Abstract
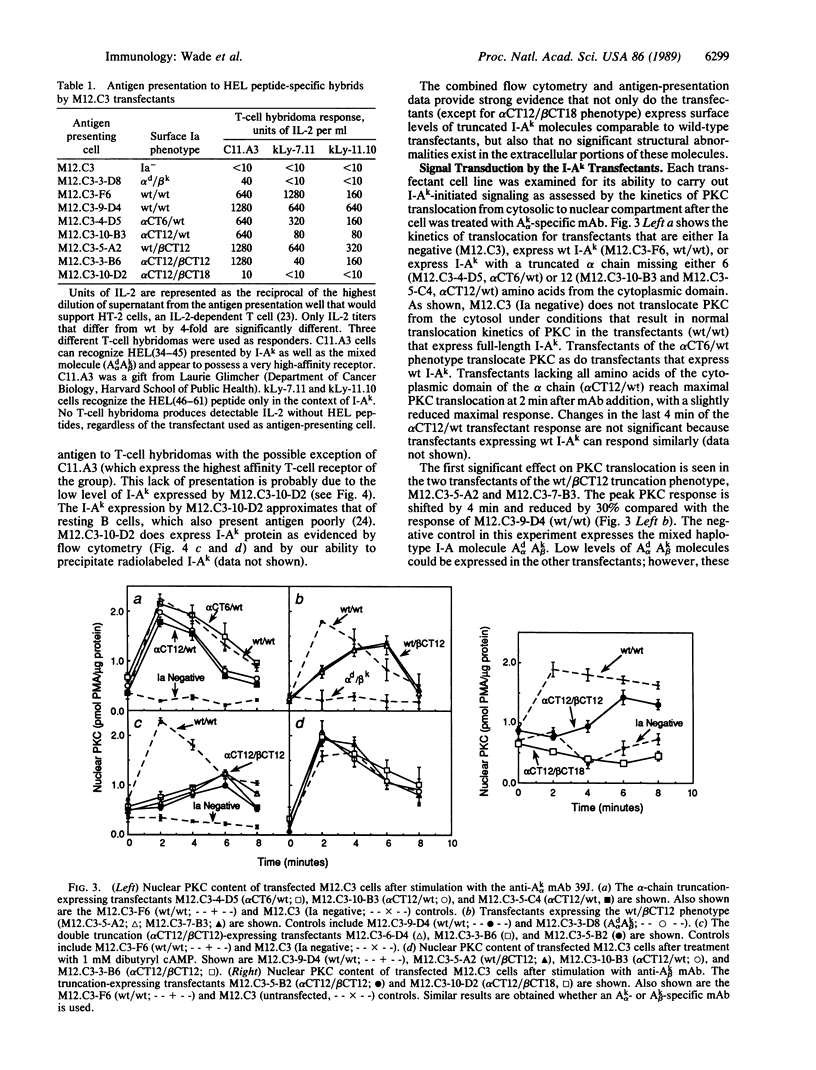
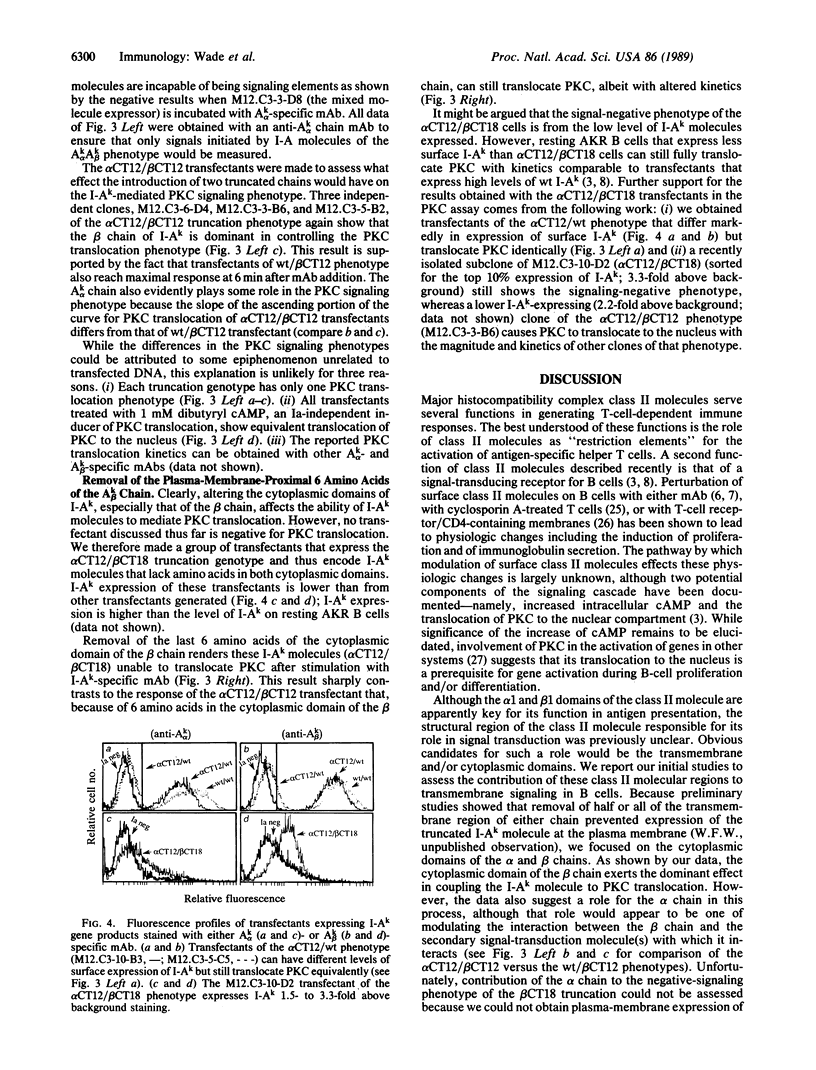
Recent evidence suggests that the major histocompatibility complex class II molecules of B lymphocytes function as signal-transducing receptors during the generation of T lymphocyte-dependent humoral immune responses. By analogy with other receptors, we postulate that perturbation of the class II molecules is coupled to the generation of intracellular second messengers through interactions involving the transmembrane and/or cytoplasmic domains of the class II molecules. We report a series of experiments that assess which amino acids of the class II molecule I-Ak are required for coupling it to the signal-transduction pathway. We prepared a series of B-lymphocyte transfectants that express I-Ak molecules with COOH-terminal truncations of either the Ak alpha or Ak beta chain or both. The ability of each transfected class II molecule to transduce a signal after being bound by monoclonal antibody was found by monitoring the translocation of protein kinase C from the cytosol to the "nuclear compartment" of the transfected B lymphocyte. Results indicate that the Ak beta chain plays the dominant role in signal transduction and that the 6 cytoplasmic amino acids of Ak beta chain most proximal to the inner plasma membrane are of greatest importance in coupling I-Ak molecules to the molecules of the signaling cascade.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck B. N., Buerstedde J. M., Krco C. J., Nilson A. E., Chase C. G., McKean D. J. Characterization of cell lines expressing mutant I-Ab and I-Ak molecules allows the definition of distinct serologic epitopes on A alpha and A beta polypeptides. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2953–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Haughton G. Induced differentiation of a transformed clone of Ly-1+ B cells by clonal T cells and antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian A. A. Stimulation of B-cell proliferation by membrane-associated molecules from activated T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):564–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Newell M. K., Justement L. B., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Chen Z. Z. Ia binding ligands and cAMP stimulate nuclear translocation of PKC in B lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):629–632. doi: 10.1038/327629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Z., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Cambier J. C. Transmembrane signaling through B cell MHC class II molecules: anti-Ia antibodies induce protein kinase C translocation to the nuclear fraction. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2345–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glimcher L. H., McKean D. J., Choi E., Seidman J. G. Complex regulation of class II gene expression: analysis with class II mutant cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3542–3550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbeck P., Huang K. P., Paul W. E. Lamin B is rapidly phosphorylated in lymphocytes after activation of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J., White J., Wegmann D., Mustain E., Marrack P. Antigen presentation by Ia+ B cell hybridomas to H-2-restricted T cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3604–3607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Ono Y., Asaoka Y., Shearman M. S., Fujii T., Ase K., Sekiguchi K., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The common structure and activities of four subspecies of rat brain protein kinase C family. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger J. I., Grammer S. F., Grey H. M., Chesnut R. W. Antigen presentation by splenic B cells: resting B cells are ineffective, whereas activated B cells are effective accessory cells for T cell responses. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):2937–2945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusemeier M., Snow E. C. Induction of lymphokine responsiveness of hapten-specific B lymphocytes promoted through an antigen-mediated T helper lymphocyte interaction. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):367–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabavi N., Ghogawala Z., Myer A., Griffith I. J., Wade W. F., Chen Z. Z., McKean D. J., Glimcher L. H. Antigen presentation abrogated in cells expressing truncated Ia molecules. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1444–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. K., Justement L. B., Miles C. R., Freed J. H. Biochemical characterization of proteins that co-purify with class II antigens of the murine MHC. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1930–1938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O., Guy K. Monoclonal antibodies against HLA-DR antigens replace T helper cells in activation of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3456–3460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Devaux C., Dosseto M., Marchetto S. Clonal analysis of B- and T-cell responses to Ia antigens. I. Topology of epitope regions on I-Ak and I-Ek molecules analyzed with 35 monoclonal alloantibodies. Immunogenetics. 1981 Dec;14(6):481–495. doi: 10.1007/BF00350120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Filburn C. R. Affinity chromatography of protein kinase C-phorbol ester receptor on polyacrylamide-immobilized phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12311–12314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann D. R., Roeder W. D., Shutter J. R., Kop J., Chiller J. M., Maki R. A. Recognition of exon-shuffled class II molecules by T helper cells. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(6):671–678. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


