Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, [Cu(C4H8NO3)(C12H8N2)(H2O)]Cl·2H2O, contains a complex cation, a chloride anion and two water molecules. The CuII ion has a distorted square-pyramidal coordination geometry formed by one bidentate phenanthroline ligand, one O,N-bidentate dl-threoninate ligand and one apical water molecule. In the crystal structure, intermolecular O—H⋯O, N—H⋯O, N—H⋯Cl and O—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds link the components into layers. A single weak intermolecular C—H⋯O interaction connects these layers into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For background to the interactions of transition-metal complexes with DNA, see: Vaidyanathan & Nair (2003 ▶); Rao et al. (2007 ▶, 2008 ▶); Kumar & Arunachalam (2007 ▶); Patel et al. (2006 ▶); Wang et al. (2007 ▶); Zhang et al. (2004 ▶). For a related structure, see: Lu et al. (2004 ▶). For standard bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(C4H8NO3)(C12H8N2)(H2O)]Cl·2H2O
M r = 451.36
Triclinic,

a = 7.1972 (1) Å
b = 11.9785 (2) Å
c = 12.2915 (2) Å
α = 65.664 (1)°
β = 78.079 (1)°
γ = 81.345 (1)°
V = 942.15 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.34 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.34 × 0.20 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.656, T max = 0.911
29845 measured reflections
8056 independent reflections
5995 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.04
8056 reflections
245 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.41 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810015278/lh5025sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810015278/lh5025Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1W1⋯Cl1 | 0.80 | 2.36 | 3.1411 (13) | 166 |
| O1W—H2W1⋯O2i | 0.82 | 1.90 | 2.7114 (18) | 167 |
| O3—H1O3⋯O1ii | 0.90 | 2.03 | 2.9089 (18) | 164 |
| N3—H1N3⋯Cl1iii | 0.86 | 2.62 | 3.3992 (13) | 151 |
| N3—H2N3⋯O2Wi | 0.94 | 2.07 | 3.0085 (19) | 175 |
| O2W—H1W2⋯Cl1i | 0.87 | 2.35 | 3.2104 (16) | 175 |
| O2W—H2W2⋯Cl1iv | 0.84 | 2.33 | 3.1463 (14) | 162 |
| O3W—H1W3⋯O2W | 1.01 | 1.95 | 2.954 (2) | 170 |
| O3W—H2W3⋯O3ii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.901 (2) | 159 |
| C7—H7A⋯O2v | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.292 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 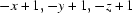 ; (ii)
; (ii) 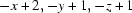 ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv) 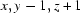 ; (v)
; (v) 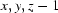 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the RU research grant (PKIMIA/815002). HKF and WSL also thank USM for the Research University Golden Goose Grant (1001/PFIZIK/811012). YHT and WSL are grateful for the award of USM fellowships for financial assistance.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The interaction of transition metal complexes with DNA is a vibrant area of research and has long been investigated in relation to the development of new reagents for molecular biology, biotechnology and medicine (Vaidyanathan et al., 2003; Rao et al., 2008; Kumar et al., 2007). Among all the transition metals, copper is the most widely used metals in these studies as it is a bioessential element with +1 and +2 oxidation states (Patel et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2007; Vaidyanathan et al., 2003). Copper(II) complexes have been found to be useful in the treatment of many diseases as well as cancer. Copper(II) complexes of 1,10-phenanthroline and its derivatives exhibit various biological activities such as antimicrobial, antimycobaterial, anticandida and antitumor activities. Copper complexes of amino acids have been reported to exhibit effective antitumor and artificial nuclease activity. Several reports have also shown that these complexes show efficient DNA cleavage activity by either oxidative or hydrolytic pathways (Kumar et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2004; Rao et al., 2007). In the title compound, aqua(DL-threoninato-κ2N,O)(1,10-phenanthroline)copper(II) chloride dihydrate, DL-threonine has been selected as the ligand for the complex.
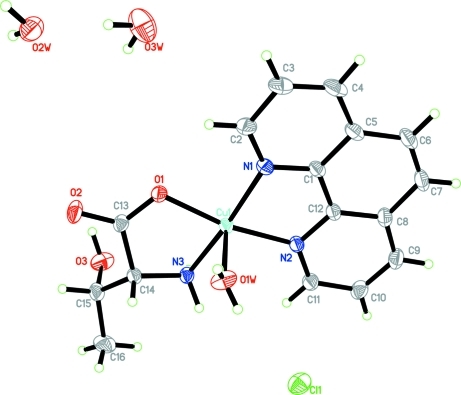
The asymmetric unit of the title compound (Fig. 1) consists of one CuII complex cation, one chlorine anion and two water molecules. The CuII ion is coordinated by N1 and N2 atoms from the phenanthroline ligand and N3 and O1 atoms from the threoninato ligand in the basal plane and the O1W water molecule is coordinated in the apical site to form a distorted square-pyramidal geometry. The bond lengths are within normal values (Allen et al., 1987) and are comparable to those observed for a closely related structure (Lu et al., 2004).
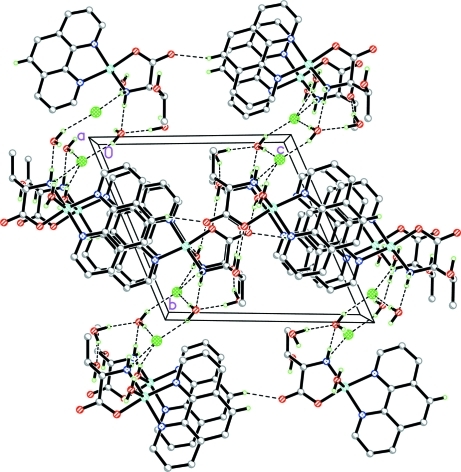
In the crystal structure (Fig. 2), intermolecular C7—H7A···O2 hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the CuII complex cations into chains along the c axis. Intermolecular O1W—H2W1···O2, O3—H1O3···O1, N3—H2N3···O2W, O3W—H2W3···O3, O3W—H1W3···O2W, N3—H1N3···Cl1, O2W—H1W2···Cl1, O2W—H2W2···Cl1 and O1W—H1W1—Cl1 interactions (Table 1) link the molecules into a three-dimensional network.
Experimental
To an ethanolic solution (10.0 ml) of copper(II) chloride dihydrate (0.1708 g, 1 mmol), an ethanolic solution (10.0 ml) of DL-threonine (0.1191 g, 1 mmol) was added. After a few minutes, an ethanolic solution (20.0 ml) of 1,10-phenanthroline (0.1982 g, 1 mmol) was added dropwise to the mixture solution. The pH of the resulting solution was then adjusted to pH 8 by adding a few drops of NaOH aqueous solution. The blue solution was filtered and left to evaporate slowly at room temperature. Blue blocky single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained after a few days.
Refinement
H atoms attached to N and O atoms were located from difference Fourier map and allowed to ride on their parent atoms and constrained to be 1.5Ueq for the water molecules and 1.2Ueq for the amino group. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq(C). A rotating-group model was applied for the methyl group [C–H = 0.93 to 0.98 Å, O–H = 0.7992 to 1.0137 Å, N–H = 0.8636 to 0.9420 Å].
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. Intermolecular interactions are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in the intermolecular interactions (dashed lines) have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Cu(C4H8NO3)(C12H8N2)(H2O)]Cl·2H2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 451.36 | F(000) = 466 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.591 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.1972 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 9968 reflections |
| b = 11.9785 (2) Å | θ = 2.9–32.7° |
| c = 12.2915 (2) Å | µ = 1.34 mm−1 |
| α = 65.664 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 78.079 (1)° | Block, blue |
| γ = 81.345 (1)° | 0.34 × 0.20 × 0.07 mm |
| V = 942.15 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 8056 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5995 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.028 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 34.7°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.656, Tmax = 0.911 | k = −18→19 |
| 29845 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0404P)2 + 0.1542P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 8056 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 245 parameters | Δρmax = 0.47 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.41 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.76442 (2) | 0.603112 (14) | 0.250328 (14) | 0.02828 (5) | |
| O1W | 0.45829 (16) | 0.66307 (10) | 0.28057 (11) | 0.0473 (3) | |
| H1W1 | 0.3972 | 0.7227 | 0.2422 | 0.071* | |
| H2W1 | 0.3770 | 0.6135 | 0.3201 | 0.071* | |
| O1 | 0.77687 (16) | 0.50694 (9) | 0.42081 (9) | 0.0359 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.7643 (2) | 0.52774 (11) | 0.59298 (9) | 0.0493 (3) | |
| O3 | 1.07351 (19) | 0.74151 (11) | 0.44492 (13) | 0.0558 (3) | |
| H1O3 | 1.0957 | 0.6609 | 0.4891 | 0.084* | |
| N1 | 0.72609 (17) | 0.45456 (11) | 0.22337 (11) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.80300 (17) | 0.67993 (11) | 0.06759 (10) | 0.0305 (2) | |
| N3 | 0.83142 (17) | 0.74053 (10) | 0.28305 (10) | 0.0296 (2) | |
| H1N3 | 0.9497 | 0.7564 | 0.2596 | 0.036* | |
| H2N3 | 0.7570 | 0.8122 | 0.2433 | 0.036* | |
| C1 | 0.74069 (19) | 0.47692 (13) | 0.10467 (13) | 0.0314 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.6821 (2) | 0.34333 (14) | 0.30518 (16) | 0.0407 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.6704 | 0.3275 | 0.3869 | 0.049* | |
| C3 | 0.6532 (3) | 0.24997 (15) | 0.27161 (19) | 0.0491 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.6223 | 0.1733 | 0.3307 | 0.059* | |
| C4 | 0.6702 (3) | 0.27118 (16) | 0.15218 (19) | 0.0484 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.6526 | 0.2088 | 0.1296 | 0.058* | |
| C5 | 0.7146 (2) | 0.38811 (15) | 0.06321 (16) | 0.0394 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.7318 (2) | 0.42233 (18) | −0.06444 (17) | 0.0482 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.7168 | 0.3641 | −0.0932 | 0.058* | |
| C7 | 0.7694 (2) | 0.53790 (18) | −0.14407 (16) | 0.0467 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.7796 | 0.5575 | −0.2265 | 0.056* | |
| C8 | 0.7939 (2) | 0.63054 (16) | −0.10411 (14) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.8273 (2) | 0.75297 (17) | −0.18067 (14) | 0.0454 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.8351 | 0.7788 | −0.2638 | 0.054* | |
| C10 | 0.8481 (2) | 0.83416 (16) | −0.13287 (14) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.8698 | 0.9154 | −0.1833 | 0.052* | |
| C11 | 0.8368 (2) | 0.79473 (14) | −0.00808 (13) | 0.0364 (3) | |
| H11A | 0.8534 | 0.8506 | 0.0232 | 0.044* | |
| C12 | 0.78101 (19) | 0.59920 (14) | 0.01996 (13) | 0.0309 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.7721 (2) | 0.57113 (13) | 0.48255 (12) | 0.0322 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.7668 (2) | 0.71093 (13) | 0.41344 (12) | 0.0319 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.6330 | 0.7421 | 0.4225 | 0.038* | |
| C15 | 0.8735 (3) | 0.77207 (14) | 0.46657 (14) | 0.0409 (3) | |
| H15A | 0.8300 | 0.7424 | 0.5541 | 0.049* | |
| C16 | 0.8433 (3) | 0.91054 (16) | 0.4121 (2) | 0.0563 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.9172 | 0.9447 | 0.4461 | 0.084* | |
| H16B | 0.7109 | 0.9346 | 0.4297 | 0.084* | |
| H16C | 0.8827 | 0.9403 | 0.3261 | 0.084* | |
| Cl1 | 0.22654 (6) | 0.87371 (4) | 0.09619 (4) | 0.04803 (10) | |
| O2W | 0.4269 (2) | 0.03917 (12) | 0.83732 (12) | 0.0539 (3) | |
| H1W2 | 0.5174 | 0.0603 | 0.8600 | 0.081* | |
| H2W2 | 0.3827 | −0.0182 | 0.9014 | 0.081* | |
| O3W | 0.6557 (2) | 0.08312 (18) | 0.59634 (17) | 0.0851 (5) | |
| H1W3 | 0.5665 | 0.0630 | 0.6763 | 0.128* | |
| H2W3 | 0.7213 | 0.1408 | 0.6002 | 0.128* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.03672 (10) | 0.02541 (8) | 0.02496 (8) | −0.00530 (6) | −0.00529 (6) | −0.01097 (6) |
| O1W | 0.0328 (5) | 0.0366 (6) | 0.0579 (7) | −0.0045 (4) | −0.0043 (5) | −0.0048 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0538 (6) | 0.0256 (4) | 0.0297 (5) | −0.0058 (4) | −0.0116 (4) | −0.0091 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0797 (9) | 0.0429 (6) | 0.0247 (5) | −0.0253 (6) | −0.0091 (5) | −0.0056 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0573 (8) | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0764 (9) | −0.0043 (5) | −0.0328 (7) | −0.0172 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0288 (6) | 0.0358 (6) | −0.0036 (5) | −0.0063 (5) | −0.0153 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0314 (6) | 0.0278 (5) | −0.0040 (5) | −0.0045 (4) | −0.0138 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0370 (6) | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0246 (5) | −0.0077 (4) | −0.0041 (4) | −0.0088 (4) |
| C1 | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0391 (7) | 0.0011 (5) | −0.0089 (5) | −0.0221 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0470 (8) | 0.0300 (7) | 0.0449 (8) | −0.0055 (6) | −0.0078 (7) | −0.0137 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0664 (12) | −0.0059 (7) | −0.0099 (9) | −0.0192 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0380 (8) | 0.0762 (13) | 0.0006 (7) | −0.0169 (9) | −0.0357 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0566 (10) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0136 (7) | −0.0326 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0598 (11) | 0.0623 (11) | 0.0067 (8) | −0.0192 (8) | −0.0464 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0663 (11) | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0066 (8) | −0.0156 (7) | −0.0378 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0530 (9) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0040 (6) | −0.0100 (6) | −0.0246 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0470 (9) | 0.0588 (10) | 0.0288 (7) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0080 (6) | −0.0165 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0308 (7) | −0.0044 (7) | −0.0045 (6) | −0.0076 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0338 (7) | 0.0319 (7) | −0.0060 (6) | −0.0033 (6) | −0.0118 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0383 (7) | 0.0324 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0066 (5) | −0.0194 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0390 (7) | 0.0303 (6) | 0.0266 (6) | −0.0096 (5) | −0.0058 (5) | −0.0080 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0275 (6) | −0.0050 (5) | −0.0042 (5) | −0.0120 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0605 (10) | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0331 (7) | −0.0103 (7) | −0.0100 (7) | −0.0161 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0703 (12) | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0740 (13) | −0.0048 (8) | −0.0184 (10) | −0.0296 (9) |
| Cl1 | 0.0520 (2) | 0.03659 (19) | 0.0500 (2) | −0.01029 (17) | −0.01205 (18) | −0.00742 (17) |
| O2W | 0.0616 (8) | 0.0483 (7) | 0.0475 (7) | −0.0081 (6) | −0.0133 (6) | −0.0114 (6) |
| O3W | 0.0749 (11) | 0.1128 (15) | 0.0905 (13) | −0.0229 (10) | −0.0039 (9) | −0.0616 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu1—O1 | 1.9450 (10) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| Cu1—N3 | 1.9921 (11) | C5—C6 | 1.432 (2) |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.0059 (12) | C6—C7 | 1.354 (3) |
| Cu1—N2 | 2.0210 (11) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| Cu1—O1W | 2.2167 (11) | C7—C8 | 1.431 (2) |
| O1W—H1W1 | 0.7992 | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| O1W—H2W1 | 0.8250 | C8—C12 | 1.398 (2) |
| O1—C13 | 1.2770 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.403 (3) |
| O2—C13 | 1.2295 (17) | C9—C10 | 1.366 (2) |
| O3—C15 | 1.429 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| O3—H1O3 | 0.9002 | C10—C11 | 1.395 (2) |
| N1—C2 | 1.3333 (19) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3545 (19) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C11 | 1.3298 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.5326 (19) |
| N2—C12 | 1.3615 (17) | C14—C15 | 1.524 (2) |
| N3—C14 | 1.4778 (17) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| N3—H1N3 | 0.8636 | C15—C16 | 1.511 (2) |
| N3—H2N3 | 0.9420 | C15—H15A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C5 | 1.4047 (19) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C12 | 1.435 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.397 (2) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | O2W—H1W2 | 0.8654 |
| C3—C4 | 1.365 (3) | O2W—H2W2 | 0.8422 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | O3W—H1W3 | 1.0137 |
| C4—C5 | 1.410 (3) | O3W—H2W3 | 0.9153 |
| O1—Cu1—N3 | 84.44 (4) | C7—C6—H6A | 119.4 |
| O1—Cu1—N1 | 92.20 (5) | C5—C6—H6A | 119.4 |
| N3—Cu1—N1 | 173.26 (5) | C6—C7—C8 | 121.40 (15) |
| O1—Cu1—N2 | 167.52 (5) | C6—C7—H7A | 119.3 |
| N3—Cu1—N2 | 99.88 (5) | C8—C7—H7A | 119.3 |
| N1—Cu1—N2 | 82.23 (5) | C12—C8—C9 | 116.68 (14) |
| O1—Cu1—O1W | 94.75 (5) | C12—C8—C7 | 118.61 (16) |
| N3—Cu1—O1W | 89.99 (5) | C9—C8—C7 | 124.70 (15) |
| N1—Cu1—O1W | 96.12 (5) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.91 (14) |
| N2—Cu1—O1W | 96.94 (5) | C10—C9—H9A | 120.0 |
| Cu1—O1W—H1W1 | 131.4 | C8—C9—H9A | 120.0 |
| Cu1—O1W—H2W1 | 121.8 | C9—C10—C11 | 119.74 (15) |
| H1W1—O1W—H2W1 | 103.0 | C9—C10—H10A | 120.1 |
| C13—O1—Cu1 | 114.26 (9) | C11—C10—H10A | 120.1 |
| C15—O3—H1O3 | 108.0 | N2—C11—C10 | 122.16 (14) |
| C2—N1—C1 | 118.50 (13) | N2—C11—H11A | 118.9 |
| C2—N1—Cu1 | 128.75 (11) | C10—C11—H11A | 118.9 |
| C1—N1—Cu1 | 112.69 (9) | N2—C12—C8 | 123.41 (14) |
| C11—N2—C12 | 118.07 (12) | N2—C12—C1 | 116.42 (12) |
| C11—N2—Cu1 | 129.83 (10) | C8—C12—C1 | 120.17 (13) |
| C12—N2—Cu1 | 112.02 (9) | O2—C13—O1 | 123.99 (13) |
| C14—N3—Cu1 | 106.69 (8) | O2—C13—C14 | 119.04 (13) |
| C14—N3—H1N3 | 113.4 | O1—C13—C14 | 116.91 (11) |
| Cu1—N3—H1N3 | 114.4 | N3—C14—C15 | 114.04 (12) |
| C14—N3—H2N3 | 105.0 | N3—C14—C13 | 109.43 (11) |
| Cu1—N3—H2N3 | 108.9 | C15—C14—C13 | 112.30 (12) |
| H1N3—N3—H2N3 | 108.0 | N3—C14—H14A | 106.9 |
| N1—C1—C5 | 123.26 (14) | C15—C14—H14A | 106.9 |
| N1—C1—C12 | 116.62 (12) | C13—C14—H14A | 106.9 |
| C5—C1—C12 | 120.10 (14) | O3—C15—C16 | 107.21 (14) |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.86 (16) | O3—C15—C14 | 110.23 (13) |
| N1—C2—H2A | 119.1 | C16—C15—C14 | 112.68 (14) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.1 | O3—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.03 (16) | C16—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.0 | C14—C15—H15A | 108.9 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.0 | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.66 (15) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.2 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.2 | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C5—C4 | 116.68 (15) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C1—C5—C6 | 118.46 (15) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 124.85 (15) | H1W2—O2W—H2W2 | 101.9 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.24 (15) | H1W3—O3W—H2W3 | 98.8 |
| N3—Cu1—O1—C13 | 16.30 (10) | C1—C5—C6—C7 | −1.0 (2) |
| N1—Cu1—O1—C13 | −169.56 (10) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 178.03 (17) |
| N2—Cu1—O1—C13 | 127.31 (19) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.1 (3) |
| O1W—Cu1—O1—C13 | −73.23 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C12 | 0.9 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—N1—C2 | 13.31 (14) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −177.91 (16) |
| N2—Cu1—N1—C2 | −177.92 (14) | C12—C8—C9—C10 | 1.0 (2) |
| O1W—Cu1—N1—C2 | −81.72 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.83 (16) |
| O1—Cu1—N1—C1 | −169.68 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.2 (3) |
| N2—Cu1—N1—C1 | −0.91 (10) | C12—N2—C11—C10 | 0.7 (2) |
| O1W—Cu1—N1—C1 | 95.29 (10) | Cu1—N2—C11—C10 | −175.89 (12) |
| O1—Cu1—N2—C11 | −117.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11—N2 | −1.1 (3) |
| N3—Cu1—N2—C11 | −8.41 (14) | C11—N2—C12—C8 | 0.6 (2) |
| N1—Cu1—N2—C11 | 178.06 (14) | Cu1—N2—C12—C8 | 177.78 (11) |
| O1W—Cu1—N2—C11 | 82.79 (13) | C11—N2—C12—C1 | −178.71 (13) |
| O1—Cu1—N2—C12 | 65.5 (2) | Cu1—N2—C12—C1 | −1.56 (15) |
| N3—Cu1—N2—C12 | 174.87 (9) | C9—C8—C12—N2 | −1.4 (2) |
| N1—Cu1—N2—C12 | 1.34 (9) | C7—C8—C12—N2 | 179.62 (14) |
| O1W—Cu1—N2—C12 | −93.92 (10) | C9—C8—C12—C1 | 177.88 (14) |
| O1—Cu1—N3—C14 | −25.06 (9) | C7—C8—C12—C1 | −1.1 (2) |
| N2—Cu1—N3—C14 | 166.76 (9) | N1—C1—C12—N2 | 0.85 (19) |
| O1W—Cu1—N3—C14 | 69.72 (9) | C5—C1—C12—N2 | 179.55 (13) |
| C2—N1—C1—C5 | −1.0 (2) | N1—C1—C12—C8 | −178.52 (13) |
| Cu1—N1—C1—C5 | −178.33 (11) | C5—C1—C12—C8 | 0.2 (2) |
| C2—N1—C1—C12 | 177.68 (13) | Cu1—O1—C13—O2 | 174.42 (13) |
| Cu1—N1—C1—C12 | 0.33 (16) | Cu1—O1—C13—C14 | −2.72 (16) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (2) | Cu1—N3—C14—C15 | 155.66 (11) |
| Cu1—N1—C2—C3 | 177.57 (12) | Cu1—N3—C14—C13 | 28.94 (13) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (3) | O2—C13—C14—N3 | 164.17 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (3) | O1—C13—C14—N3 | −18.54 (18) |
| N1—C1—C5—C4 | 0.4 (2) | O2—C13—C14—C15 | 36.5 (2) |
| C12—C1—C5—C4 | −178.26 (14) | O1—C13—C14—C15 | −146.24 (14) |
| N1—C1—C5—C6 | 179.43 (14) | N3—C14—C15—O3 | −55.86 (17) |
| C12—C1—C5—C6 | 0.8 (2) | C13—C14—C15—O3 | 69.36 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C1 | 0.6 (2) | N3—C14—C15—C16 | 63.86 (19) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −178.46 (16) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −170.93 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1W1···Cl1 | 0.80 | 2.36 | 3.1411 (13) | 166 |
| O1W—H2W1···O2i | 0.82 | 1.90 | 2.7114 (18) | 167 |
| O3—H1O3···O1ii | 0.90 | 2.03 | 2.9089 (18) | 164 |
| N3—H1N3···Cl1iii | 0.86 | 2.62 | 3.3992 (13) | 151 |
| N3—H2N3···O2Wi | 0.94 | 2.07 | 3.0085 (19) | 175 |
| O2W—H1W2···Cl1i | 0.87 | 2.35 | 3.2104 (16) | 175 |
| O2W—H2W2···Cl1iv | 0.84 | 2.33 | 3.1463 (14) | 162 |
| O3W—H1W3···O2W | 1.01 | 1.95 | 2.954 (2) | 170 |
| O3W—H2W3···O3ii | 0.91 | 2.03 | 2.901 (2) | 159 |
| C7—H7A···O2v | 0.93 | 2.41 | 3.292 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) x, y−1, z+1; (v) x, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5025).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Kumar, R. S. & Arunachalam, S. (2007). Polyhedron, 26, 3255–3262.
- Lu, L.-P., Zhu, M.-L. & Yang, P. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, m21–m23. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Patel, R. N., Singh, N., Shukla, K. K., Gundla, V. L. N. & Chauhan, U. K. (2006). Spectrochimica Acta Part A, 63, 21–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rao, R., Patra, A. K. & Chetana, P. R. (2007). Polyhedron, 26, 5331–5338.
- Rao, R., Patra, A. K. & Chetana, P. R. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 1343–1352.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, V. G. & Nair, B. U. (2003). J. Inorg. Biochem.93, 271–276. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. L., Chao, H., Peng, B. & Ji, L. N. (2007). Transition Met. Chem 32, 125–130.
- Zhang, S. C., Zhu, Y. G., Tu, C., Wei, H. Y., Yang, Z., Lin, L. P., Ding, J., Zhang, J. F. & Guo, Z. J. (2004). J. Inorg. Biochem.98, 2099–210. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810015278/lh5025sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810015278/lh5025Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report