Abstract
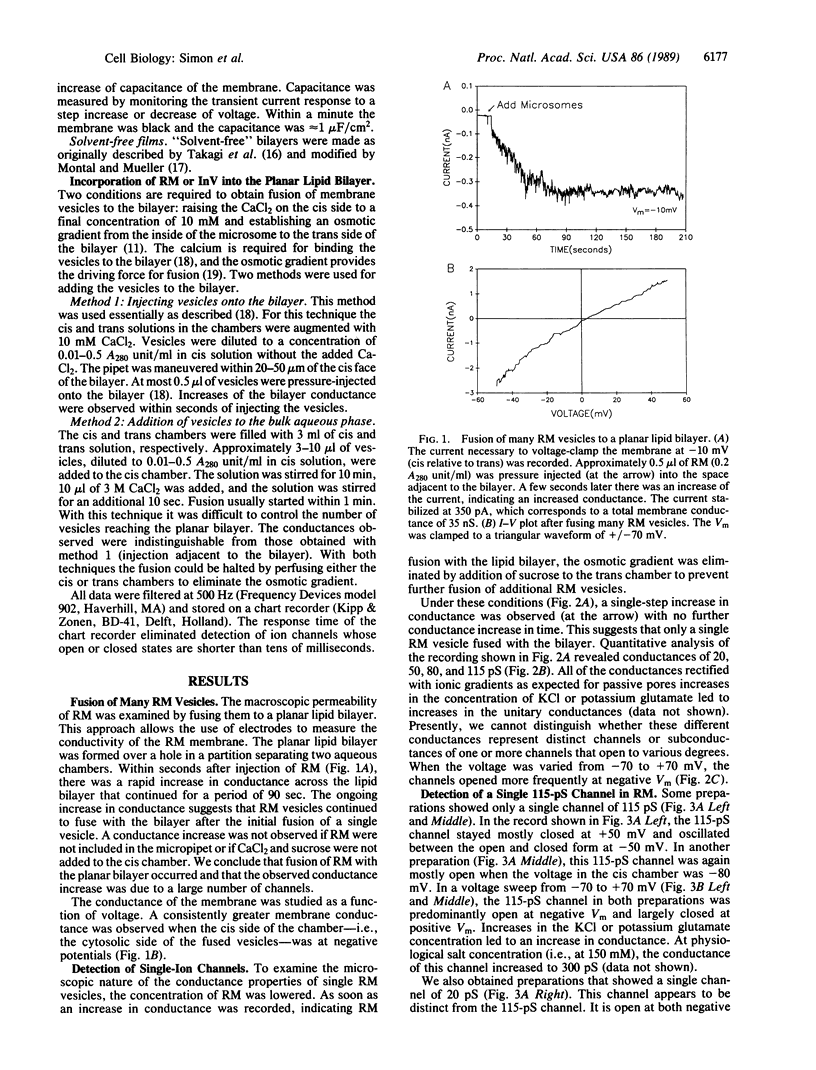
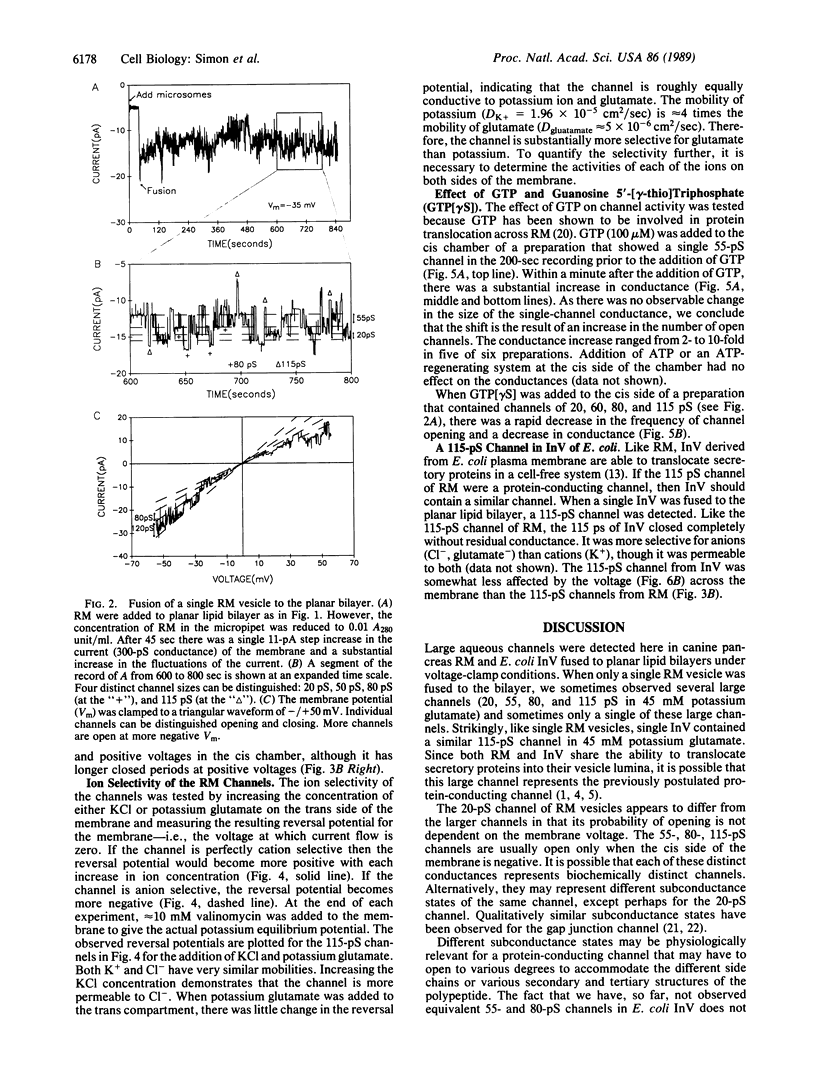
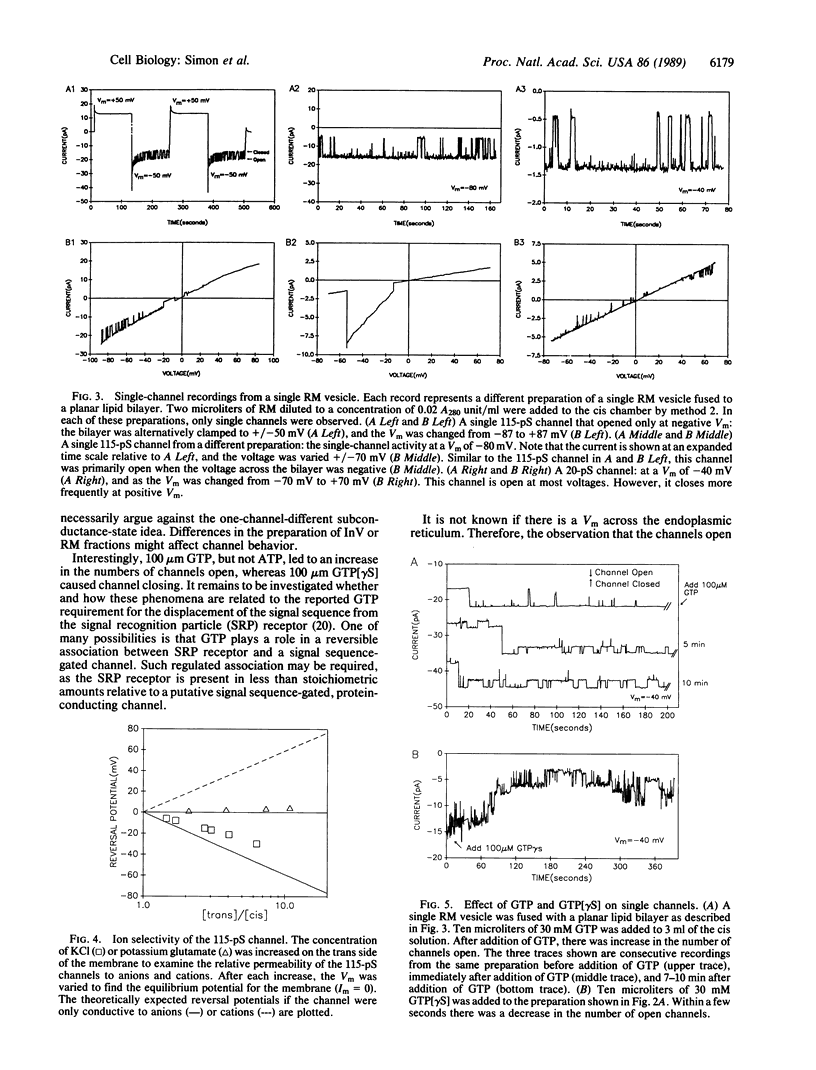
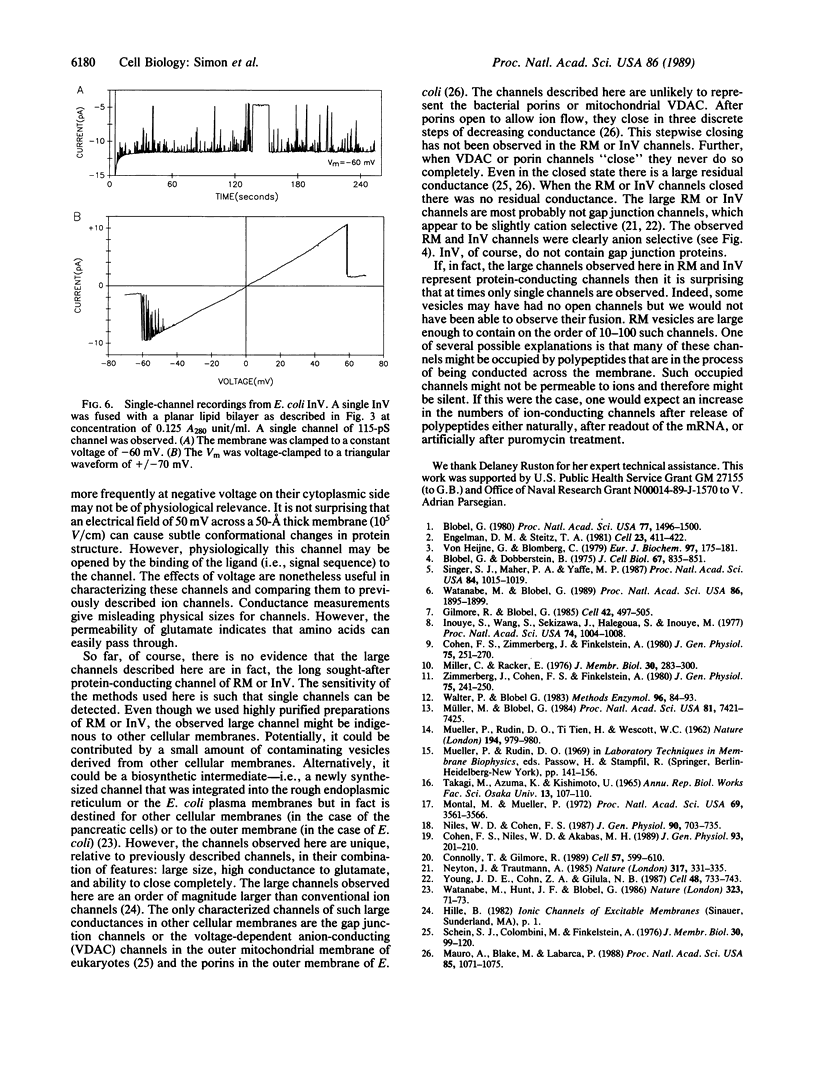
Voltage clamp conditions were used to study the membrane permeability properties of rough microsomes (RM) derived from the rough endoplasmic reticulum of canine pancreas and inverted vesicles (InV) derived from the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Membrane vesicles of RM or InV were fused to a planar lipid bilayer that was formed in a hole of a partition separating two chambers. Fusion of a single RM vesicle yielded a single-step conductance increase. Some preparations yielded unitary conductances of 20, 55, 80, and 115 pS in 45 mM potassium glutamate. These channels were largely open at negative membrane potential on the cytoplasmic side of the RM membrane, mostly closed at positive voltages, permeable to amino acids, and slightly more selective for anions than cations. There was a dramatic increase in the number of open channels when 100 microM GTP was added to the cytoplasmic side of the fused RM, whereas 100 microM guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate caused closing of channels. ATP had no effect. A large channel of 115 pS at 45 mM potassium glutamate was also detected after the fusion of InV. As both RM and InV share the ability to translocate secretory proteins, it is possible that the 115-pS channel in both membranes represents a protein-conducting channel.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. S., Niles W. D., Akabas M. H. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with a planar membrane depends on the membrane permeability of the solute used to create the osmotic pressure. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Feb;93(2):201–210. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. S., Zimmerberg J., Finkelstein A. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. II. Incorporation of a vesicular membrane marker into the planar membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):251–270. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Gilmore R. The signal recognition particle receptor mediates the GTP-dependent displacement of SRP from the signal sequence of the nascent polypeptide. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Translocation of secretory proteins across the microsomal membrane occurs through an environment accessible to aqueous perturbants. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Wang S., Sekizawa J., Halegoua S., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence for the peptide extension on the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1004–1008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P., RUDIN D. O., TIEN H. T., WESCOTT W. C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:979–980. doi: 10.1038/194979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro A., Blake M., Labarca P. Voltage gating of conductance in lipid bilayers induced by porin from outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1071–1075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1976;30(3):283–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01869673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. In vitro translocation of bacterial proteins across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7421–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Trautmann A. Single-channel currents of an intercellular junction. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):331–335. doi: 10.1038/317331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles W. D., Cohen F. S. Video fluorescence microscopy studies of phospholipid vesicle fusion with a planar phospholipid membrane. Nature of membrane-membrane interactions and detection of release of contents. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Nov;90(5):703–735. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Colombini M., Finkelstein A. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained from paramecium mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 28;30(2):99–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01869662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Maher P. A., Yaffe M. P. On the translocation of proteins across membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1015–1019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Blobel G. Site-specific antibodies against the PrlA (secY) protein of Escherichia coli inhibit protein export by interfering with plasma membrane binding of preproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1895–1899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Hunt J. F., Blobel G. In vitro synthesized bacterial outer membrane protein is integrated into bacterial inner membranes but translocated across microsomal membranes. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):71–73. doi: 10.1038/323071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Gilula N. B. Functional assembly of gap junction conductance in lipid bilayers: demonstration that the major 27 kd protein forms the junctional channel. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Cohen F. S., Finkelstein A. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. I. Discharge of vesicular contents across the planar membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):241–250. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Blomberg C. Trans-membrane translocation of proteins. The direct transfer model. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):175–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


