Abstract
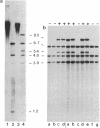
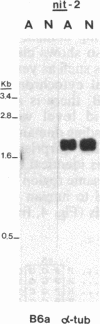
The nitrate reductase structural gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has been isolated from a genomic library by using a nitrate reductase cDNA probe from barley. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses mapped the Chlamydomonas clone (B6a) to the nitrate reductase structural gene locus nit-1. Overlapping inserts cover a region of the genome of about 24 kilobases containing the entire gene, which spans approximately 5-8 kilobases. Sequence analysis of DNA fragments from the B6a clone demonstrated a high degree of sequence similarity at the amino acid level with regions corresponding to portions of the heme and FAD/NADH-binding domains of tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana nitrate reductases and human NADH cytochrome b5 reductase. The identity of the cloned gene as nitrate reductase was confirmed by its ability to complement a nit-1 mutation upon transformation. The nitrate reductase gene produced a 3.4-kilobase transcript in cells derepressed with nitrate; the transcript was undetectable in cells grown in the presence of ammonium. In cells that contain a mutation in the putative regulatory gene nit-2, significantly lower levels of the 3.4-kilobase transcript were found, indicating that the wild-type nit-2 gene is involved in the control of nitrate reductase transcript levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calza R, Huttner E, Vincentz M, Rouzé P, Galangau F, Vaucheret H, Chérel I, Meyer C, Kronenberger J, Caboche M. Cloning of DNA fragments complementary to tobacco nitrate reductase mRNA and encoding epitopes common to the nitrate reductases from higher plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):552–562. doi: 10.1007/BF00331162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. L., Dewdney J., Kleinhofs A., Goodman H. M. Cloning and nitrate induction of nitrate reductase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6825–6828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Campbell W. H., Davis R. W. Nitrate reductase from squash: cDNA cloning and nitrate regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8073–8076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Smith M., Bellissimo D., Davis R. W. Sequence and nitrate regulation of the Arabidopsis thaliana mRNA encoding nitrate reductase, a metalloflavoprotein with three functional domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5006–5010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández E., Matagne R. F. In vivo complementation analysis of nitrate reductase-deficient mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1986;10(5):397–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00418413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A. R., Cárdenas J., Fernández E. Heteromultimeric structure of the nitrate reductase complex of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1403–1407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. Molecular cloning and analysis of the regulation of nit-3, the structural gene for nitrate reductase in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8243–8247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabard J, Marion-Poll A, Chérel I, Meyer C, Müller A, Caboche M. Isolation and characterization of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia nitrate reductase-deficient mutants: genetic and biochemical analysis of the NIA complementation group. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):596–606. doi: 10.1007/BF00331169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rahire M. Sequence, evolution and differential expression of the two genes encoding variant small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard W. D., Solomonson L. P. Quaternary structure of assimilatory NADH:nitrate reductase from Chlorella. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10243–10250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer F., Cortial S., Becam A. M., Haumont P. Y., Perez L. Complete amino acid sequence of flavocytochrome b2 from baker's yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):419–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Gerard C., Nobrega F. G. Proteolytic cleavage of horse liver cytochrome b5. Primary structure of the heme-containing moiety. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6767–6774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranum L. P., Thompson M. D., Schloss J. A., Lefebvre P. A., Silflow C. D. Mapping flagellar genes in Chlamydomonas using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics. 1988 Sep;120(1):109–122. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):831–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D., Rosenbaum J. L. mRNA abundance changes during flagellar regeneration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):424–434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., Ranum L. P. The two alpha-tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi code for slightly different proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2389–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silflow C. D., Youngblom J. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii tubulin gene structure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:18–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomonson L. P., Barber M. J., Robbins A. P., Oaks A. Functional domains of assimilatory NADH:nitrate reductase from Chlorella. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11290–11294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Chiang K. S., Kates J. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication in meiosis of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. I. Isotopic transfer experiments with a strain producing eight zoospores. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):47–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yubisui T., Miyata T., Iwanaga S., Tamura M., Takeshita M. Complete amino acid sequence of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase purified from human erythrocytes. J Biochem. 1986 Feb;99(2):407–422. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer W. E., Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D., Youngblom J., Watterson D. M. Structural organization, DNA sequence, and expression of the calmodulin gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19370–19383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]