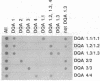
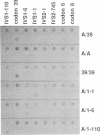
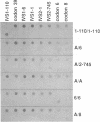
Abstract
The analysis of DNA for the presence of particular mutations or polymorphisms can be readily accomplished by differential hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. The in vitro DNA amplification technique, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), has facilitated the use of these probes by greatly increasing the number of copies of target DNA in the sample prior to hybridization. In a conventional assay with immobilized PCR product and labeled oligonucleotide probes, each probe requires a separate hybridization. Here we describe a method by which one can simultaneously screen a sample for all known allelic variants at an amplified locus. In this format, the oligonucleotides are given homopolymer tails with terminal deoxyribonucleotidyltransferase, spotted onto a nylon membrane, and covalently bound by UV irradiation. Due to their long length, the tails are preferentially bound to the nylon, leaving the oligonucleotide probe free to hybridize. The target segment of the DNA sample to be tested is PCR-amplified with biotinylated primers and then hybridized to the membrane containing the immobilized oligonucleotides under stringent conditions. Hybridization is detected nonradioactively by binding of streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase to the biotinylated DNA, followed by a simple colorimetric reaction. This technique has been applied to HLA-DQA genotyping (six types) and to the detection of Mediterranean beta-thalassemia mutations (nine alleles).
Full text
PDF

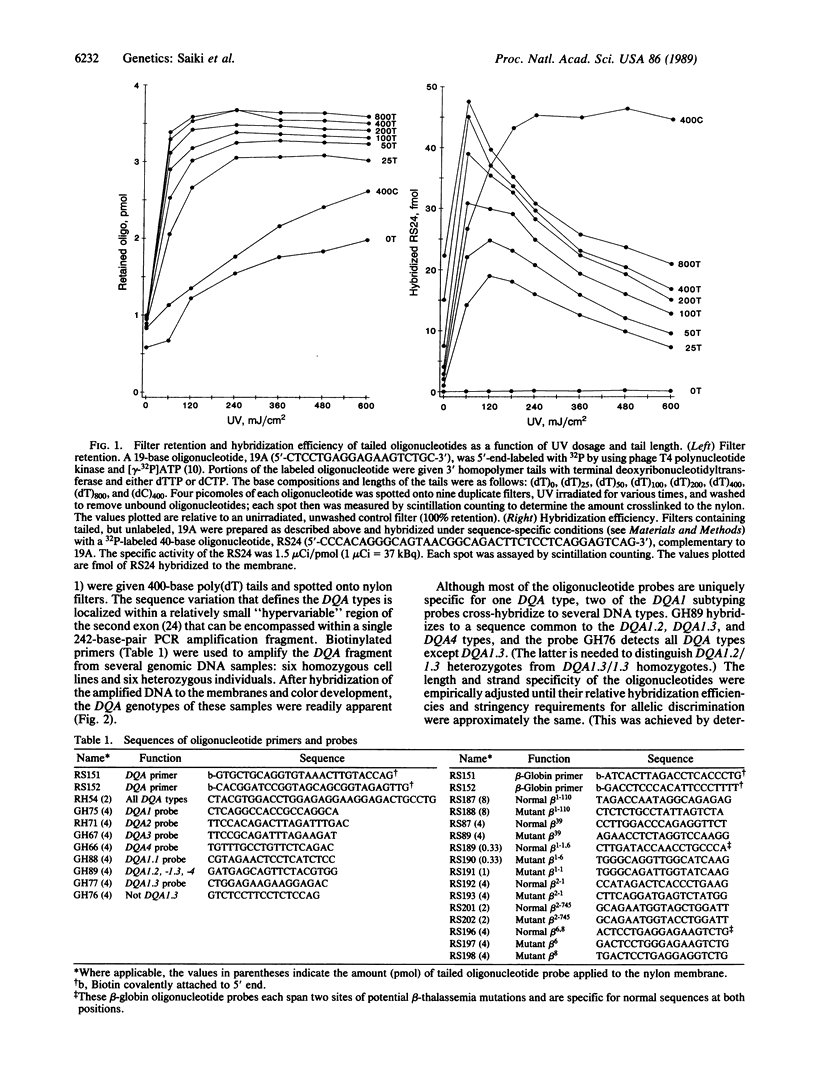

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos J. L., Verlaan-de Vries M., Jansen A. M., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J. Three different mutations in codon 61 of the human N-ras gene detected by synthetic oligonucleotide hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):9155–9163. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.9155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Nguyen P. N., Caskey C. T. Deletion screening of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus via multiplex DNA amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 9;16(23):11141–11156. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.23.11141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. J., Reyes A. A., Morin C., Itakura K., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Detection of sickle cell beta S-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):278–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly B. A. The synthesis of oligonucleotides containing a primary amino group at the 5'-terminus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3131–3139. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Cimino G. D., Isaacs S. T., Ferguson M., Hearst J. E. Reverse Southern hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9943–9954. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., von Beroldingen C. H., Sensabaugh G. F., Erlich H. A. DNA typing from single hairs. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):543–546. doi: 10.1038/332543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Esser V., Russell D. W. AvaII polymorphism in the human LDL receptor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):379–379. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Bugawan T. L., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Allelic sequence variation of the HLA-DQ loci: relationship to serology and to insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta S., Takagi K., Wallace R. B., Itakura K. Dissociation kinetics of 19 base paired oligonucleotide-DNA duplexes containing different single mismatched base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):797–811. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J. DNA sequence variants in the G gamma-, A gamma-, delta- and beta-globin genes of man. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Orkin S. H., Antonarakis S. E., Sexton J. P., Boehm C. D., Goff S. C., Waber P. G. Molecular characterization of seven beta-thalassemia mutations in Asian Indians. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):593–596. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01853.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Orkin S. H., Markham A. F., Chapman C. R., Youssoufian H., Waber P. G. Quantification of the close association between DNA haplotypes and specific beta-thalassaemia mutations in Mediterraneans. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):152–154. doi: 10.1038/310152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd V. J., Golbus M. S., Wallace R. B., Itakura K., Woo S. L. Prenatal diagnosis of alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency by direct analysis of the mutation site in the gene. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):639–642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo Y. M., Mehal W. Z., Fleming K. A. Rapid production of vector-free biotinylated probes using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8719–8719. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Brutlag D. Addition of homopolymers to the 3'-ends of duplex DNA with terminal transferase. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:41–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirastu M., Kan Y. W., Cao A., Conner B. J., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Detection of a single nucleotide mutation in DNA. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 4;309(5):284–287. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308043090506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Chang C. A., Levenson C. H., Warren T. C., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Erlich H. A. Diagnosis of sickle cell anemia and beta-thalassemia with enzymatically amplified DNA and nonradioactive allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):537–541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlaan-de Vries M., Bogaard M. E., van den Elst H., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Bos J. L. A dot-blot screening procedure for mutated ras oncogenes using synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. Z., Cai S. P., He X., Lin H. X., Lin H. J., Huang Z. G., Chehab F. F., Kan Y. W. Molecular basis of beta thalassemia in south China. Strategy for DNA analysis. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):37–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00291231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]