Abstract
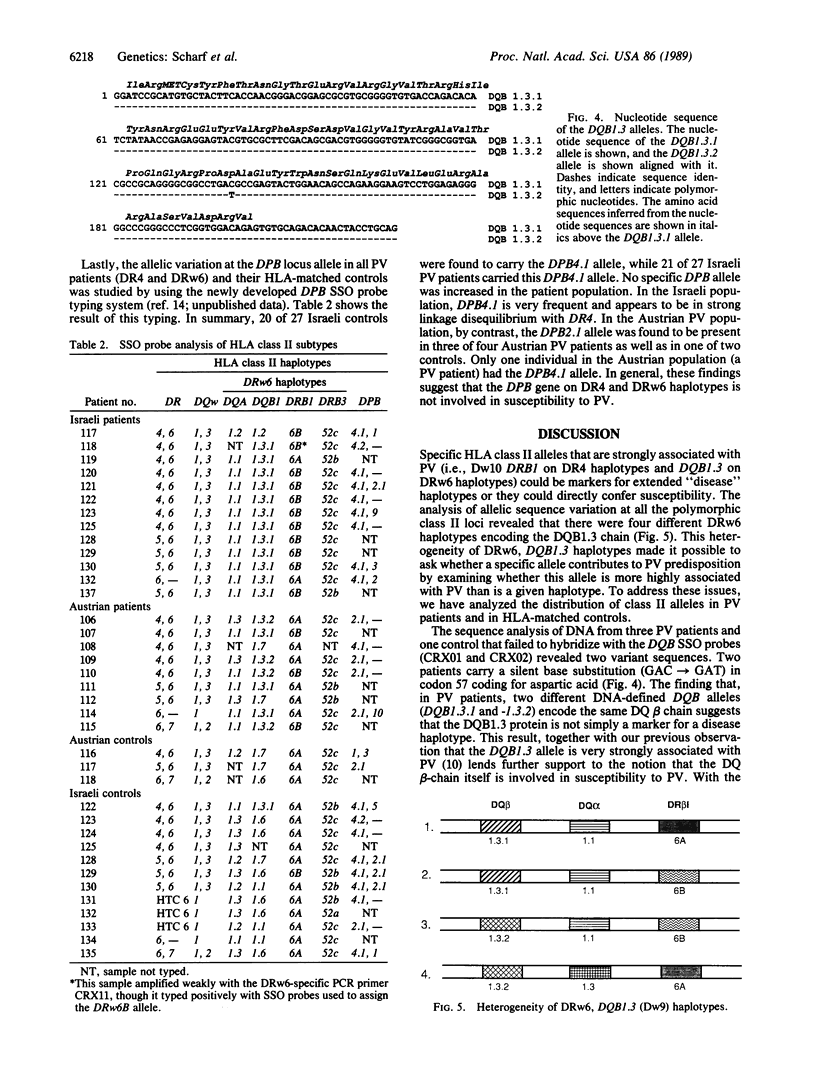
The autoimmune dermatologic disease pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is associated with the serotypes HLA-DR4 and HLA-DRw6. Based on nucleotide sequence and oligonucleotide probe analysis of enzymatically amplified DNA encoding HLA-DR beta chain (HLA-DRB) and HLA-DQ beta chain (HLA-DQB; henceforth HLA is omitted from designations), we showed previously that the DR4 susceptibility was associated with the Dw10 DRB1 allele [encoding the mixed lymphocyte culture (MLC)-defined Dw10 specificity]. The DRw6 susceptibility similarly was shown to be associated with a rare DQB allele (DQB1.3), which differed from another nonsusceptible allele by only a valine-to-aspartic acid substitution at position 57. Given the linkage disequilibrium that characterizes HLA haplotypes, it is difficult to assign disease susceptibility to a specific locus rather than to a closely linked gene(s) on the same haplotype. To address this problem, we have analyzed all of the polymorphic loci of the class II HLA region (DRB1, DRB3, DQA, DQB, and DPB) on the DRw6 haplotypes in patients and controls. In 22 PV patients, 4 different DRw6 haplotypes were found that encode the same DQ beta chain (DQB1.3) but contained silent nucleotide differences at the DQB locus as well as coding sequence differences in the DQA and DRB loci. These results, obtained by using a method for allele-specific polymerase chain reaction amplification, strongly support the hypothesis that the allele DQB1.3 confers susceptibility. This DQB allele is correlated with the MLC-defined Dw9 specificity and is associated with two different DRB1 alleles (the common "6A" associated with DRw13 and the rare "6B" associated with DRw14). Since 86% (19 of 22) of DRw6+ patients contain the DQB1.3 allele (vs. 3% of controls), whereas 64% (14 of 22) contain the DRB1 allele 6B (vs. 6% of the controls), we conclude that most of the DRw6 susceptibility to PV can be accounted for by the DQ beta chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brautbar C., Moscovitz M., Livshits T., Haim S., Hacham-Zadeh S., Cohen H. A., Sharon R., Nelken D., Cohen T. HLA-DRw4 in pemphigus vulgaris patients in Israel. Tissue Antigens. 1980 Sep;16(3):238–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1980.tb00299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocke S., Brautbar C., Steinman L., Abramsky O., Rothbard J., Neumann D., Fuchs S., Mozes E. In vitro proliferative responses and antibody titers specific to human acetylcholine receptor synthetic peptides in patients with myasthenia gravis and relation to HLA class II genes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1894–1900. doi: 10.1172/JCI113807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Long C. M., Mickelson E., Hansen J. A., Ferrara G. B., Angelini G., Erlich H. A. Analysis of HLA-DP allelic sequence polymorphism using the in vitro enzymatic DNA amplification of DP-alpha and DP-beta loci. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):4024–4030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. First domain sequence of the HLA-DRB1 chain from two HLA-DRw14 homozygous typing cell lines: TEM (Dw9) and AMALA (Dw16). Hum Immunol. 1989 Feb;24(2):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. A., Beatty P. G., Anasetti C., Martin P. J., Mickelson E., Thomas E. D. Transplantation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC). Br Med Bull. 1987 Jan;43(1):203–216. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Bugawan T. L., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Allelic sequence variation of the HLA-DQ loci: relationship to serology and to insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirmaier C., Holten D., Bylina E. J., Youvan D. C. Electron transfer in a genetically modified bacterial reaction center containing a heterodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7562–7566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. S., Bell J. I., Rust N. A., McDevitt H. O. Structural and functional variability among DQ beta alleles of DR2 subtypes. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00345459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Friedmann A., Brautbar C., Szafer F., Steinman L., Horn G., Gyllensten U., Erlich H. A. HLA class II allelic variation and susceptibility to pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Sequence analysis of the HLA-DR beta and HLA-DQ beta loci from three Pemphigus vulgaris patients. Hum Immunol. 1988 May;22(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(88)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehy M. J., Scharf S. J., Rowe J. R., Neme de Gimenez M. H., Meske L. M., Erlich H. A., Nepom B. S. A diabetes-susceptible HLA haplotype is best defined by a combination of HLA-DR and -DQ alleles. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):830–835. doi: 10.1172/JCI113965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Brautbar C., Szafer F., Friedmann A., Tzfoni E., Todd J. A., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. A newly characterized HLA DQ beta allele associated with pemphigus vulgaris. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1026–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.2894075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szafer F., Brautbar C., Tzfoni E., Frankel G., Sherman L., Cohen I., Hacham-Zadeh S., Aberer W., Tappeiner G., Holubar K. Detection of disease-specific restriction fragment length polymorphisms in pemphigus vulgaris linked to the DQw1 and DQw3 alleles of the HLA-D region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6542–6545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Powell M. B., Sakai K., Rothbard J. B., Steinman L. Multiple discrete encephalitogenic epitopes of the autoantigen myelin basic protein include a determinant for I-E class II-restricted T cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1181–1186. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]