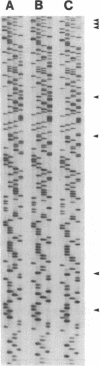
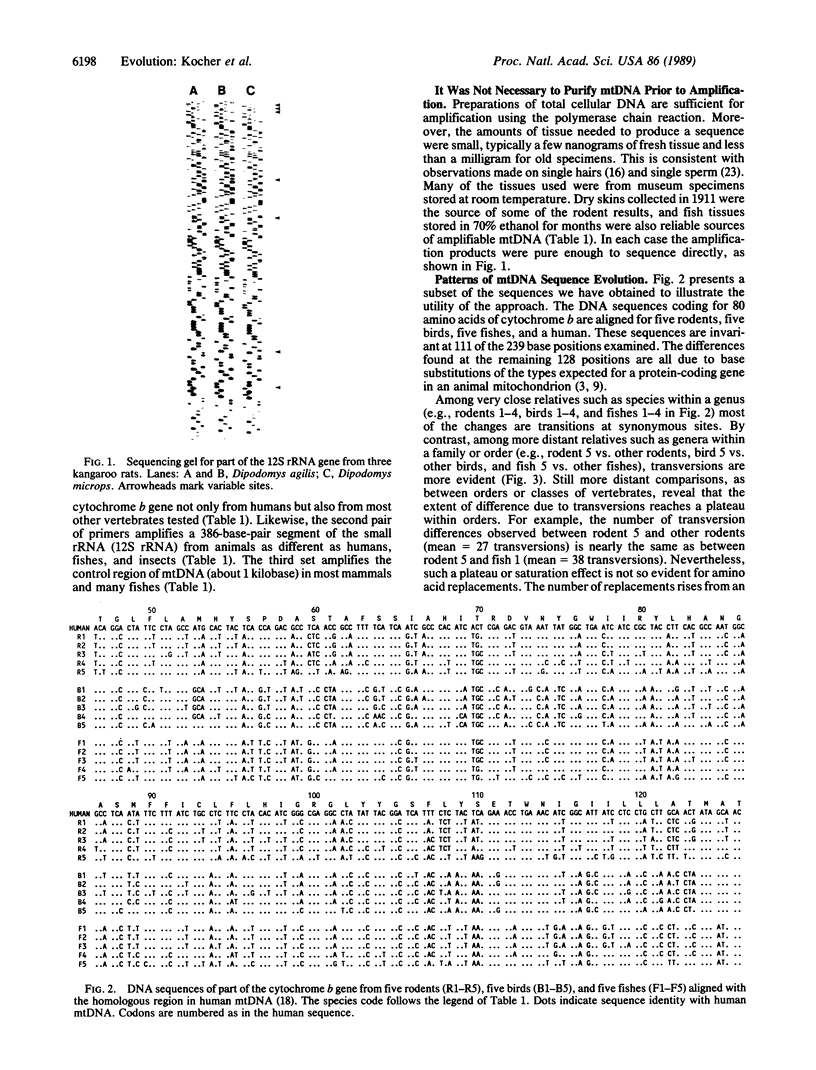
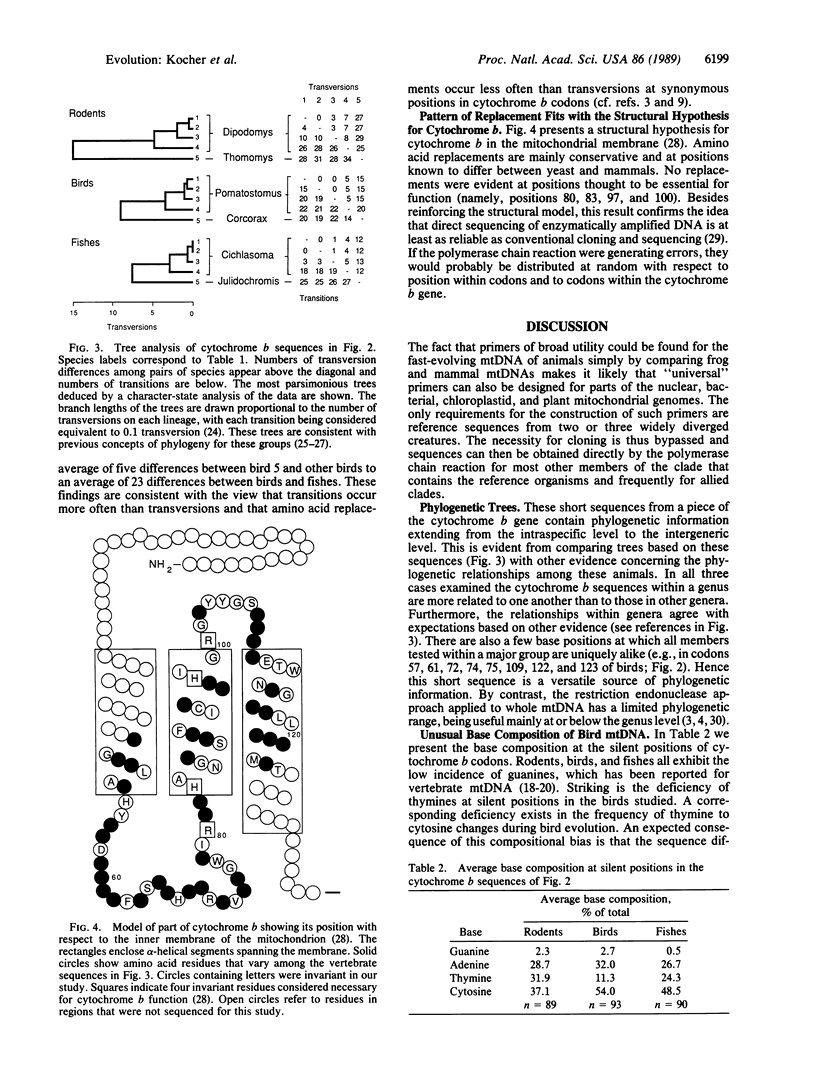
Abstract
With a standard set of primers directed toward conserved regions, we have used the polymerase chain reaction to amplify homologous segments of mtDNA from more than 100 animal species, including mammals, birds, amphibians, fishes, and some invertebrates. Amplification and direct sequencing were possible using unpurified mtDNA from nanogram samples of fresh specimens and microgram amounts of tissues preserved for months in alcohol or decades in the dry state. The bird and fish sequences evolve with the same strong bias toward transitions that holds for mammals. However, because the light strand of birds is deficient in thymine, thymine to cytosine transitions are less common than in other taxa. Amino acid replacement in a segment of the cytochrome b gene is faster in mammals and birds than in fishes and the pattern of replacements fits the structural hypothesis for cytochrome b. The unexpectedly wide taxonomic utility of these primers offers opportunities for phylogenetic and population research.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquadro C. F., Desse S. F., Bland M. M., Langley C. H., Laurie-Ahlberg C. C. Molecular population genetics of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene region of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Dec;114(4):1165–1190. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.4.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquadro C. F., Greenberg B. D. Human mitochondrial DNA variation and evolution: analysis of nucleotide sequences from seven individuals. Genetics. 1983 Feb;103(2):287–312. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avise J. C. Mitochondrial DNA and the evolutionary genetics of higher animals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Jan 29;312(1154):325–342. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clary D. O., Wolstenholme D. R. The mitochondrial DNA molecular of Drosophila yakuba: nucleotide sequence, gene organization, and genetic code. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(3):252–271. doi: 10.1007/BF02099755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSalle R., Freedman T., Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. Tempo and mode of sequence evolution in mitochondrial DNA of Hawaiian Drosophila. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):157–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02111289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm-Bychowski K. M., Wilson A. C. Rates of nuclear DNA evolution in pheasant-like birds: evidence from restriction maps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):688–692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Bowman B., Freiberger M., Ryder O. A., Wilson A. C. DNA sequences from the quagga, an extinct member of the horse family. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):282–284. doi: 10.1038/312282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Gilbert K. Mutational analysis of the mouse mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):607–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. H., Gyllensten U. B., Cui X. F., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):414–417. doi: 10.1038/335414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. L., MacArthur H., Yang S. Y. Systematic relationships of the four-toed populations of Dipodomys heermanni. J Mammal. 1976 Feb;57(1):159–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Gifford J. A., Wilson A. C. Mitochondrial DNA sequences from a 7000-year old brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9775–9787. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Wilson A. C. Polymerase chain reaction reveals cloning artefacts. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):387–388. doi: 10.1038/334387b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe B. A., Ma D. P., Wilson R. K., Wong J. F. The complete nucleotide sequence of the Xenopus laevis mitochondrial genome. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9759–9774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vawter L., Brown W. M. Nuclear and mitochondrial DNA comparisons reveal extreme rate variation in the molecular clock. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):194–196. doi: 10.1126/science.3018931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigilant L., Stoneking M., Wilson A. C. Conformational mutation in human mtDNA detected by direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5945–5955. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. J., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. The polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrischnik L. A., Higuchi R. G., Stoneking M., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA: direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):529–542. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]