Abstract
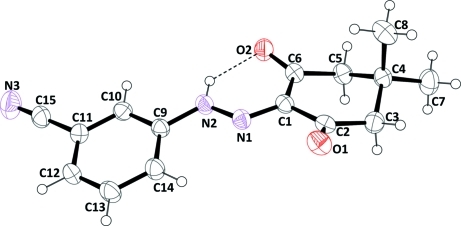
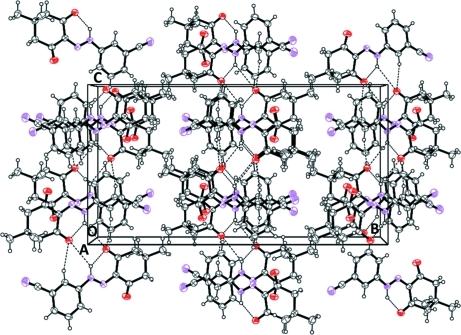
The title compound, C15H15N3O2, contains benzonitrile and 4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene groups connected via a hydrazinyl group. The structure is in the hydrazone tautomeric form in the solid state. The benzonitrile and hydrazinyl groups (3-hydrazinylbenzonitrile) are essentially coplanar with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.016 Å. Intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding helps to stabilize the molecular structure, and weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding is present in the crystal structure.
Related literature
The title compound is a tautomeric form of the azo compound; for the applications of azo compounds, see: Kobrakov et al. (2004 ▶); Karcı et al. (2004 ▶); Gale et al. (1998 ▶). For related structures of hydrazone derivatives, see: Kelemen et al. (1982 ▶); Saylam et al. (2008 ▶); Seferoğlu et al. (2008 ▶; 2009 ▶); Batchelor et al. (1997 ▶); de Lima et al. (2009 ▶); de Souza et al. (2010 ▶); Özbey et al. (1997 ▶); Alpaslan et al. (2005 ▶). For additional structural analaysis, see: Spek (2003 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15N3O2
M r = 269.30
Orthorhombic,
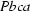
a = 12.9496 (8) Å
b = 8.6028 (6) Å
c = 24.324 (2) Å
V = 2709.8 (3) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.80 × 0.36 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS II diffractometer
Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.959, T max = 0.991
10586 measured reflections
2880 independent reflections
1557 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.052
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.090
S = 0.85
2880 reflections
185 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-RED32 (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810013164/xu2749sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810013164/xu2749Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O2 | 0.95 (2) | 1.91 (2) | 2.6461 (19) | 132.6 (18) |
| C10—H10⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.442 (2) | 156 |
Symmetry code: (i) 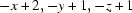 .
.
Table 2. Selected bonds compared with related hydrazone compounds (Å).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the diffractometer (purchased under grant F.279 of the University Research Fund).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
It has been known for many years that the azo compounds are a widely used class of dyes due to their application in various fields such as the dyeing of textile fibers, the coloring of different materials, colored plastics and electrochemical sensors (Kobrakov et al., 2004; Karcı et al., 2004; Gale et al., 1998).
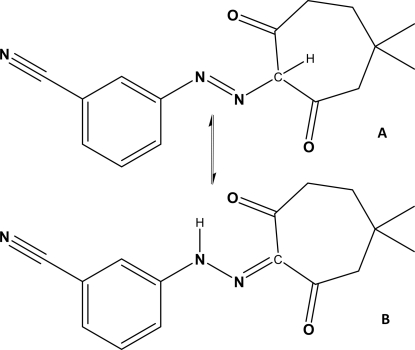
Azo dyes are known to exist in the azo-hydrazone tautomeric forms (Saylam et al., 2008; Seferoğlu et al., 2008; Seferoğlu et al., 2009). The dyes may exist in two possible tautomeric forms, namely azo form A and hydrazone form B as depicted in Figure 3. It is suggested that in a real azo compound the N=N double bond should have a length of 1.20–1.28 Å and the bond length of N–N single bonds, as in hydrazone tautomers, should be more than 1.4 Å (Kelemen et al., 1982). In the title compound, N–N bond length is 1.304 Å, between the suggested N=N double bond and N–N single bond lengths. The bond lengths of N(sp3)–C(sp2), N(sp2)–C(sp2) and N(sp3)–N(sp2) in related hydrazone tatutomers are listed in Table 2. Comparing to related bond lengths in in Table 2, C1–N1(N(sp2)–C(sp2)) and N2–C9(N(sp3)–C(sp2)) are slightly longer, and N1–N2(N(sp3)–N(sp2)) is shorter than the expected values. Also, carbonyl oxygens slightly deviates from the least-squares plane (N1, C1, C2, C6) by -0.305 (3)Å for O1 and -0.297 (3)Å for O2. From the bond lengths and these deviations, it can be concluded that the compound exists both in azo and hydrazone tautomeric forms, and is mainly in the hydrazone tautomeric form, i.e. it is close to being real hydrazone pigments. C11–C15 bond length is longer for C(sp2)-C(sp1) but in agreement with previously reported value (Batchelor et al., 1997).
Experimental
A hydrochloric acid solution (2.5 ml) of 3-aminobenzonitrile (1.18 g, 0.010 mol) and an aqueous solution (10 ml) of sodium nitrite (0.69 g, 0.010 mol) were mixed and stirred at 273 K for 1 h, followed by the addition of ethanol solution (10 ml) of the coupling component 5,5-dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione (1.40 g, 0.010 mol) and continued stirring at 273 K for 4 h. The resulting product was filtered and washed with water, dried, and crystallized from ethanol gave fine crystals of benzonitrile, 3-[2-(4,4-dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohexylidene)hydrazinyl].
Refinement
H atoms attached to carbon atoms were placed in calculated positions with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The coordinates of the amine hydrogen obtained from a difference map and refined isotropically.
Figures
Fig. 1.
An ORTEPIII drawing of title complex with the atom numbering scheme at 40% ellipsoid. A view of the title compound, with the atom-labeling scheme.
Fig. 2.
The packing diagram of the complex with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 3.
Tautomeric forms.
Crystal data
| C15H15N3O2 | F(000) = 1136 |
| Mr = 269.30 | Dx = 1.320 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 8472 reflections |
| a = 12.9496 (8) Å | θ = 1.6–27.3° |
| b = 8.6028 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 24.324 (2) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 2709.8 (3) Å3 | Prism, yellow |
| Z = 8 | 0.80 × 0.36 × 0.14 mm |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS II diffractometer | 2880 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1557 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| plane graphite | Rint = 0.052 |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.8°, θmin = 1.7° |
| rotation method scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | k = −10→7 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.991 | l = −30→27 |
| 10586 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.090 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.85 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0393P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2880 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 185 parameters | Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.80305 (13) | 0.3690 (2) | 0.40962 (7) | 0.0361 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.74316 (13) | 0.2806 (2) | 0.36821 (7) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.79117 (13) | 0.2623 (3) | 0.31243 (8) | 0.0488 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.7759 | 0.3541 | 0.2908 | 0.059* | |
| H3B | 0.7595 | 0.1741 | 0.2942 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.90833 (12) | 0.2382 (3) | 0.31345 (7) | 0.0397 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.95623 (13) | 0.3737 (3) | 0.34490 (7) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| H5A | 1.0302 | 0.3573 | 0.3473 | 0.052* | |
| H5B | 0.9449 | 0.4685 | 0.3242 | 0.052* | |
| C6 | 0.91435 (13) | 0.3956 (2) | 0.40184 (7) | 0.0386 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.95030 (15) | 0.2359 (3) | 0.25490 (8) | 0.0609 (7) | |
| H7A | 1.0241 | 0.2257 | 0.2559 | 0.091* | |
| H7B | 0.9321 | 0.3309 | 0.2366 | 0.091* | |
| H7C | 0.9211 | 0.1495 | 0.2353 | 0.091* | |
| C8 | 0.93372 (16) | 0.0846 (3) | 0.34174 (9) | 0.0588 (6) | |
| H8A | 1.0073 | 0.0732 | 0.3444 | 0.088* | |
| H8B | 0.9058 | 0.0001 | 0.3207 | 0.088* | |
| H8C | 0.9041 | 0.0838 | 0.3779 | 0.088* | |
| C9 | 0.72958 (12) | 0.5914 (2) | 0.52616 (7) | 0.0370 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.77582 (13) | 0.6709 (2) | 0.56870 (7) | 0.0405 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.8472 | 0.6696 | 0.5727 | 0.049* | |
| C11 | 0.71482 (13) | 0.7530 (2) | 0.60557 (7) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.60825 (14) | 0.7562 (3) | 0.59960 (8) | 0.0450 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.5675 | 0.8108 | 0.6245 | 0.054* | |
| C13 | 0.56389 (14) | 0.6779 (3) | 0.55664 (8) | 0.0504 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.4926 | 0.6804 | 0.5523 | 0.060* | |
| C14 | 0.62310 (13) | 0.5957 (3) | 0.51986 (8) | 0.0453 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.5919 | 0.5431 | 0.4909 | 0.054* | |
| C15 | 0.76084 (15) | 0.8376 (3) | 0.65054 (8) | 0.0503 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.74838 (11) | 0.42725 (19) | 0.45015 (6) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.79244 (12) | 0.5078 (2) | 0.48910 (6) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.79474 (14) | 0.9049 (3) | 0.68665 (8) | 0.0735 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.65786 (9) | 0.22775 (17) | 0.37853 (5) | 0.0507 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.96910 (9) | 0.43863 (18) | 0.44021 (5) | 0.0494 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.8663 (18) | 0.515 (3) | 0.4890 (8) | 0.074 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0351 (9) | 0.0363 (13) | 0.0368 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0046 (8) | 0.0001 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0371 (9) | 0.0341 (12) | 0.0455 (11) | 0.0054 (9) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0010 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0438 (10) | 0.0592 (17) | 0.0434 (12) | 0.0017 (10) | −0.0014 (8) | −0.0087 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0385 (9) | 0.0420 (14) | 0.0387 (10) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0021 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0389 (10) | 0.0464 (14) | 0.0451 (11) | −0.0030 (9) | 0.0089 (8) | −0.0006 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0360 (13) | 0.0414 (10) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0040 (8) | −0.0010 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0595 (12) | 0.077 (2) | 0.0459 (12) | −0.0031 (13) | 0.0112 (10) | −0.0101 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0562 (12) | 0.0484 (17) | 0.0716 (14) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0163 (11) | 0.0012 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0393 (13) | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0030 (9) | 0.0056 (7) | 0.0026 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0335 (10) | 0.0483 (15) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0431 (14) | 0.0359 (10) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | −0.0008 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0483 (14) | 0.0435 (11) | 0.0081 (10) | 0.0080 (8) | −0.0057 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0605 (16) | 0.0570 (13) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0051 (9) | −0.0092 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0544 (16) | 0.0455 (11) | −0.0017 (10) | 0.0026 (8) | −0.0101 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0629 (17) | 0.0443 (12) | 0.0019 (10) | 0.0076 (10) | −0.0035 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0400 (7) | 0.0382 (11) | 0.0377 (8) | 0.0007 (8) | 0.0046 (7) | −0.0002 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0347 (8) | 0.0449 (12) | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0049 (7) | −0.0047 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0686 (12) | 0.097 (2) | 0.0553 (12) | −0.0122 (12) | 0.0018 (10) | −0.0218 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0493 (10) | 0.0656 (9) | −0.0065 (6) | 0.0061 (6) | −0.0052 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0378 (7) | 0.0661 (12) | 0.0443 (8) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0005 (6) | −0.0118 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.313 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.472 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.481 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C2—O1 | 1.221 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.377 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.501 (2) | C9—C14 | 1.388 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.532 (2) | C9—N2 | 1.412 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C10—C11 | 1.388 (2) |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C7 | 1.524 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.388 (2) |
| C4—C8 | 1.526 (3) | C11—C15 | 1.442 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.526 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.370 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.499 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.374 (3) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9700 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C6—O2 | 1.229 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9600 | C15—N3 | 1.140 (2) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9600 | N1—N2 | 1.305 (2) |
| C7—H7C | 0.9600 | N2—H2 | 0.96 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 124.40 (17) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 115.10 (15) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.35 (16) | C4—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C1 | 121.69 (17) | C4—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 121.42 (17) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 116.87 (16) | C4—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 114.21 (15) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 108.7 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 108.7 | C10—C9—C14 | 120.13 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3B | 108.7 | C10—C9—N2 | 118.83 (15) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 108.7 | C14—C9—N2 | 121.04 (18) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.6 | C9—C10—C11 | 119.38 (16) |
| C7—C4—C8 | 109.47 (18) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.3 |
| C7—C4—C5 | 109.47 (16) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.3 |
| C8—C4—C5 | 110.37 (17) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.55 (18) |
| C7—C4—C3 | 109.86 (16) | C12—C11—C15 | 118.70 (17) |
| C8—C4—C3 | 109.75 (16) | C10—C11—C15 | 120.75 (16) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 107.90 (16) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.15 (18) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 114.32 (16) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.7 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.4 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 108.7 | C12—C13—C14 | 121.05 (18) |
| C6—C5—H5B | 108.7 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 108.7 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.5 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.6 | C13—C14—C9 | 119.74 (19) |
| O2—C6—C1 | 120.94 (16) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| O2—C6—C5 | 122.05 (15) | C9—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 116.97 (16) | N3—C15—C11 | 178.2 (2) |
| C4—C7—H7A | 109.5 | N2—N1—C1 | 120.80 (15) |
| C4—C7—H7B | 109.5 | N1—N2—C9 | 118.82 (16) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | N1—N2—H2 | 118.0 (13) |
| C4—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C9—N2—H2 | 122.9 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2—O1 | −20.3 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −38.1 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 163.84 (18) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | 1.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 158.29 (18) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | −179.69 (19) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −17.5 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.4 (3) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −143.91 (19) | C9—C10—C11—C15 | −179.95 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 37.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | −174.81 (19) | C15—C11—C12—C13 | 179.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C8 | 64.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −55.5 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.0 (3) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 175.37 (17) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.8 (3) |
| C8—C4—C5—C6 | −64.1 (2) | N2—C9—C14—C13 | 179.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 55.8 (2) | C6—C1—N1—N2 | −4.2 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—O2 | 20.1 (3) | C2—C1—N1—N2 | −179.81 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—O2 | −164.49 (19) | C1—N1—N2—C9 | 168.70 (18) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −157.67 (19) | C10—C9—N2—N1 | 177.20 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 17.8 (3) | C14—C9—N2—N1 | −3.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—O2 | 144.2 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O2 | 0.95 (2) | 1.91 (2) | 2.6461 (19) | 132.6 (18) |
| C10—H10···O2i | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.442 (2) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Table 2 Selected bonds compared with related hydrazone compounds (Å) [should this be 1.313 and 1.305 for current work?]
| Nsp3—Csp2 | Nsp2—Csp2 | Nsp3—Nsp2 | Reference |
| 1.412 | 1.313 | 1.305 | Current work |
| 1.406 | 1.313 | 1.300 | Alpaslan et al. (2005) |
| 1.382 | 1.289 | 1.364 | de Lima et al. (2009) |
| 1.347 | 1.282 | 1.378 | de Souza et al. (2010) |
| 1.376-1.384 | 1.300-1.325 | 1.319-1.325 | Özbey et al. (1997) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU2749).
References
- Alpaslan, G., Özdamar, O., Odabaşogˇlu, M., Ersanlı, C. C., Erdönmez, A. & Ocak Ískeleli, N. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3442–o3444.
- Batchelor, R. A., Hunter, C. A. & Simpson, J. (1997). Acta Cryst. C53, 1117–1119.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Gale, P. A., Chen, Z., Drew, M. G. B., Heath, J. A. & Beer, P. D. (1998). Polyhedron, 4, 405–412.
- Karcı, F., Şener, İ. & Deligöz, H. (2004). Dyes Pigments, 62, 131–140.
- Kelemen, J., Kormany, G. & Rihs, G. (1982). Dyes Pigments, 3, 249–271.
- Kobrakov, K. I., Glyadyaeva, O. Yu., Stankevich, G. S. & Kovtun, L. G. (2004). Fibre Chem.36, 41–42.
- Lima, G. M. de, Tiekink, E. R. T., Wardell, J. L. & Wardell, S. M. S. V. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o3241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Özbey, S., Temel, A., Özgün, B. H. & Ertan, N. (1997). Acta Cryst. C53, 113–116.
- Saylam, A., Seferoğlu, Z. & Ertan, N. (2008). Dyes Pigments, 76, 470–476.
- Seferoğlu, Z., Ertan, N., Hökelek, T. & Şahin, E. (2008). Dyes Pigments, 77, 614–625.
- Seferoğlu, Z., Ertan, N., Kickelbick, G. & Hökelek, T. (2009). Dyes Pigments, 82, 20–25.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Souza, M. V. N. de, Howie, R. A., Tiekink, E. R. T., Wardell, J. L., Wardell, S. M. S. V. & Kaiser, C. R. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o698–o699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-AREA and X-RED32 Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810013164/xu2749sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810013164/xu2749Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report