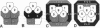Abstract
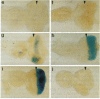
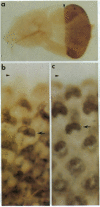
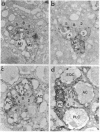
The sevenless gene encodes a cell surface receptor that has protein-tyrosine kinase activity and is expressed in a highly specific and complex pattern in the developing Drosophila eye. We have coupled the sevenless promoter to the reporter gene lacZ and have examined the pattern of beta-galactosidase expression in the developing eyes of transgenic larvae. Our results indicate that the dynamic pattern of sevenless protein expression is regulated transcriptionally. Promoter sequences located 5' of the coding region are insufficient for the wild-type level of gene expression but appear to be able to confer the correct pattern of expression. In contrast, enhancer sequences within the body of the gene can confer both the correct pattern and a normal level of expression on either the sevenless promoter or heterologous promoters. Thus the complex pattern of sevenless expression is redundantly encoded within proximal promoter sequences and enhancer elements internal to the gene but relies on these enhancer sequences for correct quantitative expression.
Full text
PDF


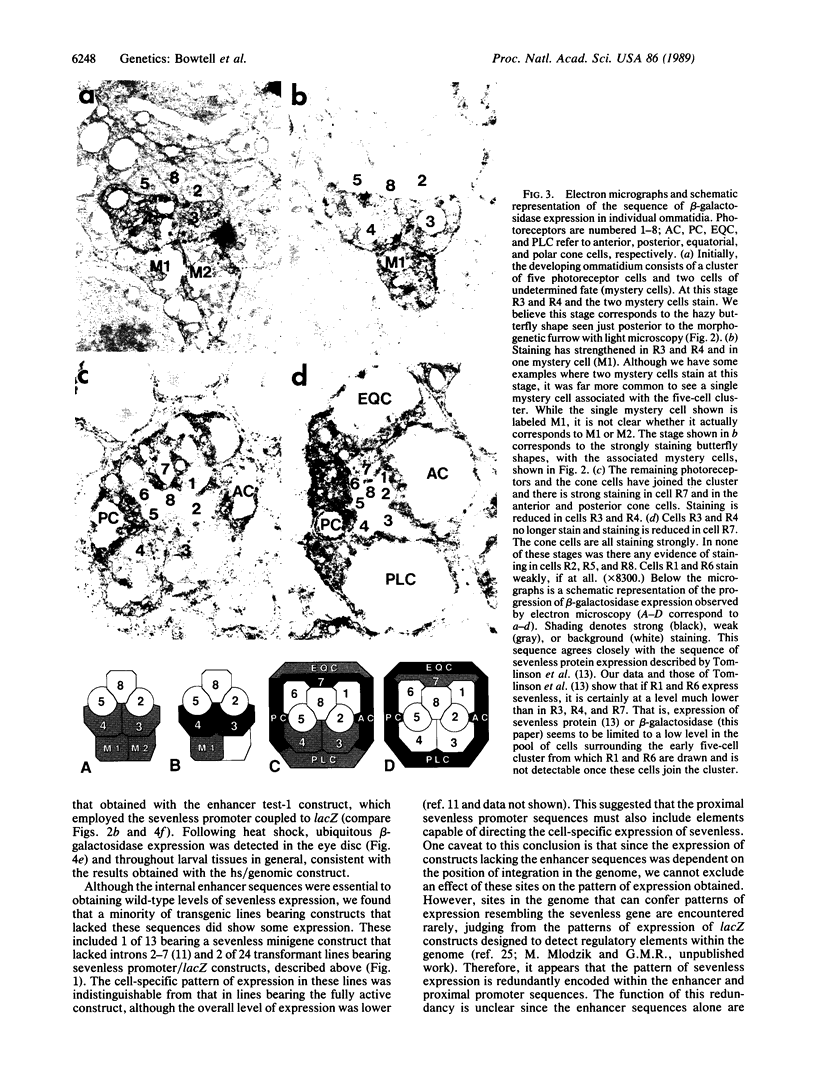

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee U., Renfranz P. J., Hinton D. R., Rabin B. A., Benzer S. The sevenless+ protein is expressed apically in cell membranes of developing Drosophila retina; it is not restricted to cell R7. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee U., Renfranz P. J., Pollock J. A., Benzer S. Molecular characterization and expression of sevenless, a gene involved in neuronal pattern formation in the Drosophila eye. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90569-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Hafen E. Control of photoreceptor cell fate by the sevenless protein requires a functional tyrosine kinase domain. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basler K., Hafen E. Ubiquitous expression of sevenless: position-dependent specification of cell fate. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):931–934. doi: 10.1126/science.2493159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond B. J., Davidson N. The Drosophila melanogaster actin 5C gene uses two transcription initiation sites and three polyadenylation sites to express multiple mRNA species. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2080–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Nucleotide sequence and structure of the sevenless gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):620–634. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Ommatidia in the developing Drosophila eye require and can respond to sevenless for only a restricted period. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90626-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanet R., Magana-Schwencke N., Fabre F. Potential DNA-binding domains in the RAD18 gene product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. A., Stark W. S., Walker J. A. Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol. 1976 Apr;256(2):415–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A., Green S. M. Cell lineage in the developing retina of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):142–152. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liposits Z., Sétáló G., Flerkó B. Application of the silver-gold intensified 3,3'-diaminobenzidine chromogen to the light and electron microscopic detection of the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone system of the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1984 Oct;13(2):513–525. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Simon J. A., Sutton C. A. New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mismer D., Rubin G. M. Analysis of the promoter of the ninaE opsin gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):565–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane C. J., Gehring W. J. Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9123–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ready D. F., Hanson T. E., Benzer S. Development of the Drosophila retina, a neurocrystalline lattice. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):217–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Development of the Drosophila retina: inductive events studied at single cell resolution. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):519–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Sutton C. A., Lobell R. B., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T. Determinants of heat shock-induced chromosome puffing. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90340-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. Regulated expression of genes injected into early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):165–173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Bowtell D. D., Hafen E., Rubin G. M. Localization of the sevenless protein, a putative receptor for positional information, in the eye imaginal disc of Drosophila. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A. Cellular interactions in the developing Drosophila eye. Development. 1988 Oct;104(2):183–193. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Cell fate in the Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):264–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Ready D. F. Neuronal differentiation in Drosophila ommatidium. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):366–376. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]