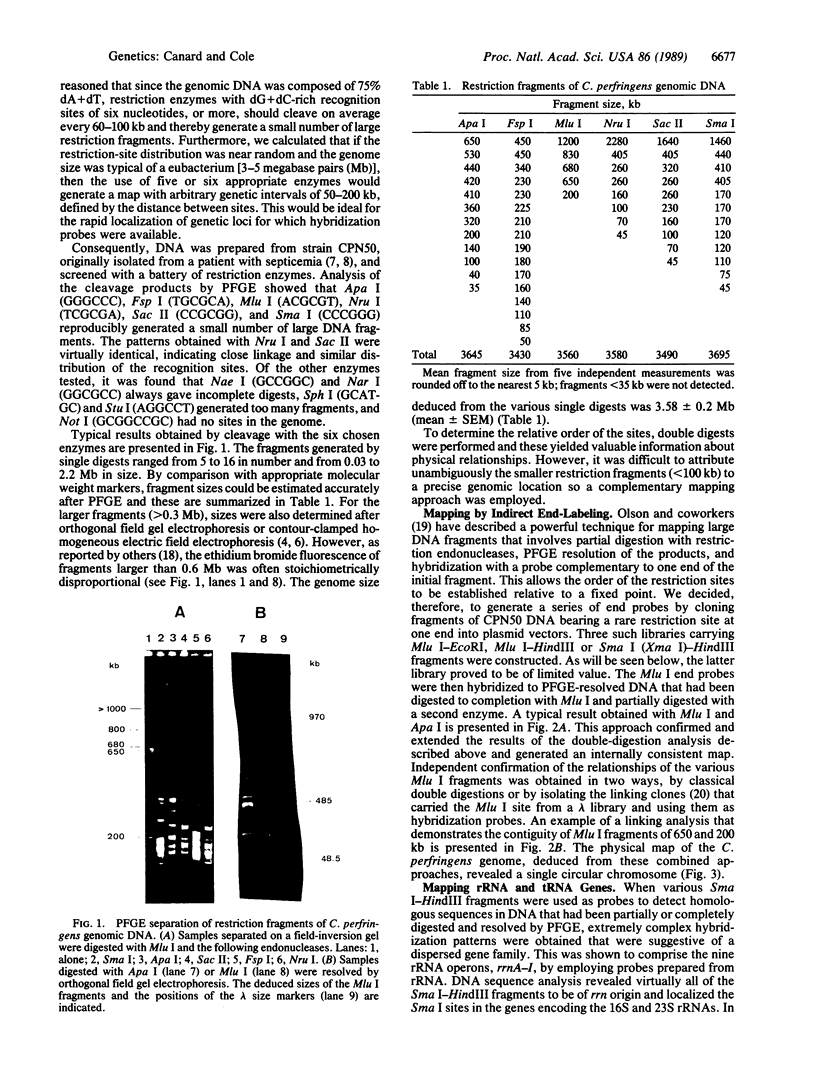
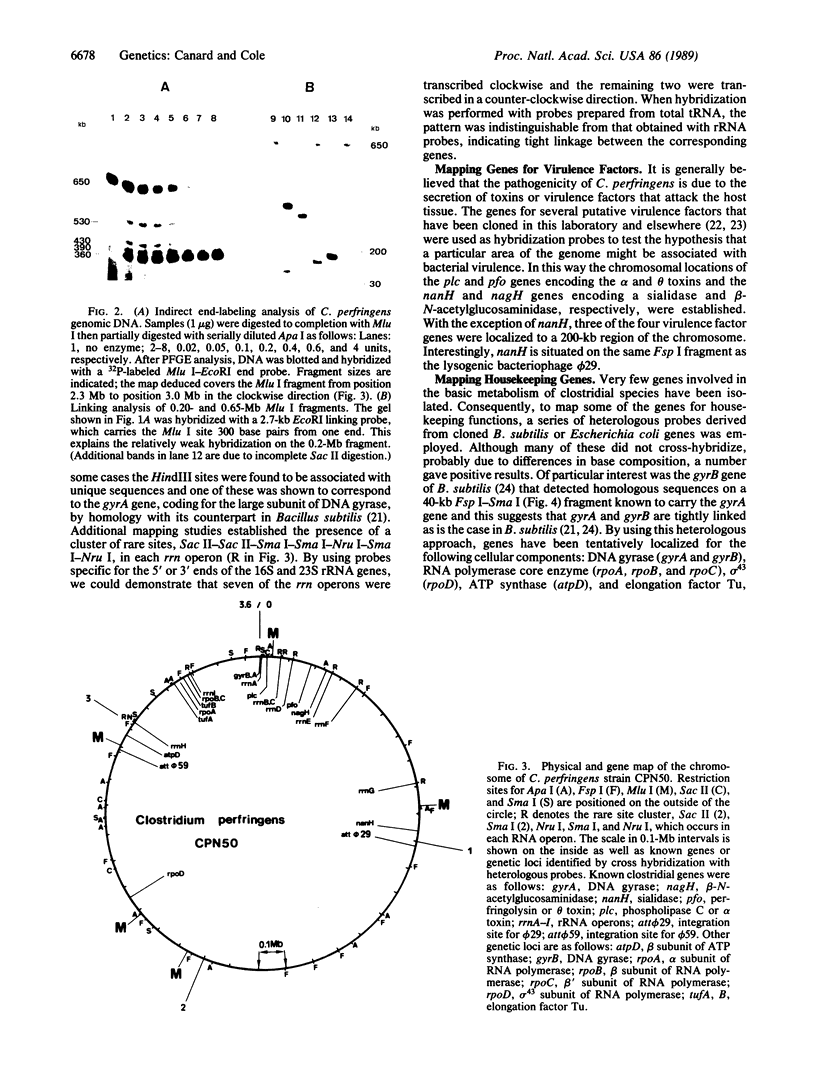
Abstract
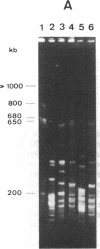
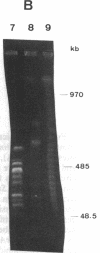
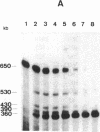
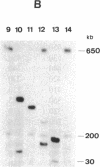
A physical map of the genome of Clostridium perfringens, an important human pathogen, has been established by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Recognition sites for six rare-cutting endonucleases were situated on a single circular chromosome of approximately 3.6 million base pairs thus defining 50 arbitrary genetic intervals of between 10 and 250 kilobase pairs. This considerably facilitated the chromosomal localization of some 24 genes and loci for which probes were available and allowed the construction of the genome map of a clostridial species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brefort G., Magot M., Ionesco H., Sebald M. Characterization and transferability of Clostridium perfringens plasmids. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):52–66. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. P., Prior S. E., Barstow D. A., Minton N. P. The pMTL nic- cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. Y., Otani T., Boime I., Olson M. V., Carle G. F., Chaplin D. D. Cosmid mapping of the human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit genes by field-inversion gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4437–4448. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henckes G., Vannier F., Seiki M., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H., Seror-Laurent S. J. Ribosomal RNA genes in the replication origin region of Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):268–271. doi: 10.1038/299268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. D., Widom R. L., LaFauci G., Setoguchi Y., Richter I. R., Rudner R. Chromosomal organization of rRNA operons in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):625–635. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. F., Bott K. F. Genetic and physical organization of the cloned gyrA and gyrB genes of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.78-84.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya S., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Structure and function of the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. III. Nucleotide sequence of some 10,000 base pairs in the origin region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2251–2265. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Hoch J. A. Revised genetic linkage map of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):158–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.158-179.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggentin P., Rothe B., Lottspeich F., Schauer R. Cloning and sequencing of a Clostridium perfringens sialidase gene. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 26;238(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela S., Yogev D., Razin S., Bercovier H. Duplication of the tuf gene: a new insight into the phylogeny of eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):581–584. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.581-584.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the perfringolysin O (theta-toxin) gene from Clostridium perfringens and characterization of the gene product. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3228–3234. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3228-3234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vold B. S. Structure and organization of genes for transfer ribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.71-80.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil M. D., McClelland M. Enzymatic cleavage of a bacterial genome at a 10-base-pair recognition site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):51–55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]