Abstract
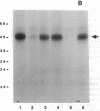
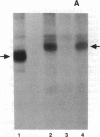
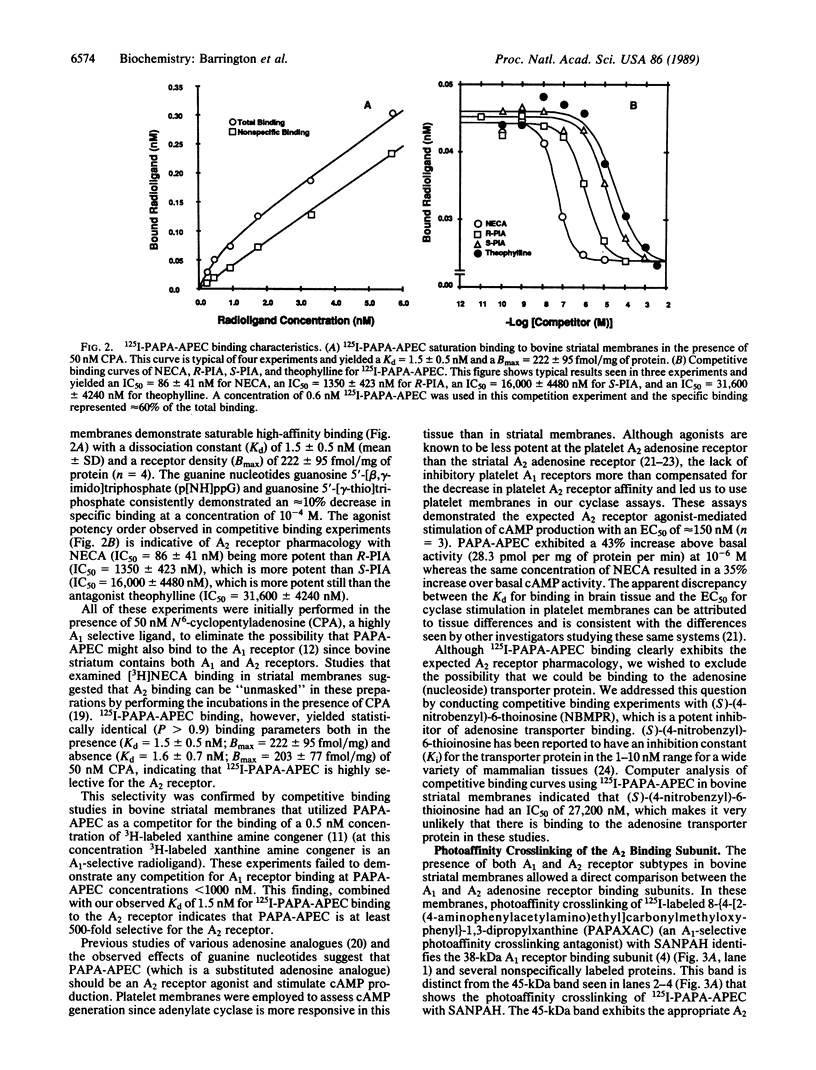
A high-affinity iodinated agonist radioligand for the A2 adenosine receptor has been synthesized to facilitate studies of the A2 adenosine receptor binding subunit. The radioligand 125I-labeled PAPA-APEC (125I-labeled 2-[4-(2-[2-[(4- aminophenyl)methylcarbonylamino]ethylaminocarbonyl]- ethyl)phenyl]ethylamino-5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine) was synthesized and found to bind to the A2 adenosine receptor in bovine striatal membranes with high affinity (Kd = 1.5 nM) and A2 receptor selectivity. Competitive binding studies reveal the appropriate A2 receptor pharmacologic potency order with 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) greater than (-)-N6-[(R)-1-methyl- 2-phenylethyl]adenosine (R-PIA) greater than (+)-N6-[(S)-1-methyl-2- phenylethyl]adenosine (S-PIA). Adenylate cyclase assays, in human platelet membranes, demonstrate a dose-dependent stimulation of cAMP production. PAPA-APEC (1 microM) produces a 43% increase in cAMP production, which is essentially the same degree of increase produced by 5'-N- ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (the prototypic A2 receptor agonist). These findings combined with the observed guanine nucleotide-mediated decrease in binding suggest that PAPA-APEC is a full A2 agonist. The A2 receptor binding subunit was identified by photoaffinity-crosslinking studies using 125I-labeled PAPA-APEC and the heterobifunctional crosslinking agent N-succinimidyl 6-(4'-azido-2'-nitrophenylamino)hexanoate (SANPAH). After covalent incorporation, a single specifically radiolabeled protein with an apparent molecular mass of 45 kDa was observed on NaDodSO4/PAGE/autoradiography. Incorporation of 125I-labeled PAPA-APEC into this polypeptide is blocked by agonists and antagonists with the expected potency for A2 receptors (see above) and is decreased in the presence of 10(-4) M guanosine 5'-[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate. Photoaffinity crosslinking of the A1 adenosine receptor binding subunit with 125I-labeled 8-[4-[2-(4- aminophenylacetylamino)ethyl]carbonylmethyloxyphenyl]-1,3-di propylxanthine (PAPAXAC) (an A1 selective photoaffinity probe) in the same tissue reveals a 38-kDa peptide that exhibits the appropriate A1 receptor pharmacology. 125I-labeled PAPA-APEC, therefore, has identified the A2 receptor binding subunit as a 45-kDa protein that is unique and distinct from the A1 binding subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., Stiles G. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Photoaffinity labelling of mammalian beta-adrenergic receptors: metal-dependent proteolysis explains apparent heterogeneity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):504–511. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Fergus J. H., Badger E. W., Bristol J. A., Santay L. A., Hays S. J. PD 115,199: an antagonist ligand for adenosine A2 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;335(1):64–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00165038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., O'Donnell J. P. Photoaffinity labels as pharmacological tools. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 15;33(8):1167–1180. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. A., Ukena D., Kirk K. L., Daly J. W. [3H]xanthine amine congener of 1,3-dipropyl-8-phenylxanthine: an antagonist radioligand for adenosine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4089–4093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz K. N., Cristalli G., Grifantini M., Vittori S., Lohse M. J. Photoaffinity labeling of A1-adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14659–14664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavin T. N., Nambi P., Heald S. L., Jeffs P. W., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. 125I-labeled p-azidobenzylcarazolol, a photoaffinity label for the beta-adrenergic receptor. Characterization of the ligand and photoaffinity labeling of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12332–12340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Klotz K. N., Schwabe U. Agonist photoaffinity labeling of A1 adenosine receptors: persistent activation reveals spare receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;30(4):403–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman K. D., Williams L. T., Bishopric N. H., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of alpha-adrenergic receptors in human platelets by [3H]dihydroergocryptine binding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):395–402. doi: 10.1172/JCI108950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A., Craig R. H., Daluge S. M., Linden J. 125I-BW-A844U, an antagonist radioligand with high affinity and selectivity for adenosine A1 receptors, and 125I-azido-BW-A844U, a photoaffinity label. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Daly D. T., Olsson R. A. Characterization of the A1 adenosine receptor-adenylate cyclase system of cerebral cortex using an agonist photoaffinity ligand. J Neurochem. 1986 Oct;47(4):1020–1025. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Daly D. T., Olsson R. A. The A1 adenosine receptor. Identification of the binding subunit by photoaffinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10806–10811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Jacobson K. A. A new high affinity, iodinated adenosine receptor antagonist as a radioligand/photoaffinity crosslinking probe. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;32(1):184–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Photoaffinity cross-linked A1 adenosine receptor-binding subunits. Homologous glycoprotein expression by different tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10839–10843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena D., Böhme E., Schwabe U. Effects of several 5'-carboxamide derivatives of adenosine on adenosine receptors of human platelets and rat fat cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Aug;327(1):36–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00504989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukena D., Jacobson K. A., Kirk K. L., Daly J. W. A [3H]amine congener of 1,3-dipropyl-8-phenylxanthine. A new radioligand for A2 adenosine receptors of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 21;199(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80493-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]