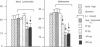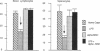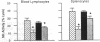Abstract
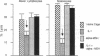
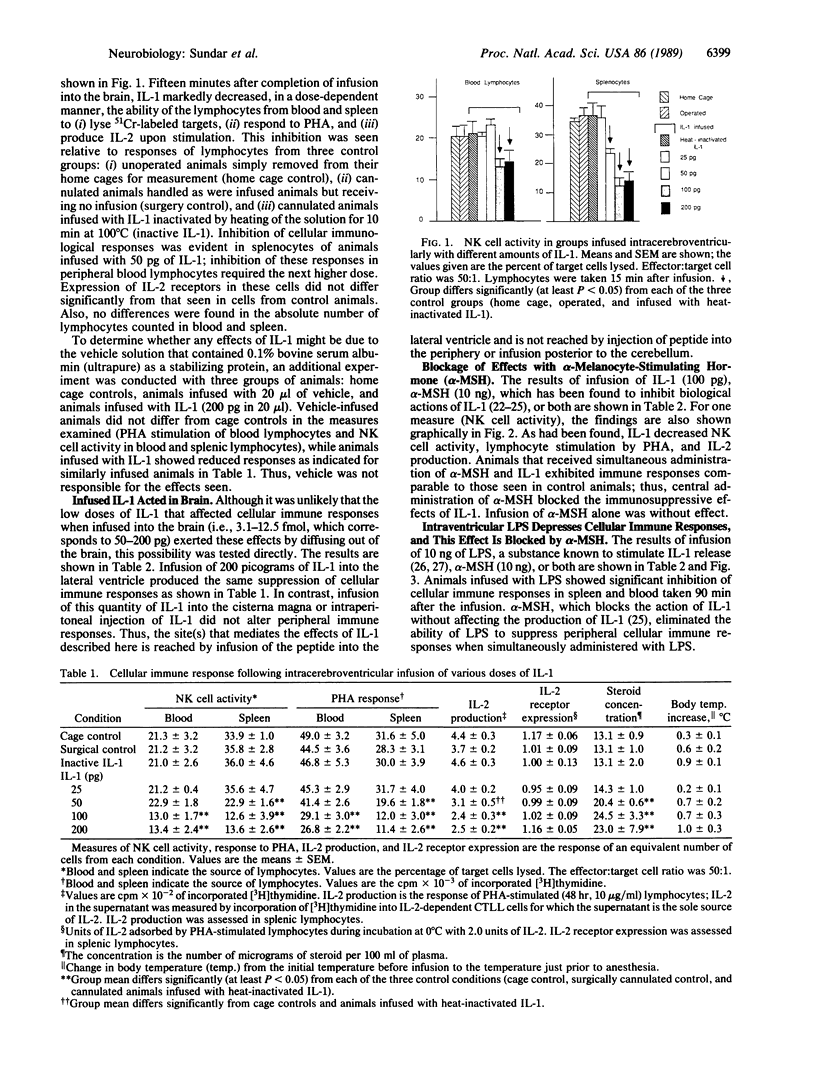
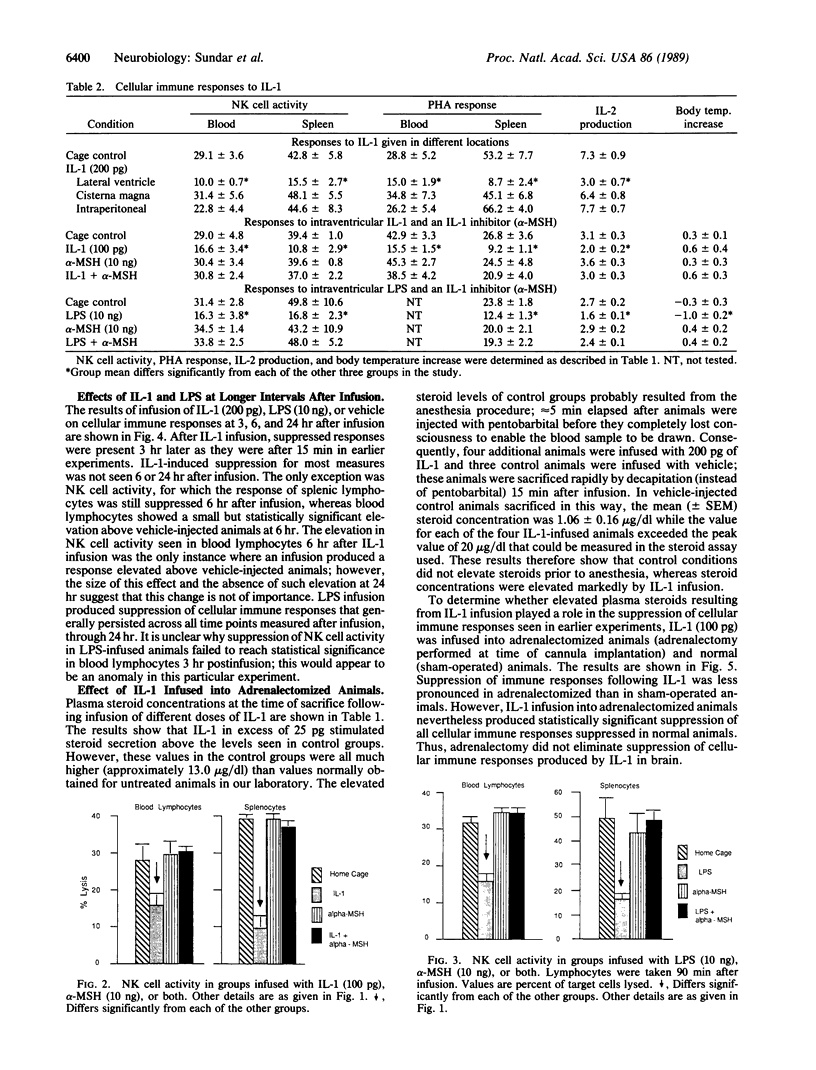
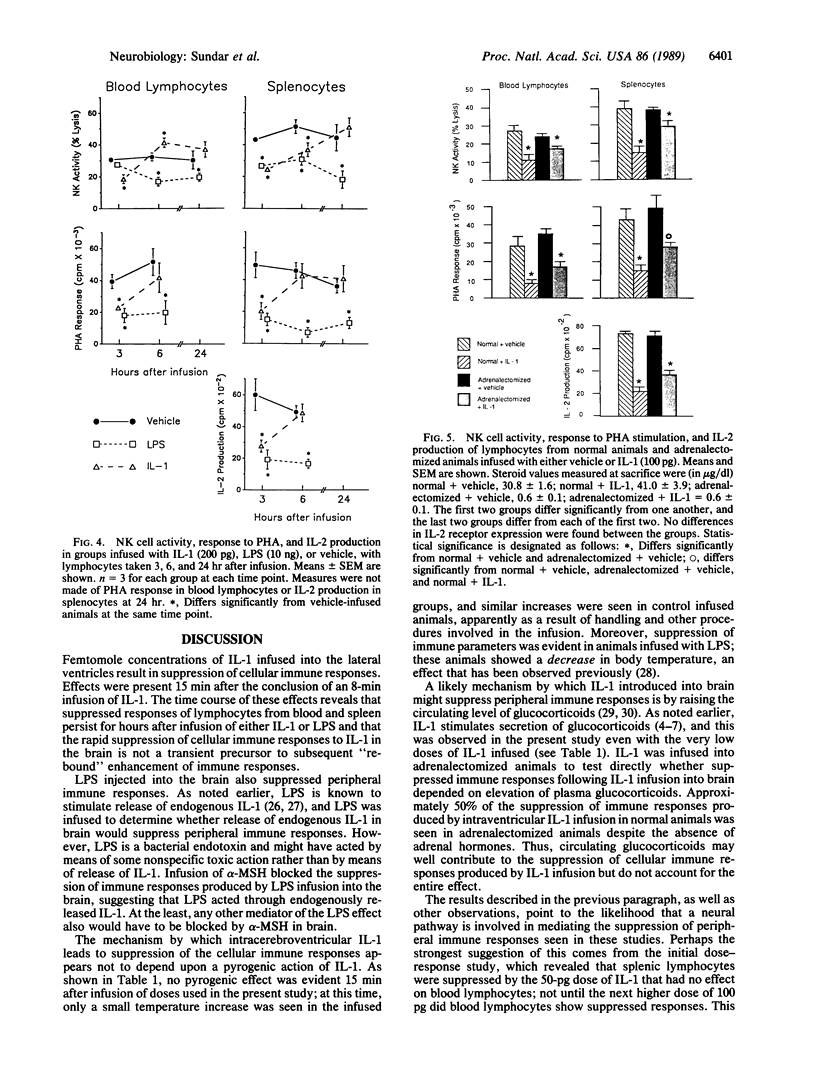
Low doses (50-200 pg or 3.1-12.4 fmol) of interleukin 1 (IL-1) infused into the brain of rats produced rapid suppression of various cellular immune responses in peripheral lymphocytes of rats. Fifteen minutes after infusion of purified IL-1 beta into the lateral ventricle, natural killer cell activity, response to phytohemagglutinin stimulation, and interleukin 2 production were markedly suppressed in lymphocytes isolated from blood and spleen. These effects were due to infusion of IL-1 into brain since they did not occur when IL-1 was infused into the cisterna magna (essentially posterior to brain) or was injected intraperitoneally. Effects of IL-1 in brain could be blocked by simultaneous infusion of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, which is known to block the biological actions of IL-1. To stimulate release of endogenous IL-1 in brain, lipopolysaccharide was infused; this produced similar effects as IL-1, and these effects also were blocked by alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. At longer intervals after infusion of IL-1 and lipopolysaccharide (3, 6, and 24 hr), immune responses returned to baseline or remained suppressed; i.e., "rebound" immunopotentiation did not occur. Finally, IL-1 infusion suppressed cellular immune responses in adrenalectomized animals, thereby showing that the effects of central IL-1 on peripheral cellular immune responses were, at least in part, independent of the stimulatory effect of IL-1 on secretion of adrenal hormones. These results indicate a link from brain to peripheral immune responses by means of action of a cytokine acting in the brain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkenbosch F., van Oers J., del Rey A., Tilders F., Besedovsky H. Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2443979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Beach J. E., Holaday J. W., Smallridge R. C., Fein H. G. Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2821620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatteis C. M., Bealer S. L., Hunter W. S., Llanos-Q J., Ahokas R. A., Mashburn T. A., Jr Suppression of fever after lesions of the anteroventral third ventricle in guinea pigs. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Nov;11(5):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Smith L. R., Blalock J. E. Interleukin 1 and interleukin 2 enhance proopiomelanocortin gene expression in pituitary cells. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3181–3183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tatro J. B., Reichlin S., Dinarello C. A. Alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone inhibits immunostimulatory and inflammatory actions of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2232–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. G., Holdeman M., Lipton J. M. Analysis of the antipyretic action of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in rabbits. J Physiol. 1985 Feb;359:459–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Dinarello C. A. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious cat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90883-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha enhancement of nonspecific antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2061–2065. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2061-2065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daynes R. A., Robertson B. A., Cho B. H., Burnham D. K., Newton R. Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone exhibits target cell selectivity in its capacity to affect interleukin 1-inducible responses in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clowes G. H., Jr, Gordon A. H., Saravis C. A., Wolff S. M. Cleavage of human interleukin 1: isolation of a peptide fragment from plasma of febrile humans and activated monocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L., Ackerman K. D., Wiegand S. J., Felten S. Y. Noradrenergic sympathetic innervation of the spleen: I. Nerve fibers associate with lymphocytes and macrophages in specific compartments of the splenic white pulp. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(1):28-36, 118-21. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L., Felten S. Y., Bellinger D. L., Carlson S. L., Ackerman K. D., Madden K. S., Olschowki J. A., Livnat S. Noradrenergic sympathetic neural interactions with the immune system: structure and function. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:225–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Grob P. J. Astrocyte-derived interleukin-1-like factors. Lymphokine Res. 1984;3(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Crabtree G. R., Smith K. A. Glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of T cell growth factor production. II. The effect on the in vitro generation of cytolytic T cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):594–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman M., Khorram O., Samson W. K., Lipton J. M. Fever-specific changes in central MSH and CRF concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):R125–R129. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1985.248.1.R125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. M., Walter J., Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M., Chedid L. Sleep-promoting effects of endogenous pyrogen (interleukin-1). Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):R994–R999. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.6.R994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuribayashi K., Gillis S., Kern D. E., Henney C. S. Murine NK cell cultures: effects of interleukin-2 and interferon on cell growth and cytotoxic reactivity. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2321–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain C. J., Cohen D., Ott L., Dinarello C. A., Young B. Ventricular fluid interleukin-1 activity in patients with head injury. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Jul;110(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. T., Richards D. B., Lipton J. M. Antipyretic potency of centrally administered alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone. Science. 1983 Jul 8;221(4606):192–193. doi: 10.1126/science.6602381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor M. R., Krishnan K. R., Manepalli A. N., Ritchie J. C., Jr, Wilson W. H., Carroll B. J. Circadian rhythm of adrenergic regulation of adrenocorticotropin and cortisol secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):404–406. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Brown M. C., Gordon S. The macrophage response to central and peripheral nerve injury. A possible role for macrophages in regeneration. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1218–1223. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson W. K., Lipton J. M., Zimmer J. A., Glyn J. R. The effect of fever on central alpha-MSH concentrations in the rabbit. Peptides. 1981 Winter;2(4):419–423. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(81)80098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T., Shimada S. G. A comparison of the febrile responses of the Brattleboro and Sprague-Dawley strains of rats to endotoxin and endogenous pyrogens. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;65(6):1377–1381. doi: 10.1139/y87-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler I., Borbély A. A., Schwyzer M., Fontana A. Interleukin-1 derived from astrocytes enhances slow wave activity in sleep EEG of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):191–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. M., Simson P. G., Hoffman L. J., Ambrose M. J., Cooper S., Webster A. Infusion of adrenergic receptor agonists and antagonists into the locus coeruleus and ventricular system of the brain. Effects on swim-motivated and spontaneous motor activity. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Apr;25(4):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90231-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]