resolution R-banding patterns. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):409–411. doi: 10.1007/BF00274703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Faro S. H., Clark W. J., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Cloning a cDNA for the pro-alpha 2 chain of human type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Stewart G. D., Newcomb P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Drabkin H. A., Kurnit D. M. Human chromosome 21-encoded cDNA clones. Gene. 1986;49(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. P., Wurster-Hill D. H., Andrews P. A., Cooley W. C., Graham J. M., Jr Free proximal trisomy 21 without the Down syndrome. Clin Genet. 1987 Nov;32(5):342–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. L., Kidd K. K., Willard H. F. Report of the committee on human gene mapping by recombinant DNA techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):390–566. doi: 10.1159/000132487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier M. C., Laffage M., Philip N., Passage E., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F. Trisomy 21q223 and Down's phenotype correlation evidenced by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):277–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01790097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlisny M. B., Lee G., Selkoe D. J. Gene dosage of the amyloid beta precursor protein in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):669–671. doi: 10.1126/science.2960019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poissonnier M., Saint-Paul B., Dutrillaux B., Chassaigne M., Gruyer P., de Blignières-Strouk G. Trisomie 21 partielle (21q21 leads to 21q22.2) Ann Genet. 1976 Mar;19(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoul O., Carpentier S., Dutrillaux B., Mallet R., Lejeune J. Trisomies partielles du chromosome 21 par translocation maternelle t(15;21) (q26; q21. Ann Genet. 1976 Sep;19(3):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Cheng S. V., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Drabkin H. A., Patterson D., Haines J. H., Papas T. S. The ETS genes on chromosome 21 are distal to the breakpoint of the acute myelogenous leukemia translocation (8;21). Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Nalbantoglu J., Sergovich F. R., Papas T. S. Human ETS2 gene on chromosome 21 is not rearranged in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7675–7679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Poissonnier M., Raoul O., Rethore M. O., Allard D., Lejeune J., Jerome H. Trisomie 21 et superoxyde dismutase-1 (IPO-A). Tentative de localisation sur la sous bande 21Q22.1. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Bird E. D., Latt S. A., Neve R. L. The amyloid beta protein gene is not duplicated in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):666–669. doi: 10.1126/science.2890207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Watkins P. C., Drabkin H. A., Jabs E. W., Gusella J. F., Patterson D. Regional localization of DNA sequences on chromosome 21 using somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):793–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]