Abstract
The title molecule, C18H13NO4, shows a dihedral angle between the terminal acetyl group (r.m.s. deviation = 0.0081 Å) and remaining non-H atoms (r.m.s. = 0.0734 Å) of 53.45 (7)°. The configuration about the central olefinic bond is Z and overall the molecule has a U-shaped conformation. Supramolecular chains along the b-axis direction are found in the crystal structure. These are stabilized by (C=O)⋯π(ring centroid of the 1,3-oxazole ring) interactions [3.370 (2) Å].
Related literature
For background to the biological activity of 1,3-oxazole and imidazoles, see: Williams & Fu (2010 ▶); Khbnadidah et al. (2003 ▶). For related structures, see: Sun et al. (2007 ▶); Jotani & Baldaniya (2008 ▶).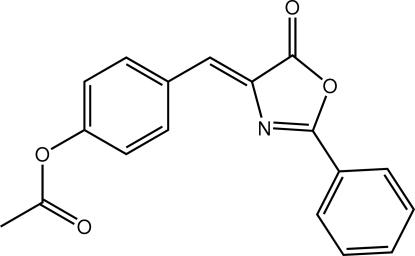
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H13NO4
M r = 307.29
Monoclinic,

a = 13.3507 (15) Å
b = 3.9443 (9) Å
c = 28.527 (5) Å
β = 98.025 (11)°
V = 1487.5 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.81 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.40 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.852, T max = 0.997
2593 measured reflections
2491 independent reflections
1795 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.054
2 standard reflections every 3600 min intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.140
S = 1.06
2491 reflections
210 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: XCAD4 (Harms & Wocadlo, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: XCAD4; data reduction: XCAD4; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810014911/lh5032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810014911/lh5032Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), and the SAIF, I.I.T. Madras, Chennai, India, for the X-ray data collection. MMJ is grateful to the University Grant Commission (Western Regional Office), India, for a Minor Research Project F. No.47-254/07.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The 1,3-oxazole ring is known to have biological activity in its own right (Williams & Fu, 2010) and serves as a useful synthetic intermediate for the synthesis of imidazoles that are also possess a wide spectrum of biological activities, such as herbicides, fungicides, anti-bacterials, etc. (Khbnadidah et al., 2003). In continuation of structural studies of oxazole compounds (Jotani & Baldaniya, 2008), the crystal structure of title compound, (I), is described herein.
The molecule of (I) is twisted around the C3–O2 bond as seen in the C2–O2–C3–C4 torsion angle of 58.2 (3) °. This results in a dihedral angle of 53.45 (7) ° between the acetyl residue [r.m.s. deviation = 0.0081 Å] and the remaining non-hydrogen atoms [r.m.s. = 0.0734 Å]; the dihedral angle formed between the two benzene rings is 5.10 (12) °. The configuration about the C9═C10 bond [1.343 (3) Å] is Z, and as the two benzene rings are orientated to the same side of the molecule, the overall molecular conformation is U-shaped. A similar conformation was reported in a di-methoxy derivative of (I), namely 2,6-dimethoxy-4-(5-oxo-2-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-4-ylidenemethyl)- phenyl acetate (Sun et al., 2007).
The crystal packing is dominated by (C═O)···π interactions that connect molecules into a linear supramolecular chain along the b axis, Fig. 2. The parameters defining this interaction are C11═O3···ring centroid(1,3-oxazole ring)i = 3.370 (2) Å and angle = 85.11 (14) ° for i: x, 1+y, z.
Experimental
A mixture of 4-acetoxyoxy benzaldehyde (0.25 mol), benzoyl amino acetic acid (0.25 mol), acetyl acetate (0.30 mol) and anhydrous sodium acetate (0.25 mol) were taken in a 500 ml round bottom flask and heated on an electric hot plate with constant stirring. After the complete liquefaction of the mixture, the flask was transferred to a sand bath and further heated for 2.5 h. Ethanol (100 ml) was added slowly to the flask and the mixture was allowed to stand overnight. The crystalline product obtained was filtered with ice-cold alcohol and then with boiling water. The crude product was crystallised from ethanol (95%) to obtain the final product (78% yield; m.pt. 428 K). The colourless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation from an ethanol solution of (I).
Refinement
The H atoms were geometrically placed (C–H = 0.93–0.96 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom-labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids at the 35% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A supramolecular chain aligned along the b axis in (I), mediated by (C═ O)···π interactions (purple dashed lines). Colour code: O, red; N, blue; C, grey; and H, green.
Crystal data
| C18H13NO4 | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 307.29 | Dx = 1.372 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54180 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 13.3507 (15) Å | θ = 20.0–30.0° |
| b = 3.9443 (9) Å | µ = 0.81 mm−1 |
| c = 28.527 (5) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 98.025 (11)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1487.5 (5) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | 1795 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.054 |
| graphite | θmax = 64.9°, θmin = 3.1° |
| 2θ scan | h = 0→15 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | k = 0→4 |
| Tmin = 0.852, Tmax = 0.997 | l = −33→33 |
| 2593 measured reflections | 2 standard reflections every 3600 min |
| 2491 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.140 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0834P)2 + 0.1813P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2491 reflections | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 210 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0081 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.98210 (13) | −0.0744 (6) | 0.36427 (7) | 0.0805 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.96858 (10) | −0.3277 (4) | 0.43327 (5) | 0.0501 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.36614 (12) | 0.4187 (5) | 0.44993 (6) | 0.0606 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.32332 (10) | 0.1834 (4) | 0.37774 (5) | 0.0466 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.47109 (13) | −0.0534 (5) | 0.36494 (6) | 0.0430 (5) | |
| C1 | 1.12156 (18) | −0.3904 (7) | 0.40327 (10) | 0.0628 (7) | |
| H1A | 1.1314 | −0.5250 | 0.3763 | 0.094* | |
| H1B | 1.1304 | −0.5297 | 0.4311 | 0.094* | |
| H1C | 1.1700 | −0.2091 | 0.4069 | 0.094* | |
| C2 | 1.01799 (17) | −0.2475 (7) | 0.39635 (9) | 0.0496 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.86835 (15) | −0.2184 (6) | 0.43289 (8) | 0.0425 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.79303 (16) | −0.3064 (6) | 0.39696 (8) | 0.0447 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.8082 | −0.4318 | 0.3713 | 0.054* | |
| C5 | 0.69517 (15) | −0.2074 (6) | 0.39935 (7) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.6442 | −0.2660 | 0.3751 | 0.050* | |
| C6 | 0.67139 (15) | −0.0187 (6) | 0.43805 (7) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.74930 (16) | 0.0581 (6) | 0.47402 (8) | 0.0453 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.7348 | 0.1787 | 0.5003 | 0.054* | |
| C8 | 0.84763 (16) | −0.0399 (6) | 0.47180 (7) | 0.0479 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.8990 | 0.0138 | 0.4962 | 0.057* | |
| C9 | 0.57088 (15) | 0.1106 (6) | 0.44158 (7) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.5640 | 0.2187 | 0.4699 | 0.049* | |
| C10 | 0.48645 (15) | 0.0971 (6) | 0.40999 (7) | 0.0396 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.39108 (16) | 0.2560 (6) | 0.41824 (8) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.37851 (15) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.34861 (7) | 0.0410 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.32449 (17) | −0.1052 (6) | 0.30296 (8) | 0.0449 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.22131 (19) | −0.0575 (7) | 0.29152 (9) | 0.0566 (7) | |
| H14 | 0.1849 | 0.0484 | 0.3129 | 0.068* | |
| C15 | 0.1725 (2) | −0.1672 (8) | 0.24835 (10) | 0.0686 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.1030 | −0.1381 | 0.2409 | 0.082* | |
| C16 | 0.2258 (2) | −0.3186 (7) | 0.21650 (9) | 0.0692 (8) | |
| H16 | 0.1924 | −0.3929 | 0.1875 | 0.083* | |
| C17 | 0.3283 (2) | −0.3612 (7) | 0.22719 (9) | 0.0673 (8) | |
| H17 | 0.3644 | −0.4603 | 0.2051 | 0.081* | |
| C18 | 0.3783 (2) | −0.2584 (7) | 0.27036 (8) | 0.0567 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.4477 | −0.2913 | 0.2777 | 0.068* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0539 (11) | 0.1108 (18) | 0.0780 (13) | 0.0078 (11) | 0.0130 (9) | 0.0395 (13) |
| O2 | 0.0390 (8) | 0.0609 (11) | 0.0510 (9) | 0.0101 (7) | 0.0086 (7) | 0.0066 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0503 (10) | 0.0774 (13) | 0.0557 (10) | 0.0091 (9) | 0.0136 (8) | −0.0205 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0387 (8) | 0.0522 (10) | 0.0487 (9) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0056 (6) | −0.0073 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0431 (11) | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0031 (9) | 0.0060 (8) | −0.0049 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0478 (14) | 0.0644 (18) | 0.0793 (17) | 0.0082 (13) | 0.0195 (12) | −0.0008 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0418 (12) | 0.0538 (16) | 0.0533 (13) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0075 (10) | −0.0007 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0450 (13) | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0036 (10) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0089 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0455 (12) | 0.0452 (14) | 0.0442 (12) | 0.0020 (11) | 0.0088 (9) | −0.0014 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0422 (13) | 0.0401 (11) | −0.0019 (10) | 0.0034 (9) | −0.0006 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0407 (11) | 0.0385 (13) | 0.0380 (10) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0085 (9) | 0.0045 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0442 (12) | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0400 (11) | 0.0002 (11) | 0.0070 (9) | −0.0052 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0397 (12) | 0.0605 (16) | 0.0423 (12) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0023 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0411 (13) | 0.0400 (11) | −0.0015 (10) | 0.0096 (9) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0402 (11) | 0.0386 (13) | 0.0410 (11) | 0.0010 (10) | 0.0088 (9) | −0.0017 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0410 (11) | 0.0472 (14) | 0.0430 (11) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0078 (9) | −0.0021 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0420 (12) | 0.0377 (12) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0013 (10) | 0.0088 (9) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0534 (13) | 0.0385 (13) | 0.0414 (11) | −0.0013 (10) | 0.0019 (9) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0571 (15) | 0.0563 (16) | 0.0531 (14) | 0.0004 (12) | −0.0033 (11) | 0.0013 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0656 (16) | 0.0642 (19) | 0.0689 (17) | −0.0058 (15) | −0.0158 (14) | 0.0039 (15) |
| C16 | 0.100 (2) | 0.0493 (17) | 0.0513 (15) | −0.0104 (16) | −0.0120 (15) | −0.0002 (13) |
| C17 | 0.095 (2) | 0.0578 (18) | 0.0476 (14) | 0.0008 (15) | 0.0035 (14) | −0.0093 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0656 (16) | 0.0528 (16) | 0.0512 (14) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0065 (11) | −0.0057 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C2 | 1.188 (3) | C6—C9 | 1.452 (3) |
| O2—C2 | 1.356 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.378 (3) |
| O2—C3 | 1.404 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C11 | 1.193 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C12 | 1.385 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.343 (3) |
| O4—C11 | 1.394 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C12 | 1.277 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.468 (3) |
| N1—C10 | 1.404 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.460 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.481 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.384 (3) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C13—C18 | 1.390 (3) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.380 (4) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C8 | 1.375 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.367 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.374 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.371 (4) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.404 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.377 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.389 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C2—O2—C3 | 119.26 (17) | C10—C9—C6 | 129.6 (2) |
| C12—O4—C11 | 105.40 (16) | C10—C9—H9 | 115.2 |
| C12—N1—C10 | 105.77 (17) | C6—C9—H9 | 115.2 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C9—C10—N1 | 129.26 (19) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C9—C10—C11 | 122.8 (2) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | N1—C10—C11 | 107.96 (18) |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | O3—C11—O4 | 121.40 (19) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | O3—C11—C10 | 133.7 (2) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | O4—C11—C10 | 104.85 (18) |
| O1—C2—O2 | 123.0 (2) | N1—C12—O4 | 115.99 (18) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 126.2 (2) | N1—C12—C13 | 127.46 (19) |
| O2—C2—C1 | 110.7 (2) | O4—C12—C13 | 116.54 (18) |
| C8—C3—C4 | 121.5 (2) | C14—C13—C18 | 119.5 (2) |
| C8—C3—O2 | 116.73 (19) | C14—C13—C12 | 121.5 (2) |
| C4—C3—O2 | 121.6 (2) | C18—C13—C12 | 119.0 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.5 (2) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.9 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.3 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.3 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.7 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 117.93 (19) | C15—C16—C17 | 120.1 (2) |
| C7—C6—C9 | 118.43 (19) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C5—C6—C9 | 123.59 (19) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.6 (2) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.5 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.2 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.2 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C3—C8—C7 | 118.7 (2) | C17—C18—C13 | 119.7 (3) |
| C3—C8—H8 | 120.6 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.6 | C13—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5032).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1996). XCAD4 University of Marburg, Germany.
- Jotani, M. M. & Baldaniya, B. B. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, C398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Khbnadidah, S., Rezaei, Z., Khalafi-Nehad, A., Bahrinajafi, R., Mohamadi, R. & Farrokroz, A. A. (2003). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 13, 2863–2865. [DOI] [PubMed]
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-F., Wang, X.-L., Li, J.-K., Zheng, Z.-B. & Wu, R.-T. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4426.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst.43 Submitted.
- Williams, D. R. & Fu, L. (2010). Org. Lett 12, 808–811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810014911/lh5032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810014911/lh5032Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




