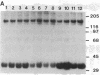
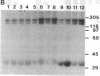
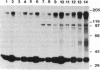
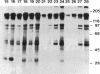
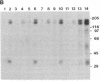
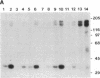
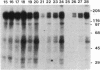
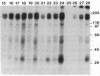
Abstract
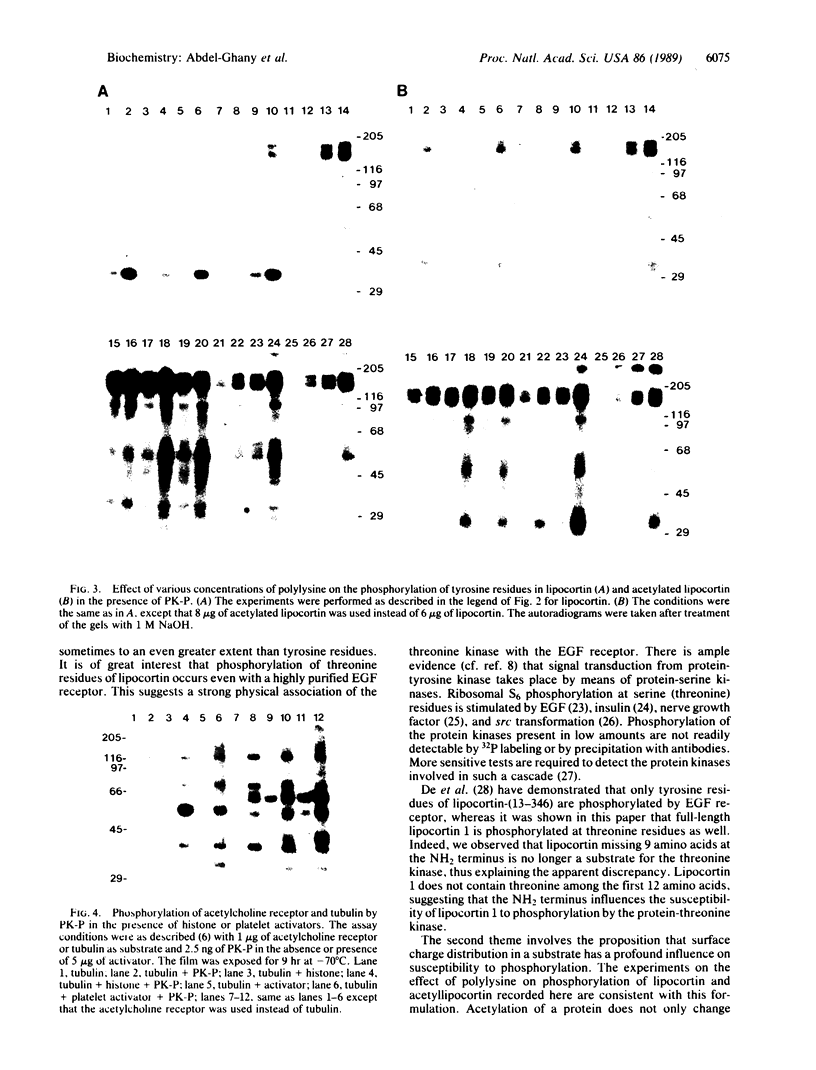
In this paper we show that epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates the phosphorylation of lipocortin 1, at threonine as well as at tyrosine residues, by a highly purified preparation of the EGF receptor. The phosphorylation of threonine residues is catalyzed by an enzyme that contaminates the receptor preparations, since crude extracts of A431 plasma membranes contain larger amounts of the threonine kinase than does the receptor preparation. Protein kinase P (2.5 ng) inhibits both threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation of lipocortin 1 while greatly stimulating the autophosphorylation of the EGF receptor. Acetyllipocortin 1 is poorly phosphorylated at tyrosine residues by the EGF receptor kinase, but it becomes readily phosphorylated in the presence of polylysine. The most likely explanation for this observation is that there is an interaction between polylysine and acetyllipocortin that converts the latter into a suitable substrate for the EGF receptor. These and other experiments described in this paper point to a role of surface charges in the susceptibility of substrates to attach by protein kinases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Ghany M., Kole H. K., Racker E. Effect of protein kinase P on phosphorylations catalyzed by the epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8888–8892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Ghany M., el-Gendy K., Zhang S., Raden D., Racker E. Brain protein kinase C phosphorylating poly(arginine,serine) or lamin B is stimulated by anions and by an activator purified from bovine serum albumin preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1761–1765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed K., Goueli S. A., Williams-Ashman H. G. Characteristics of polyamine stimulation of cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinase reactions. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):767–771. doi: 10.1042/bj2320767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Klarlund J. K., Yagaloff K. A., Bradford A. P., Lewis R. E. Insulin receptor signaling. Activation of multiple serine kinases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11017–11020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Platelet-derived growth factor mimics phorbol diester action on epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4080–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farron-Furstenthal F., Lightholder J. R. Effects of polyamines and histones on the phosphorylation of non-histone proteins in isolated rat liver nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jul 14;83(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Cohen S. Isolation of a calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase from A-431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2636–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Cooper J. A., Bretscher A., Hunter T. The protein-tyrosine kinase substrate, p81, is homologous to a chicken microvillar core protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):660–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., GRAVES D. J., FISCHER E. H. Factors affecting the activity of muscle phosphorylase b kinase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2867–2873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole H. K., Abdel-Ghany M., Racker E. Specific dephosphorylation of phosphoproteins by protein-serine and -tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5849–5853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Guroff G. Purification and mechanism of activation of a nerve growth factor-sensitive S6 kinase from PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2832–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Abdel Ghany M., Racker E. Inhibition of tyrosine protein kinases by halomethyl ketones. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6138–6144. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Sinclair L. K. Epidermal growth factor-dependent phosphorylation of lipocortin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):81–84. doi: 10.1038/321081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. The search for oncogene targets. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 Feb 15;81(4):247–251. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.4.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., King M. J., Sale G. J. Two systems in vitro that show insulin-stimulated serine kinase activity towards the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):509–519. doi: 10.1042/bj2500509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommercorn J., Mulligan J. A., Lozeman F. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of casein kinase II in response to insulin and to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8834–8838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C., Teitelbaum D., Herz A., Arnon R., Sela M. Molecular requirements involved in suppression of EAE by synthetic basic copolymers of amino acids. Immunochemistry. 1976 Apr;13(4):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagita Y., Abdel-Ghany M., Raden D., Nelson N., Racker E. Polypeptide-dependent protein kinase from bakers' yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]