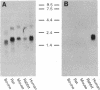
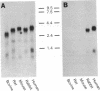
Abstract
ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) are small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that enhance the enzymatic activities of cholera toxin. Two ARF cDNAs, ARF1 and ARF3, were cloned from a human cerebellum library. Based on deduced amino acid sequences and patterns of hybridization of cDNA and oligonucleotide probes with mammalian brain poly(A)+ RNA, human ARF1 is the homologue of bovine ARF1. Human ARF3, which differs from bovine ARF1 and bovine ARF2, appears to represent a newly identified third type of ARF. Hybridization patterns of human ARF cDNA and clone-specific oligonucleotides with poly(A)+ RNA are consistent with the presence of at least two, and perhaps four, separate ARF messages in human brain. In vitro translation of ARF1, ARF2, and ARF3 produced proteins that behaved, by SDS/PAGE, similar to a purified soluble brain ARF. Deduced amino acid sequences of human ARF1 and ARF3 contain regions, similar to those in other G proteins, that are believed to be involved in GTP binding and hydrolysis. ARFs also exhibit a modest degree of homology with a bovine phospholipase C. The observations reported here support the conclusion that the ARFs are members of a multigene family of small guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Definition of the regulation of ARF mRNAs and of function(s) of recombinant ARF proteins will aid in the elucidation of the physiologic role(s) of ARFs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allende J. E. GTP-mediated macromolecular interactions: the common features of different systems. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2356–2367. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.2452111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Do GTPases direct membrane traffic in secretion? Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):669–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90081-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Puskas R. S., Berger S. L. Homopolymeric tailing. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:337–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday K. R. Regional homology in GTP-binding proto-oncogene products and elongation factors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(6):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7906–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Goddard C., Newkirk M. Chemical and immunological characterization of the 21-kDa ADP-ribosylation factor of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8282–8287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Matsui Y., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. A novel small molecular weight GTP-binding protein with the same putative effector domain as the ras proteins in bovine brain membranes. Purification, determination of primary structure, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18965–18971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell L. G., Merril C. R. Affinity generation of single-stranded DNA for dideoxy sequencing following the polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 1;178(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90631-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of guanyl nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins by bacterial toxins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:303–379. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narumiya S., Sekine A., Fujiwara M. Substrate for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase, Gb, has an amino acid sequence homologous to a putative rho gene product. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17255–17257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizon V., Chardin P., Lerosey I., Olofsson B., Tavitian A. Human cDNAs rap1 and rap2 homologous to the Drosophila gene Dras3 encode proteins closely related to ras in the 'effector' region. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price S. R., Nightingale M., Tsai S. C., Williamson K. C., Adamik R., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins that enhance choleragen ADP-ribosyltransferase activity: nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of an ADP-ribosylation factor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5488–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell J. L., Kahn R. A. Sequences of the bovine and yeast ADP-ribosylation factor and comparison to other GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Chang P. P., Chen H. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. Stimulation of choleragen enzymatic activities by GTP and two soluble proteins purified from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1768–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. C., Noda M., Adamik R., Moss J., Vaughan M. Enhancement of choleragen ADP-ribosyltransferase activities by guanyl nucleotides and a 19-kDa membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5139–5142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Meurs K. P., Angus C. W., Lavu S., Kung H. F., Czarnecki S. K., Moss J., Vaughan M. Deduced amino acid sequence of bovine retinal Go alpha: similarities to other guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Kondo J., Hishida T., Teranishi Y., Takai Y. Purification and characterization of a GTP-binding protein with a molecular weight of 20,000 in bovine brain membranes. Identification as the rho gene product. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9926–9932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]