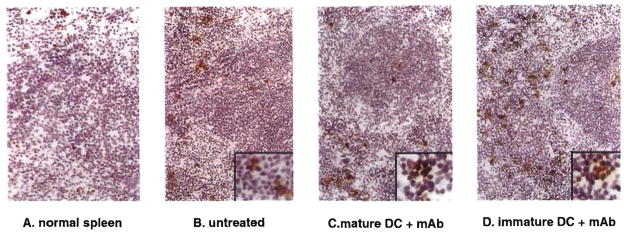
Figure 4.
A–D, Detection of TUNEL+ (apoptotic cells) in spleen T cell and red pulp areas of (A) normal C3H mice or (B–D) C3H recipients of B10 cardiac allografts 7 days posttransplant. Heart-transplanted animals were either untreated (B), pretreated (day –7) with mature donor-derived DC (C), or immature donor DC + anti-CD40L mAb (D). The comparatively high numbers of apoptotic cells seen in mice given immature donor DC+mAb (D) correlates with the 2- to 3-fold increase in apoptotic activity (DNA fragmentation) detected by spectrofluorometric assay in spleen cells from this group, compared with untreated heart-grafted controls (Table 1). Pretreatment with donor mature DC, that accelerated graft rejection, was associated with an apparent reduction in the incidence of apoptotic cells in the spleen. Magnification: main, ×100, inset, ×400. Counterstained with hematoxylin.