Abstract
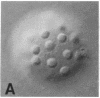
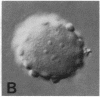
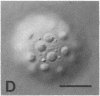
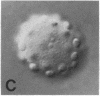
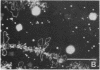
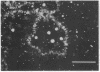
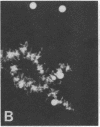
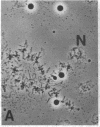
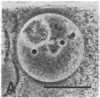
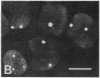
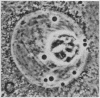
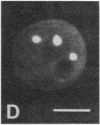
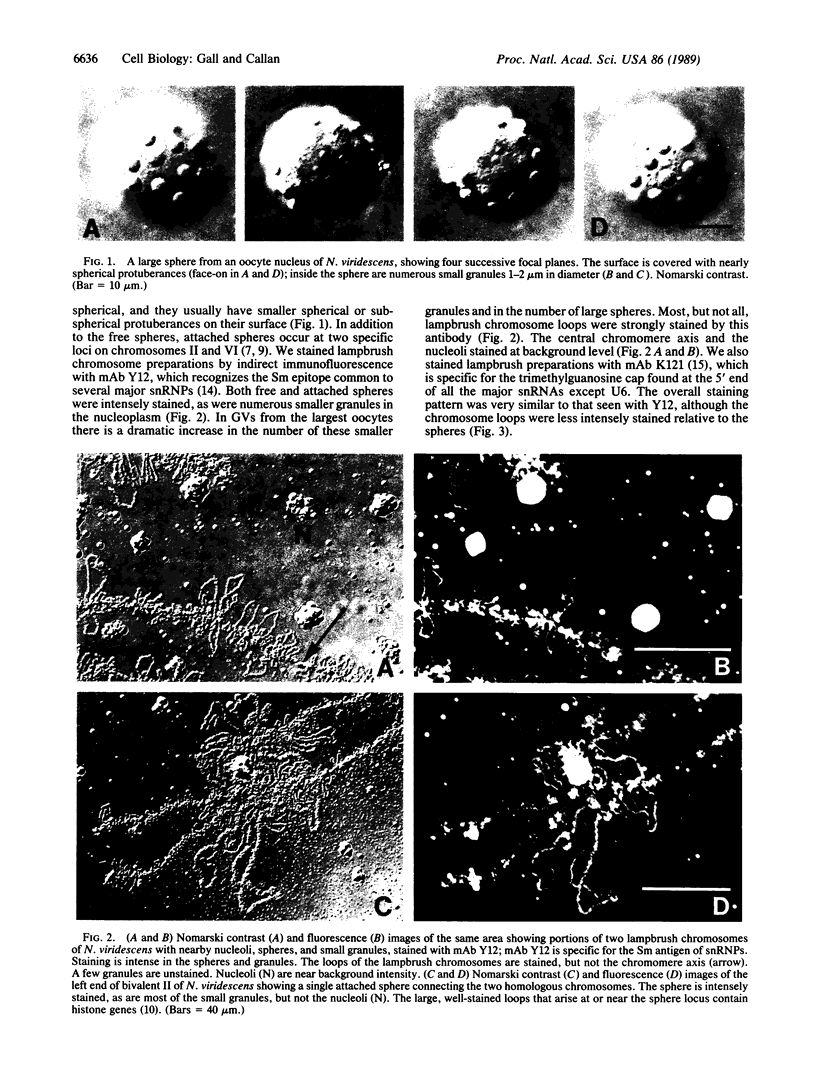
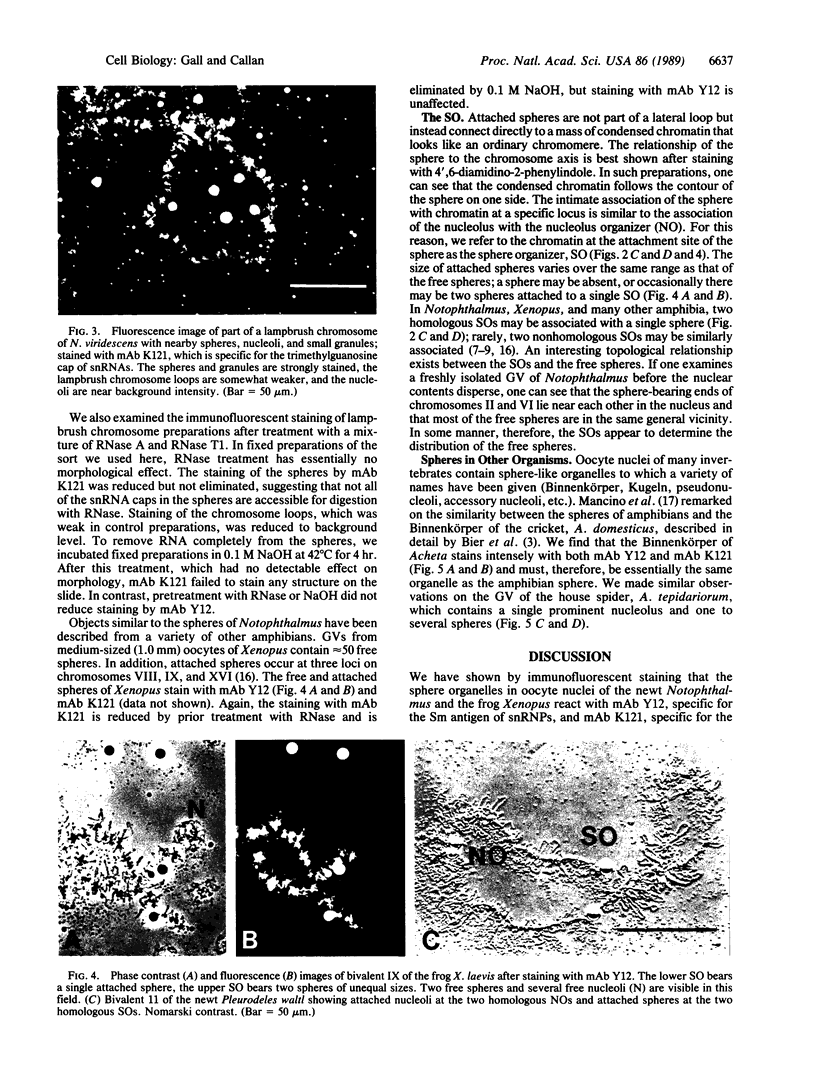
We show by immunofluorescence microscopy of amphibian oocyte nuclei that small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) occur in lampbrush chromosome loops, in a few dozen extrachromosomal organelles previously described as "spheres," and in thousands of smaller granules. Spheres are variable in size (up to approximately 20 microns in diameter in the newt Notophthalmus and approximately 10 microns in the frog Xenopus) and are easily distinguishable from nucleoli by morphology and composition. Spheres occur both free in the nucleoplasm and attached to specific chromosome loci, the sphere organizers. Oocyte nuclei of a cricket and a spider contain essentially similar organelles, suggesting that spheres may be common throughout the animal kingdom. We suggest that spheres play a role in the assembly of snRNP complexes for the nucleus comparable to the way that nucleoli assemble ribosomal RNP complexes for the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bier K., Kunz W., Ribbert D. Struktur und Funktion der Oocytenchromosomen und Nukleolen sowie der Extra-DNS während der Oogenese panoistischer und meroistischer Insekten. Chromosoma. 1967;23(2):214–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00331114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G., Gall J. G., Berg C. A. The lampbrush chromosomes of Xenopus laevis: preparation, identification, and distribution of 5S DNA sequences. Chromosoma. 1987;95(4):236–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00294780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Lienhard S., Parisot R. F. Intracellular transport of microinjected 5S and small nuclear RNAs. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):572–577. doi: 10.1038/295572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G. Histone genes are located at the sphere loci of newt lampbrush chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;84(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00399128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausen P., Dreyer C. Urea reactivates antigens in paraffin sections for immunofluorescent staining. Stain Technol. 1982 Sep;57(5):321–324. doi: 10.3109/10520298209066731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsebos T. J., Hackstein J. H., Hennig W. Lampbrush loop-specific protein of Drosophila hydei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3404–3408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R. Pre-mRNA splicing by complementation with purified human U1, U2, U4/U6 and U5 snRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9415–9429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. C., Azzouz R., Boucher D., Abbadie C., Pyne C. K., Charlemagne J. Monoclonal antibodies to lampbrush chromosome antigens of Pleurodeles waltlii. Chromosoma. 1985;92(1):69–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00327246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancino G., Barsacchi G., Nardi I. The lamphbrush chromosomes of Salamandra salamandra (L.) (Amphibia Urodela). Chromosoma. 1969;26(4):365–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00326350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Lührmann R. 5'-Terminal caps of snRNAs are reactive with antibodies specific for 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine in whole cells and nuclear matrices. Double-label immunofluorescent studies with anti-m3G antibodies and with anti-RNP and anti-Sm autoantibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Oct;154(2):548–560. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H., Pederson T. Transcription-dependent localization of U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins at major sites of gene activity in polytene chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):911–926. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Smith H. C. Redistribution of U-snRNPs during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Mar;163(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeller R., Nyffenegger T., De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of snRNPs and stockpiled snRNA-binding proteins during oogenesis and early development in Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]