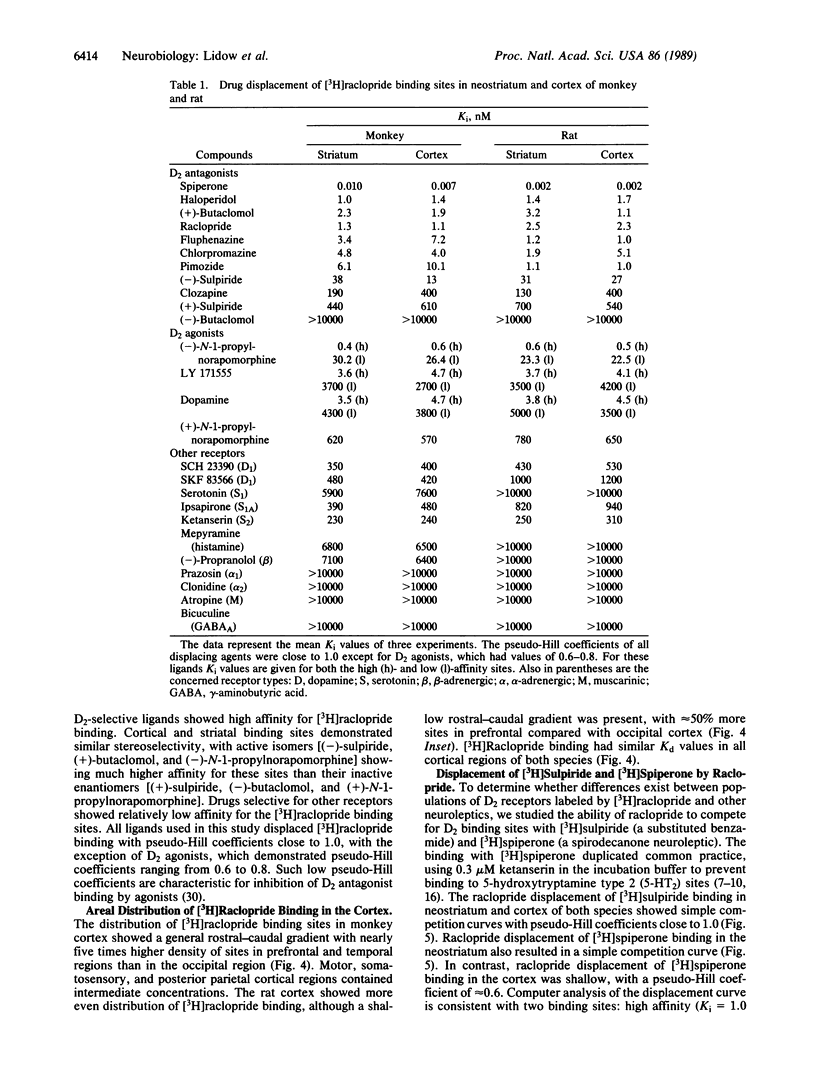
Abstract
An apparent involvement of dopamine in the regulation of cognitive functions and the recognition of a widespread dopaminergic innervation of the cortex have focused attention on the identity of cortical dopamine receptors. However, only the presence and distribution of dopamine D1 receptors in the cortex have been well documented. Comparable information on cortical D2 sites is lacking. We report here the results of binding studies in the cortex and neostriatum of rat and monkey using the D2 selective antagonist [3H]raclopride. In both structures [3H]raclopride bound in a sodium-dependent and saturable manner to a single population of sites with pharmacological profiles of dopamine D2 receptors. D2 sites were present in all regions of the cortex, although their density was much lower than in the neostriatum. The density of these sites in both monkey and, to a lesser extent, rat cortex displayed a rostral-caudal gradient with highest concentrations in the prefrontal and lowest concentrations in the occipital cortex, corresponding to dopamine levels in these areas. Thus, the present study establishes the presence and widespread distribution of dopamine D2 receptors in the cortex.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altar C. A., Kim H., Marshall J. F. Computer imaging and analysis of dopamine (D2) and serotonin (S2) binding sites in rat basal ganglia or neocortex labeled by [3H]spiroperidol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):527–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon M. J., Reinhard J. F., Jr, Bunney E. B., Roth R. H. Unique response to antipsychotic drugs is due to absence of terminal autoreceptors in mesocortical dopamine neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):444–446. doi: 10.1038/296444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B., Trottier S., Gaspar P., Verney C., Alvarez C. Major dopamine innervation of the cortical motor areas in the cynomolgus monkey. A radioautographic study with comparative assessment of serotonergic afferents. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 12;72(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouthenet M. L., Martres M. P., Sales N., Schwartz J. C. A detailed mapping of dopamine D-2 receptors in rat central nervous system by autoradiography with [125I]iodosulpride. Neuroscience. 1987 Jan;20(1):117–155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyson S. J., McGonigle P., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative autoradiographic localization of the D1 and D2 subtypes of dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3177–3188. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03177.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Crane A. M., Goldman P. S. Regional distribution of monoamines in the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures of the rhesus monkey: concentrations and in vivo synthesis rates. Brain Res. 1979 May 18;168(1):133–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camus A., Javoy-Agid F., Dubois A., Scatton B. Autoradiographic localization and quantification of dopamine D2 receptors in normal human brain with [3H]N-n-propylnorapomorphine. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 4;375(1):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90966-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charuchinda C., Supavilai P., Karobath M., Palacios J. M. Dopamine D2 receptors in the rat brain: autoradiographic visualization using a high-affinity selective agonist ligand. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1352–1360. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01352.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Keyser J., Claeys A., De Backer J. P., Ebinger G., Roels F., Vauquelin G. Autoradiographic localization of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 31;91(2):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois A., Savasta M., Curet O., Scatton B. Autoradiographic distribution of the D1 agonist [3H]SKF 38393, in the rat brain and spinal cord. Comparison with the distribution of D2 dopamine receptors. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall H., Wedel I., Sallemark M. Effects of temperature on the in vitro binding of 3H-raclopride to rat striatal dopamine-D2 receptors. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988 Aug;63(2):118–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1988.tb00922.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehr W., Lindqvist M., Carlsson A. Distribution of dopamine in the rat cerebral cortex. J Neural Transm. 1976;38(3-4):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01249437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koslow S. H., Cattabeni F., Costa E. Norepinephrine and dopamine: assay by mass fragmentography in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Hall H., Ogren S. O., Gawell L. Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of 3H-raclopride. A potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 1;34(13):2251–2259. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Radesäter A. C. Autoradiographic visualization of dopamine D-2 receptors in the monkey brain using the selective benzamide drug [3H]raclopride. Neurosci Lett. 1986 May 6;66(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liskowsky D. R., Potter L. T. D-2 dopamine receptors in the frontal cortex of rat and human. Life Sci. 1985 Apr 22;36(16):1551–1559. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson O., Fowler C. J., Mohringe B., Wijkström A., Ogren S. O. Comparison of the effects of haloperidol, remoxipride and raclopride on "pre"- and postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;337(4):379–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00169527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Sales N., Sokoloff P., Schwartz J. C. Widespread distribution of brain dopamine receptors evidenced with [125I]iodosulpride, a highly selective ligand. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.3838821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martres M. P., Sales N., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Localisation and pharmacological characterisation of D-2 dopamine receptors in rat cerebral neocortex and cerebellum using [125I]iodosulpride. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 3;118(3):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O., Hall H., Köhler C., Magnusson O., Sjöstrand S. E. The selective dopamine D2 receptor antagonist raclopride discriminates between dopamine-mediated motor functions. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1986;90(3):287–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00179179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penit-Soria J., Audinat E., Crepel F. Excitation of rat prefrontal cortical neurons by dopamine: an in vitro electrophysiological study. Brain Res. 1987 Nov 10;425(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Neuroleptic drug interactions with norepinephrine alpha receptor binding sites in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Sep;16(9):549–556. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P., Goldman-Rakic P. S., Gallager D. Quantitative autoradiography of major neurotransmitter receptors in the monkey striate and extrastriate cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3670–3690. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03670.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Lee T., Chau-Wong M., Wong K. Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature. 1976 Jun 24;261(5562):717–719. doi: 10.1038/261717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Watanabe M., Grigoriadis D., Tedesco J. L., George S. R., Svensson U., Nilsson J. L., Neumeyer J. L. Dopamine D2 receptor binding sites for agonists. A tetrahedral model. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;28(5):391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini E., Ortu A. M., Vernaleone F., Gessa G. L. [3H] (-)sulpiride binding in rat striatum, cortex and anterior pituitary: an improved assay. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1987 Nov;19(11):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(87)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorou A. E., Hall M. D., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Cation regulation differentiates specific binding of [3H]sulpiride and [3H]spiperone to rat striatal preparations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;32(6):441–444. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Le Douarin C., Penit J., Ferron A., Glowinski J. Variation in the ability of neuroleptics to block the inhibitory influence of dopaminergic neurons on the activity of cells in the rat prefrontal cortex. Brain Res Bull. 1986 Feb;16(2):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(86)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Stinus L., Blanc G., Glowinski J. Some evidence for the existence of dopaminergic neurons in the rat cortex. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 14;50(1):230–234. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usdin T. B., Creese I., Snyder S. H. Regulation by cations of [3H]spiroperidol binding associated with dopamine receptors of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):669–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



