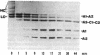
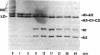
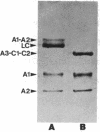
Abstract
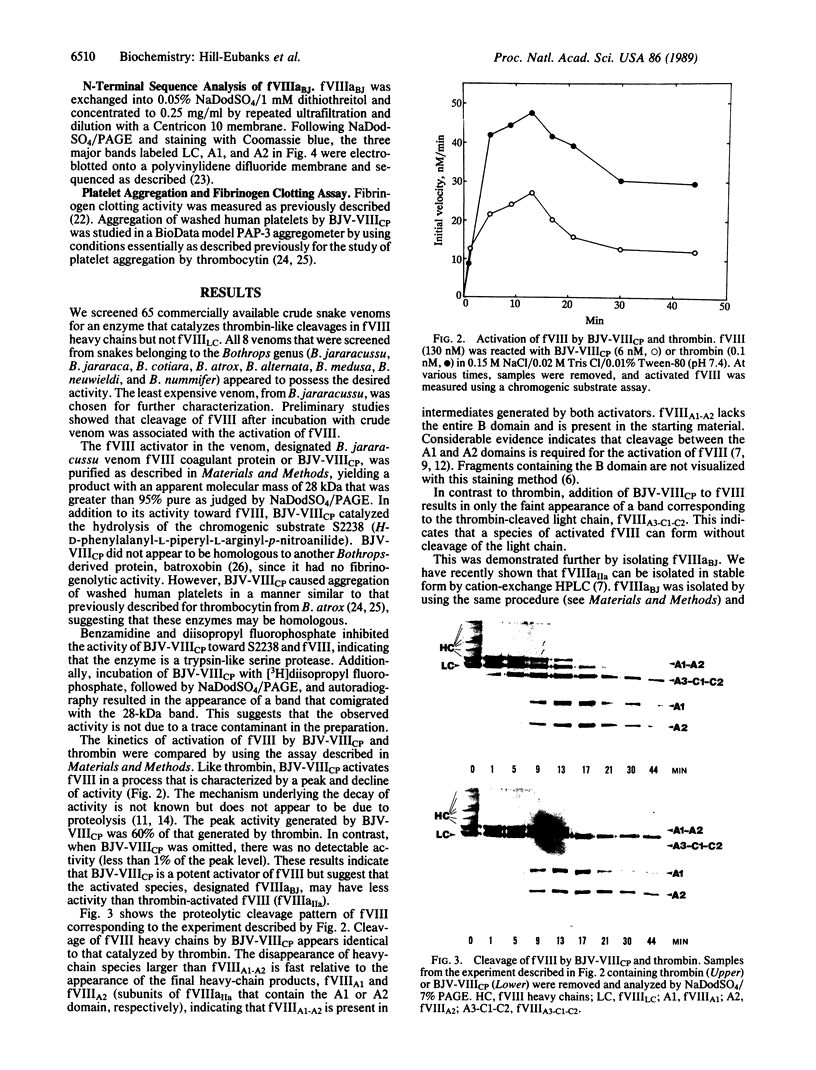
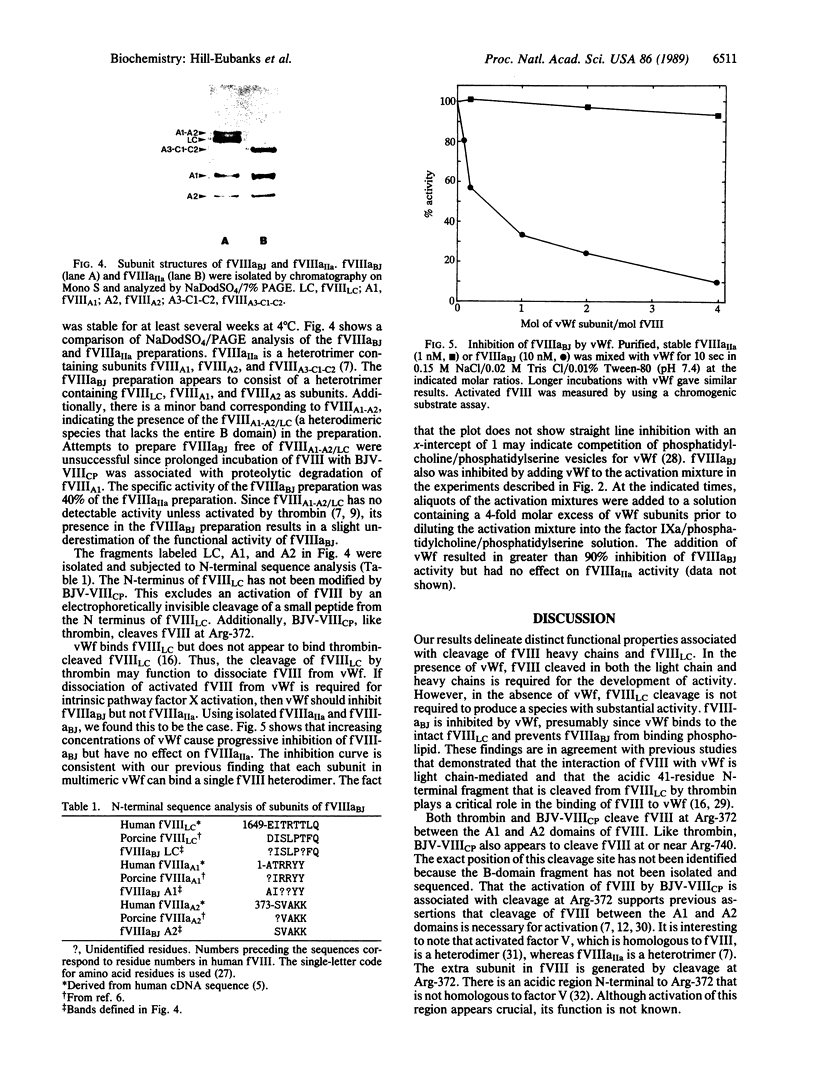
Blood coagulation factor VIII (fVIII) is a plasma protein that is decreased or absent in hemophilia A. It is isolated as a mixture of heterodimers that contain a variably sized heavy chain and a common light chain. Thrombin catalyzes the activation of fVIII in a reaction that is associated with cleavages in both types of chain. We isolated a serine protease from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom that catalyzes thrombin-like heavy-chain cleavage but not light-chain cleavage in porcine fVIII as judged by NaDodSO4/PAGE and N-terminal sequence analysis. Using a plasma-free assay of the ability of activated fVIII to function as a cofactor in the activation of factor X by factor IXa, we found that fVIII is activated by the venom enzyme. The venom enzyme-activated fVIII was isolated in stable form by cation-exchange HPLC. von Willebrand factor inhibited venom enzyme-activated fVIII but not thrombin-activated fVIII. These results suggest that the binding of fVIII to von Willebrand factor depends on the presence of an intact light chain and that activated fVIII must dissociate from von Willebrand factor to exert its cofactor effect. Thus, proteolytic activation of fVIII-von Willebrand factor complex appears to be differentially regulated by light-chain cleavage to dissociate the complex and heavy-chain cleavage to activate the cofactor function.
Full text
PDF
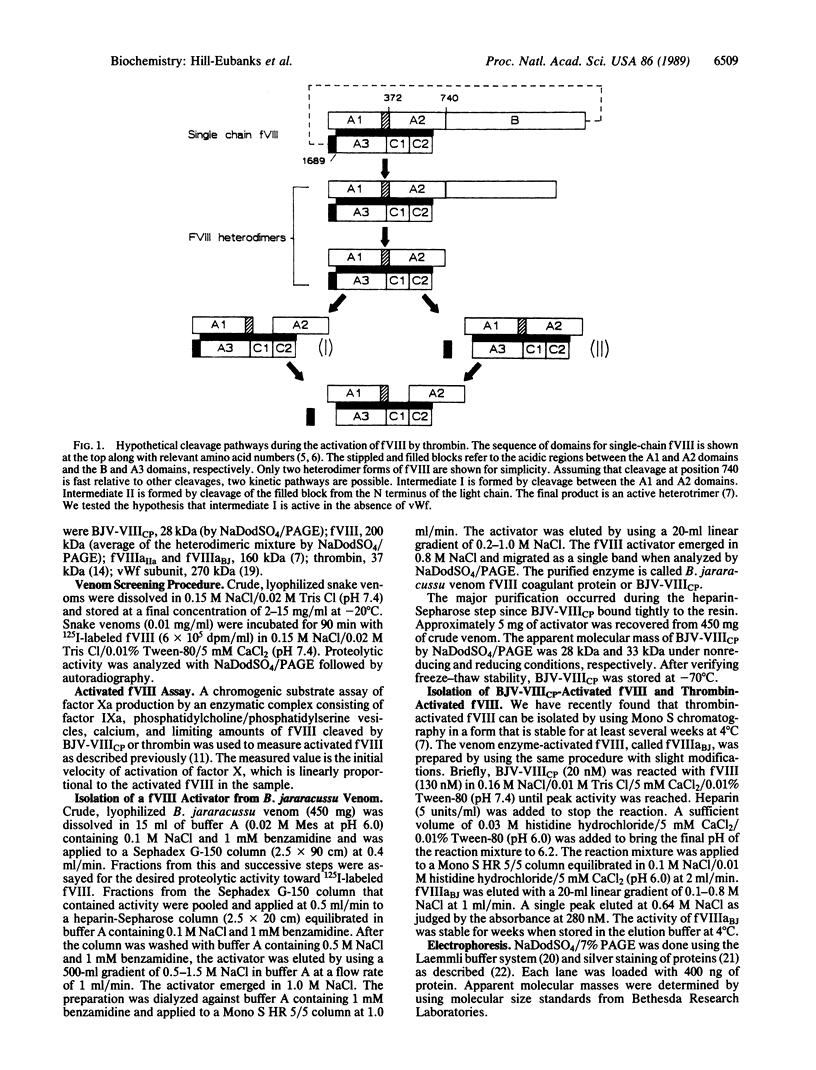

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Brown J. E. Interaction of factor VIII-von Willebrand Factor with phospholipid vesicles. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2000161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Sandberg H., Garris J. B., Mattsson C., Palm M., Griggs T., Read M. S. Purified human factor VIII procoagulant protein: comparative hemostatic response after infusions into hemophilic and von Willebrand disease dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8752–8756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopek M. W., Girma J. P., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W., Titani K. Human von Willebrand factor: a multivalent protein composed of identical subunits. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3146–3155. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Rodriguez H., Vehar G. A. Proteolytic processing of human factor VIII. Correlation of specific cleavages by thrombin, factor Xa, and activated protein C with activation and inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):505–512. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The subunit structure of thrombin-activated factor V. Isolation of activated factor V, separation of subunits, and reconstitution of biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):964–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass D. N., Knutson G. J., Katzmann J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to porcine factor VIII coagulant and their use in the isolation of active coagulant protein. Blood. 1982 Mar;59(3):594–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Anderson M. T., Chavin S. I., Marder V. J. The size of human factor VIII heterodimers and the effects produced by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 23;871(3):268–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster P. A., Fulcher C. A., Houghten R. A., Zimmerman T. S. An immunogenic region within residues Val1670-Glu1684 of the factor VIII light chain induces antibodies which inhibit binding of factor VIII to von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5230–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenny R. J., Pittman D. D., Toole J. J., Kriz R. W., Aldape R. A., Hewick R. M., Kaufman R. J., Mann K. G. Complete cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of human factor V. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4846–4850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Davie E. W. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):539–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Dorner A. J. Synthesis, processing, and secretion of recombinant human factor VIII expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6352–6362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby E. P., Niewiarowski S., Stocker K., Kettner C., Shaw E., Brudzynski T. M. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 1. Purification and characterization of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3564–3570. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Hill-Eubanks D. C., Parker C. G. Association of the factor VIII light chain with von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10451–10455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Knutson G. J., Fass D. N. Activation of porcine factor VIII:C by thrombin and factor Xa. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8056–8064. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Knutson G. J., Fass D. N. Stabilization of thrombin-activated porcine factor VIII:C by factor IXa phospholipid. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1303–1308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Parker C. G., Kajenski P. J., Litwiller R. D., Fass D. N. Degradation of coagulation proteins by an enzyme from Malayan pit viper (Akistrodon rhodostoma) venom. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7627–7636. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Parker C. G. Stoichiometry of the porcine factor VIII-von Willebrand factor association. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17572–17576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Parker C. G. Subunit structure of thrombin-activated porcine factor VIII. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):666–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Parker C. G., Tracy R. P. Molecular characterization of commercial porcine factor VIII concentrate. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Jenny R. J., Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Kirby E. P., Brudzynski T. M., Stocker K. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 2. Interaction with platelets and plasma-clotting factors. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3570–3577. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Proteolytic requirements for thrombin activation of anti-hemophilic factor (factor VIII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Platelets and von Willebrand disease. Semin Hematol. 1985 Jul;22(3):203–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker K., Barlow G. H. The coagulant enzyme from Bothrops atrox venom (batroxobin). Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:214–223. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straughn W., 3rd, Wagner R. H. A simple method for preparing fibrinogen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jul 31;16(1):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Knopf J. L., Wozney J. M., Sultzman L. A., Buecker J. L., Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J., Brown E., Shoemaker C., Orr E. C. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):342–347. doi: 10.1038/312342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Keyt B., Eaton D., Rodriguez H., O'Brien D. P., Rotblat F., Oppermann H., Keck R., Wood W. I., Harkins R. N. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):337–342. doi: 10.1038/312337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iersel J., Jzn J. F., Duine J. A. Determination of absorption coefficients of purified proteins by conventional ultraviolet spectrophotometry and chromatography combined with multiwavelength detection. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;151(1):196–204. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]