Abstract
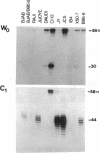
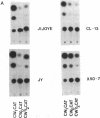
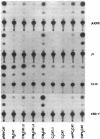
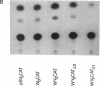
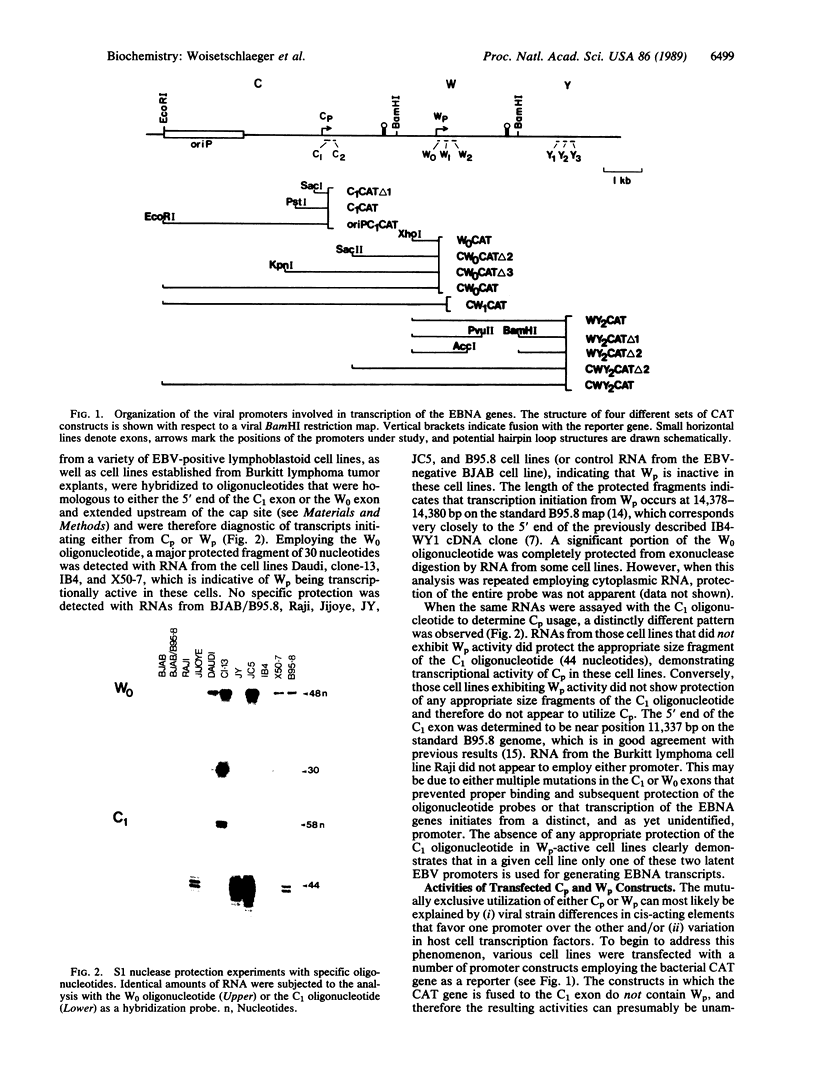
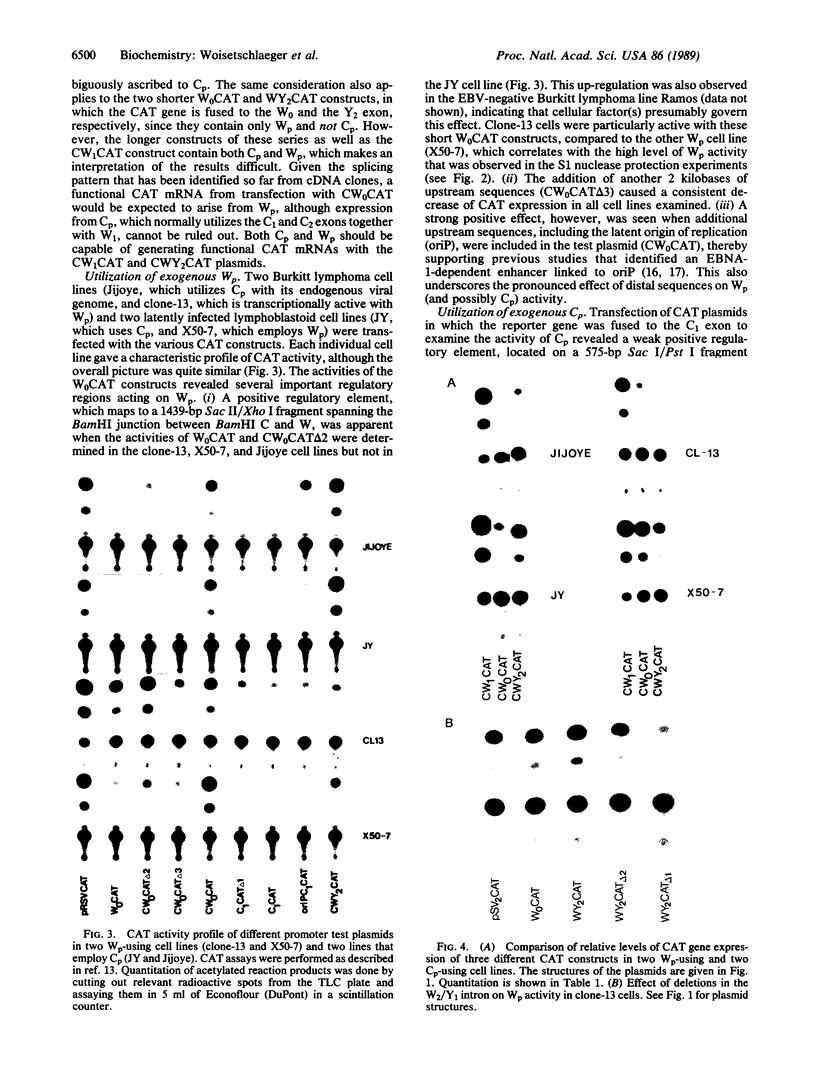
Of the eight viral antigens known to be expressed during Epstein-Barr virus latency, six are transcribed from a major rightward transcriptional unit, which gives rise to mRNAs containing common 5' exons. Analysis of cDNA clones has identified the use of two different promoters (Wp and Cp), located near the left-hand end of the viral genome, in generating these viral messages. Characterization of the activities of these two viral promoters in a number of Burkitt lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines has revealed exclusive usage of only one of these promoters in all cell lines examined. Transfection of reporter constructs containing Wp and/or Cp linked to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene into several different Epstein-Barr virus-infected cell lines generally supports a model in which the mutually exclusive use of Cp or Wp is determined by cellular factors and not by viral strain variation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S. Significant potential secondary structures in the Epstein-Barr virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6915–6919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Thomas-Powell A. L., Raab-Traub N., Hawke M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):506–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.506-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Cadwallader K., Petti L., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Distinction between Epstein-Barr virus type A (EBNA 2A) and type B (EBNA 2B) isolates extends to the EBNA 3 family of nuclear proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1031-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Epstein-Barr virus transformation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1987;34:189–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]