Abstract
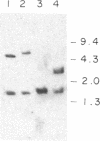
The yeast nuclear gene MSD1 coding for mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetase has been cloned and sequenced. The identity of the gene is confirmed by the following evidence. (i) The primary structure of the protein derived from the gene sequence is similar to that of the yeast cytoplasmic aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. (ii) In situ disruption of MSD1 in a respiratory-competent haploid strain of yeast induces a pleiotropic phenotype consistent with a lesion in mitochondrial protein synthesis. (iii) Mitochondria from a mutant with a disrupted chromosomal copy of MSD1 are unable to acylate mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA. The primary structures of the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial aspartyl-tRNA synthetases are similar to the yeast cytoplasmic lysyl-tRNA synthetase, suggesting that the two types of synthetases may have a common evolutionary origin. Searches of the current protein banks also have revealed a high degree of sequence similarity of the lysyl-tRNA synthetase to the product of the Escherichia coli herC gene and to the partial sequence of a protein encoded by an unidentified reading frame located adjacent to the E. coli frdA gene. Based on the sequence similarities and the map positions of the herC and frdA loci, we propose herC to be the structural gene of the constitutively expressed lysyl-tRNA synthetase of E. coli and the unidentified reading frame to be the structural gene of the heat-inducible lysyl-tRNA synthetase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. G., Winter G. Conserved cysteine and histidine residues in the structures of the tyrosyl and methionyl-tRNA synthetases. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 23;145(2):191–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Walter P., Ebel J. P., Lacroute F., Fasiolo F. The yeast VAS1 gene encodes both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic valyl-tRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T. Nucleotide sequence coding for the flavoprotein subunit of the fumarate reductase of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):479–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Cook R. G., Tate W. P., Caskey C. T. Bacterial peptide chain release factors: conserved primary structure and possible frameshift regulation of release factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3616–3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich R. V., Hirshfield I. N. Mapping of the constitutive lysyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5311–5313. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5311-5313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Kujawa C., Fukuhara H. Physical and genetic organization of petite and grande yeast mitochondrial DNA. IV. In vivo transcription products of mitochondrial DNA and localization of 23 S ribosomal RNA in petite mutants of saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):185–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck J. D., Hatfield G. W. Valyl-tRNA synthetase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Primary structure and homology within a family of aminoacyl-TRNA synthetases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):868–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Dessen P., Blanquet S. Sequence similarities among the family of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jue R. A., Woodbury N. W., Doolittle R. F. Sequence homologies among E. coli ribosomal proteins: evidence for evolutionarily related groupings and internal duplications. J Mol Evol. 1980 May;15(2):129–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01732666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Jönsson Y. H., Björk G. R., Ikeda H., Nakamura Y. Chromosomal location and structure of the operon encoding peptide-chain-release factor 2 of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Myers A. M., Lee S., Tzagoloff A. Isolation and characterization of the yeast gene coding for the alpha subunit of mitochondrial phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3690–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macino G., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system: two separate genes coding for threonyl-tRNA in the mitochondrial DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 31;169(2):183–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00271669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirande M., Waller J. P. The yeast lysyl-tRNA synthetase gene. Evidence for general amino acid control of its expression and domain structure of the encoded protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18443–18451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Pape L. K., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2087–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. MSW, a yeast gene coding for mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15371–15377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene (MST1) coding for the mitochondrial threonyl-tRNA1 synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15362–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Improved separation of transfer RNA's on polychlorotrifuoroethylene-supported reversed-phase chromatography columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 11;228(3):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90748-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel P. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases: general scheme of structure-function relationships in the polypeptides and recognition of transfer RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:125–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellami M., Fasiolo F., Dirheimer G., Ebel J. P., Gangloff J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for yeast cytoplasmic aspartyl-tRNA synthetase (APS); mapping of the 5' and 3' termini of AspRS mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1657–1666. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Foury F. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system XVI. Modified form of the ATPase proteolipid in oligomycin-resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 15;65(3):391–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Kurkulos M., Repetto B. Homology of yeast mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase and isoleucyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):850–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Needleman R. B. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system: isolation of nuclear and cytoplasmic mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with specific defects in mitochondrial functions. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.826-831.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Vambutas A., Akai A. Characterization of MSM1, the structural gene for yeast mitochondrial methionyl-tRNA synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V., Neidhardt F. C. Gene for heat-inducible lysyl-tRNA synthetase (lysU) maps near cadA in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1066–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1066-1068.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Berge A. M., Zoutewelle G., Needleman R. B. Regulation of maltose fermentation in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. 3. Constitutive mutations at the MAL6-locus and suppressors changing a constitutive phenotype into a maltose negative phenotype. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00266147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]