Abstract
In the title compound, [Cd2(C6H8O4)2(C16H20N4)(H2O)4]n, pentagonal-bipyramidally coordinated CdII ions are connected into {Cd2(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2(H2O)4} centrosymmetric dimeric clusters. In turn, these clusters are linked by tethering 1,4-bis(3-pyridylmethyl)piperazine (3-bpmp) ligands into [Cd2(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2(3-bpmp)(H2O)4]n coordination polymer chains. The chain motifs are oriented parallel to [1 0]. Individual chains are connected into supramolecular layers via O—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding mechanisms.
0]. Individual chains are connected into supramolecular layers via O—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen-bonding mechanisms.
Related literature
For other dicarboxylate coordination polymers containing 3-bpmp ligands, see: Johnston et al. (2008 ▶). For the preparation of 3-bpmp, see: Niu et al. (2001 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cd2(C6H8O4)2(C16H20N4)(H2O)4]
M r = 426.74
Triclinic,

a = 9.275 (3) Å
b = 10.378 (3) Å
c = 10.625 (5) Å
α = 114.461 (3)°
β = 101.274 (3)°
γ = 106.687 (2)°
V = 831.6 (5) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.34 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.26 × 0.18 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.723, T max = 0.840
12027 measured reflections
3047 independent reflections
2909 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.058
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.035
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.16
3047 reflections
222 parameters
6 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.65 e Å−3
Δρmin = −1.07 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: CrystalMaker (Palmer, 2007 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018799/lh5049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018799/lh5049Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5C⋯O4 | 0.84 (4) | 1.93 (2) | 2.705 (3) | 154 (4) |
| O5—H5D⋯O1i | 0.83 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.744 (3) | 152 (3) |
| O6—H6C⋯O3ii | 0.85 (2) | 1.84 (2) | 2.679 (3) | 171 (4) |
| O6—H6D⋯N2iii | 0.83 (2) | 2.03 (2) | 2.851 (4) | 173 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the donors of the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund for funding this work. We also thank Anthony H. LaDuca for experimental assistance.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently we have been investigating bis(3-pyridylmethyl)piperazine (3-bpmp) as a neutral dipodal tethering ligand for the construction of divalent metal coordination polymers in tandem with aromatic dicarboxylate ligands (Johnston et al., 2008). This chemistry has been extended into an aliphatic dicarboxylate system with the synthesis of the title compound.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains a CdII ion, one 2,2-dimethylsuccinate ligand, two aqua ligands, and one-half of a 3-bpmp ligand whose central piperazinyl ring is situated over a crystallographic inversion centre. The CdII ion is pentagonal bipyramidally coordinated in a {CdO6N} environment, with its apical positions occupied by aqua ligands. Its basal plane consists of two chelating carboxylate groups from two 2,2-dimethylsuccinate ligands and one pyridyl N donor atom from a 3-bpmp ligand. A pair of CdII ions is aggregated into a centrosymmetric {Cd2(H2O)4(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2} dinuclear cluster (Fig. 1) by two bis(chelating) 2,2-dimethylsuccinate ligands, which adopt a gauche conformation.
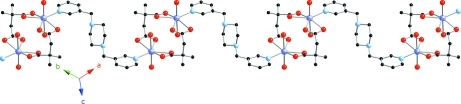
{Cd2(H2O)4(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2} dinuclear clusters are connected by tethering 3-bpmp ligands into one-dimensional [Cd2(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2(H2O)4(3-bpmp)]n coordination polymer chains, which are oriented parallel to the (1 1 0) crystal direction (Fig. 2). The through-ligand Cd···Cd contact distance is 13.381 (6) Å. Individual chains are connected into supramolecular pseudo layers (Fig. 3) via O—H···N and O—H···O interactions (Table 1). Within the pseudo layers, aqua ligands (O6) donate hydrogen bonds to piperazinyl N atoms of 3-bpmp ligands and ligated 2,2-dimethylsuccinate carboxylate O atoms in neighboring chains. Neighboring pseudo layers stack into the three-dimensional crystal structure (Fig. 4) of the title compound by crystal packing forces.
Experimental
All starting materials were obtained commercially, except for 3-bpmp, which was prepared by a published procedure (Niu et al., 2001). A mixture of cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate (114 mg, 0.37 mmol), 2,2-dimethylsuccinic acid (54 mg, 0.37 mmol), 3-bpmp (199 mg, 0.742 mmol) and 10.0 g water (550 mmol) was placed into a 23 ml Teflon-lined Parr acid digestion bomb, which was then heated under autogenous pressure at 393 K for 72 h. Colourless blocks of the title compound (57 mg, 26% yield) were isolated after washing with distilled water and acetone, and drying in air.
Refinement
All H atoms bound to C atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.95 Å, and refined in riding mode with Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C). The H atoms bound to the aqua ligand O atom were found in a difference Fourier map, restrained with with O—H = 0.85 Å and refined with Uiso = 1.2Ueq(O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The coordination environment and dinuclear cluster of the title compound, showing 50% probability ellipsoids and partial atom numbering scheme. Hydrogen atom positions are shown as grey sticks. Color codes: violet Cd, red O, light blue N, black C. Symmetry code: (i) -x, -y + 1, -z + 1.
Fig. 2.
A single [Cd2(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2(H2O)4 (3-bpmp)]n coordination polymer chain
Fig. 3.
Supramolecular layer of [Cd2(2,2-dimethylsuccinate)2(H2O)4 (3-bpmp)]n chains. Although the H atoms have been omitted the O—H···N and O—H···O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines between the donor and acceptor atoms.
Fig. 4.
Stacking of supramolecular layers in the title compound.
Crystal data
| [Cd2(C6H8O4)2(C16H20N4)(H2O)4] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 426.74 | F(000) = 432 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.704 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.275 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 12027 reflections |
| b = 10.378 (3) Å | θ = 2.3–25.4° |
| c = 10.625 (5) Å | µ = 1.34 mm−1 |
| α = 114.461 (3)° | T = 173 K |
| β = 101.274 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 106.687 (2)° | 0.26 × 0.18 × 0.13 mm |
| V = 831.6 (5) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 3047 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2909 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.058 |
| ω–φ scans | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.723, Tmax = 0.840 | k = −12→12 |
| 12027 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.16 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0539P)2 + 0.0373P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3047 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 222 parameters | Δρmax = 0.65 e Å−3 |
| 6 restraints | Δρmin = −1.06 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The largest peak of 0.645 e- Å3 was located 0.90 Å from Cd1. The largest hole of -1.065 e- Å3 was located 0.94 Å from Cd1. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cd1 | 0.18482 (2) | 0.45331 (2) | 0.36199 (2) | 0.03562 (13) | |
| O1 | 0.0456 (2) | 0.6107 (3) | 0.3511 (2) | 0.0425 (5) | |
| O2 | −0.0444 (3) | 0.3806 (3) | 0.1510 (3) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| O3 | −0.3418 (3) | 0.5696 (3) | 0.4297 (3) | 0.0452 (5) | |
| O4 | −0.2497 (3) | 0.3895 (3) | 0.3798 (3) | 0.0423 (5) | |
| O5 | −0.0262 (3) | 0.2695 (3) | 0.3722 (3) | 0.0413 (5) | |
| H5C | −0.098 (4) | 0.297 (5) | 0.346 (4) | 0.050* | |
| H5D | −0.007 (4) | 0.295 (4) | 0.461 (2) | 0.050* | |
| O6 | 0.4016 (3) | 0.6335 (3) | 0.3687 (3) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| H6C | 0.483 (3) | 0.611 (4) | 0.379 (4) | 0.047* | |
| H6D | 0.430 (4) | 0.720 (3) | 0.441 (3) | 0.047* | |
| N1 | 0.2421 (3) | 0.2552 (3) | 0.2065 (3) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.5008 (3) | 0.0578 (3) | 0.3970 (3) | 0.0367 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.1678 (4) | 0.1796 (4) | 0.0587 (4) | 0.0418 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.0989 | 0.2150 | 0.0165 | 0.050* | |
| C2 | 0.1890 (4) | 0.0519 (4) | −0.0333 (4) | 0.0460 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.1354 | 0.0005 | −0.1376 | 0.055* | |
| C3 | 0.2875 (4) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0262 (4) | 0.0435 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.2997 | −0.0904 | −0.0364 | 0.052* | |
| C4 | 0.3700 (4) | 0.0788 (4) | 0.1793 (4) | 0.0375 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.3413 (4) | 0.2057 (4) | 0.2633 (4) | 0.0392 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.3956 | 0.2609 | 0.3677 | 0.047* | |
| C6 | 0.4891 (4) | 0.0317 (4) | 0.2474 (4) | 0.0405 (7) | |
| H6A | 0.4588 | −0.0801 | 0.1810 | 0.049* | |
| H6B | 0.5971 | 0.0900 | 0.2520 | 0.049* | |
| C7 | 0.3498 (4) | −0.0430 (4) | 0.3945 (4) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| H7A | 0.3231 | −0.1530 | 0.3243 | 0.048* | |
| H7B | 0.2605 | −0.0176 | 0.3595 | 0.048* | |
| C8 | 0.6337 (4) | 0.0216 (4) | 0.4535 (4) | 0.0400 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.7361 | 0.0906 | 0.4580 | 0.048* | |
| H8B | 0.6126 | −0.0871 | 0.3846 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | −0.0570 (4) | 0.5055 (4) | 0.2235 (3) | 0.0373 (7) | |
| C10 | −0.2056 (4) | 0.5280 (4) | 0.1593 (4) | 0.0390 (7) | |
| C11 | −0.3507 (4) | 0.4289 (4) | 0.1793 (3) | 0.0400 (7) | |
| H11A | −0.4454 | 0.4496 | 0.1483 | 0.048* | |
| H11B | −0.3787 | 0.3173 | 0.1142 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | −0.3141 (3) | 0.4641 (4) | 0.3390 (3) | 0.0377 (7) | |
| C13 | −0.2436 (4) | 0.4650 (4) | −0.0073 (4) | 0.0471 (8) | |
| H13A | −0.3426 | 0.4721 | −0.0503 | 0.071* | |
| H13B | −0.2585 | 0.3561 | −0.0552 | 0.071* | |
| H13C | −0.1540 | 0.5264 | −0.0228 | 0.071* | |
| C14 | −0.1754 (4) | 0.6995 (4) | 0.2367 (4) | 0.0478 (8) | |
| H14A | −0.0781 | 0.7601 | 0.2292 | 0.072* | |
| H14B | −0.1607 | 0.7363 | 0.3414 | 0.072* | |
| H14C | −0.2681 | 0.7121 | 0.1892 | 0.072* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cd1 | 0.03706 (18) | 0.03714 (18) | 0.03548 (19) | 0.01797 (13) | 0.01430 (13) | 0.01828 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0399 (12) | 0.0476 (12) | 0.0378 (12) | 0.0189 (10) | 0.0107 (10) | 0.0205 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0480 (13) | 0.0440 (12) | 0.0446 (12) | 0.0250 (10) | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0223 (11) |
| O3 | 0.0475 (13) | 0.0516 (14) | 0.0391 (12) | 0.0263 (11) | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0197 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0431 (12) | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0227 (10) | 0.0174 (10) | 0.0239 (11) |
| O5 | 0.0441 (13) | 0.0429 (13) | 0.0388 (13) | 0.0205 (11) | 0.0149 (11) | 0.0205 (11) |
| O6 | 0.0414 (12) | 0.0383 (12) | 0.0373 (13) | 0.0188 (10) | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0177 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0372 (13) | 0.0380 (13) | 0.0382 (14) | 0.0173 (11) | 0.0150 (11) | 0.0194 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0397 (13) | 0.0369 (13) | 0.0395 (14) | 0.0181 (11) | 0.0170 (11) | 0.0215 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0429 (17) | 0.0438 (17) | 0.0412 (17) | 0.0193 (14) | 0.0141 (14) | 0.0230 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0541 (19) | 0.0447 (18) | 0.0343 (17) | 0.0216 (15) | 0.0125 (15) | 0.0161 (15) |
| C3 | 0.0505 (18) | 0.0384 (16) | 0.0423 (18) | 0.0214 (14) | 0.0194 (15) | 0.0175 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0427 (16) | 0.0366 (15) | 0.0379 (16) | 0.0167 (13) | 0.0190 (14) | 0.0204 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0393 (16) | 0.0405 (16) | 0.0379 (16) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0135 (13) | 0.0193 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0492 (18) | 0.0394 (16) | 0.0417 (17) | 0.0224 (14) | 0.0221 (14) | 0.0226 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0386 (15) | 0.0405 (16) | 0.0454 (17) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0165 (13) | 0.0234 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0404 (16) | 0.0403 (16) | 0.0456 (17) | 0.0197 (13) | 0.0181 (13) | 0.0236 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0398 (16) | 0.0461 (17) | 0.0380 (16) | 0.0211 (14) | 0.0201 (14) | 0.0264 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0426 (17) | 0.0429 (17) | 0.0370 (17) | 0.0206 (14) | 0.0142 (14) | 0.0227 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0368 (16) | 0.0447 (17) | 0.0396 (17) | 0.0207 (14) | 0.0114 (13) | 0.0205 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0316 (16) | 0.0445 (18) | 0.0385 (16) | 0.0153 (14) | 0.0144 (13) | 0.0217 (15) |
| C13 | 0.053 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0372 (17) | 0.0269 (17) | 0.0162 (15) | 0.0268 (16) |
| C14 | 0.058 (2) | 0.0441 (18) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0275 (16) | 0.0221 (17) | 0.0280 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cd1—O6 | 2.284 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| Cd1—N1 | 2.323 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.386 (4) |
| Cd1—O5 | 2.364 (2) | C4—C6 | 1.507 (5) |
| Cd1—O4i | 2.374 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| Cd1—O1 | 2.378 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| Cd1—O2 | 2.435 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| Cd1—O3i | 2.540 (2) | C7—C8ii | 1.506 (4) |
| O1—C9 | 1.268 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C9 | 1.258 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| O3—C12 | 1.256 (4) | C8—C7ii | 1.506 (4) |
| O4—C12 | 1.259 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| O5—H5C | 0.84 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| O5—H5D | 0.830 (18) | C9—C10 | 1.539 (4) |
| O6—H6C | 0.851 (18) | C10—C14 | 1.528 (4) |
| O6—H6D | 0.825 (18) | C10—C13 | 1.532 (4) |
| N1—C5 | 1.336 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.553 (5) |
| N1—C1 | 1.342 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.523 (4) |
| N2—C6 | 1.474 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C7 | 1.475 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| N2—C8 | 1.478 (4) | C13—H13A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (5) | C13—H13B | 0.9800 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C13—H13C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.369 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (5) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 | C5—C4—C6 | 122.3 (3) |
| O6—Cd1—N1 | 90.10 (9) | C3—C4—C6 | 121.2 (3) |
| O6—Cd1—O5 | 175.51 (7) | N1—C5—C4 | 124.1 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—O5 | 90.19 (9) | N1—C5—H5 | 118.0 |
| O6—Cd1—O4i | 90.71 (8) | C4—C5—H5 | 118.0 |
| N1—Cd1—O4i | 138.03 (8) | N2—C6—C4 | 115.3 (3) |
| O5—Cd1—O4i | 86.08 (8) | N2—C6—H6A | 108.5 |
| O6—Cd1—O1 | 86.80 (8) | C4—C6—H6A | 108.5 |
| N1—Cd1—O1 | 140.28 (8) | N2—C6—H6B | 108.5 |
| O5—Cd1—O1 | 95.83 (8) | C4—C6—H6B | 108.5 |
| O4i—Cd1—O1 | 81.63 (8) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.5 |
| O6—Cd1—O2 | 106.73 (8) | N2—C7—C8ii | 110.9 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—O2 | 88.92 (8) | N2—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| O5—Cd1—O2 | 77.76 (8) | C8ii—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| O4i—Cd1—O2 | 130.56 (8) | N2—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| O1—Cd1—O2 | 54.59 (7) | C8ii—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| O6—Cd1—O3i | 95.93 (8) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.1 |
| N1—Cd1—O3i | 85.50 (8) | N2—C8—C7ii | 111.1 (2) |
| O5—Cd1—O3i | 79.62 (8) | N2—C8—H8A | 109.4 |
| O4i—Cd1—O3i | 52.70 (8) | C7ii—C8—H8A | 109.4 |
| O1—Cd1—O3i | 134.21 (7) | N2—C8—H8B | 109.4 |
| O2—Cd1—O3i | 156.67 (9) | C7ii—C8—H8B | 109.4 |
| O6—Cd1—C9 | 98.97 (9) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.0 |
| N1—Cd1—C9 | 115.36 (9) | O2—C9—O1 | 121.9 (3) |
| O5—Cd1—C9 | 84.95 (9) | O2—C9—C10 | 119.1 (3) |
| O4i—Cd1—C9 | 105.92 (9) | O1—C9—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—C9 | 27.43 (8) | O2—C9—Cd1 | 62.34 (16) |
| O2—Cd1—C9 | 27.24 (8) | O1—C9—Cd1 | 59.80 (16) |
| O3i—Cd1—C9 | 154.14 (8) | C10—C9—Cd1 | 171.7 (2) |
| C9—O1—Cd1 | 92.76 (18) | C14—C10—C13 | 110.1 (3) |
| C9—O2—Cd1 | 90.42 (18) | C14—C10—C9 | 110.8 (3) |
| C12—O3—Cd1i | 89.11 (19) | C13—C10—C9 | 109.0 (3) |
| C12—O4—Cd1i | 96.79 (19) | C14—C10—C11 | 111.3 (3) |
| Cd1—O5—H5C | 96 (3) | C13—C10—C11 | 107.9 (3) |
| Cd1—O5—H5D | 107 (3) | C9—C10—C11 | 107.5 (3) |
| H5C—O5—H5D | 108 (3) | C12—C11—C10 | 112.2 (3) |
| Cd1—O6—H6C | 111 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| Cd1—O6—H6D | 110 (3) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| H6C—O6—H6D | 106 (3) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 118.2 (3) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C5—N1—Cd1 | 120.3 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C1—N1—Cd1 | 121.3 (2) | O3—C12—O4 | 120.7 (3) |
| C6—N2—C7 | 111.3 (3) | O3—C12—C11 | 120.6 (3) |
| C6—N2—C8 | 108.4 (2) | O4—C12—C11 | 118.6 (3) |
| C7—N2—C8 | 108.8 (2) | C10—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.6 (3) | C10—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 119.2 | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.2 | C10—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.8 (3) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.1 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C10—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.8 (3) | C10—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 | C10—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 116.5 (3) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O6—Cd1—O1—C9 | 116.54 (18) | C5—C4—C6—N2 | 34.4 (4) |
| N1—Cd1—O1—C9 | 30.2 (2) | C3—C4—C6—N2 | −148.3 (3) |
| O5—Cd1—O1—C9 | −67.12 (18) | C6—N2—C7—C8ii | 176.9 (2) |
| O4i—Cd1—O1—C9 | −152.27 (18) | C8—N2—C7—C8ii | 57.5 (3) |
| O2—Cd1—O1—C9 | 3.36 (16) | C6—N2—C8—C7ii | −178.9 (2) |
| O3i—Cd1—O1—C9 | −148.30 (17) | C7—N2—C8—C7ii | −57.7 (4) |
| O6—Cd1—O2—C9 | −76.80 (18) | Cd1—O2—C9—O1 | 6.1 (3) |
| N1—Cd1—O2—C9 | −166.58 (17) | Cd1—O2—C9—C10 | −170.7 (2) |
| O5—Cd1—O2—C9 | 102.99 (18) | Cd1—O1—C9—O2 | −6.2 (3) |
| O4i—Cd1—O2—C9 | 29.1 (2) | Cd1—O1—C9—C10 | 170.6 (2) |
| O1—Cd1—O2—C9 | −3.38 (16) | O6—Cd1—C9—O2 | 109.28 (17) |
| O3i—Cd1—O2—C9 | 117.4 (2) | N1—Cd1—C9—O2 | 14.88 (19) |
| O6—Cd1—N1—C5 | 89.2 (2) | O5—Cd1—C9—O2 | −72.93 (17) |
| O5—Cd1—N1—C5 | −86.3 (2) | O4i—Cd1—C9—O2 | −157.39 (16) |
| O4i—Cd1—N1—C5 | −1.9 (3) | O1—Cd1—C9—O2 | 174.0 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—N1—C5 | 174.34 (19) | O3i—Cd1—C9—O2 | −126.3 (2) |
| O2—Cd1—N1—C5 | −164.0 (2) | O6—Cd1—C9—O1 | −64.73 (18) |
| O3i—Cd1—N1—C5 | −6.7 (2) | N1—Cd1—C9—O1 | −159.13 (16) |
| C9—Cd1—N1—C5 | −170.8 (2) | O5—Cd1—C9—O1 | 113.06 (18) |
| O6—Cd1—N1—C1 | −96.0 (2) | O4i—Cd1—C9—O1 | 28.61 (18) |
| O5—Cd1—N1—C1 | 88.5 (2) | O2—Cd1—C9—O1 | −174.0 (3) |
| O4i—Cd1—N1—C1 | 172.8 (2) | O3i—Cd1—C9—O1 | 59.7 (3) |
| O1—Cd1—N1—C1 | −10.9 (3) | O2—C9—C10—C14 | −162.7 (3) |
| O2—Cd1—N1—C1 | 10.7 (2) | O1—C9—C10—C14 | 20.4 (4) |
| O3i—Cd1—N1—C1 | 168.1 (2) | O2—C9—C10—C13 | −41.4 (4) |
| C9—Cd1—N1—C1 | 4.0 (3) | O1—C9—C10—C13 | 141.7 (3) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 1.5 (5) | O2—C9—C10—C11 | 75.4 (3) |
| Cd1—N1—C1—C2 | −173.4 (2) | O1—C9—C10—C11 | −101.5 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (5) | C14—C10—C11—C12 | −68.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.1 (5) | C13—C10—C11—C12 | 170.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 2.1 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 53.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C6 | −175.2 (3) | Cd1i—O3—C12—O4 | 8.2 (3) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −1.4 (5) | Cd1i—O3—C12—C11 | −169.0 (2) |
| Cd1—N1—C5—C4 | 173.5 (2) | Cd1i—O4—C12—O3 | −8.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −0.4 (5) | Cd1i—O4—C12—C11 | 168.4 (2) |
| C6—C4—C5—N1 | 176.9 (3) | C10—C11—C12—O3 | 89.1 (3) |
| C7—N2—C6—C4 | 66.3 (3) | C10—C11—C12—O4 | −88.2 (3) |
| C8—N2—C6—C4 | −174.1 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5C···O4 | 0.84 (4) | 1.93 (2) | 2.705 (3) | 154 (4) |
| O5—H5D···O1i | 0.83 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.744 (3) | 152 (3) |
| O6—H6C···O3iii | 0.85 (2) | 1.84 (2) | 2.679 (3) | 171 (4) |
| O6—H6D···N2iv | 0.83 (2) | 2.03 (2) | 2.851 (4) | 173 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x+1, y, z; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH5049).
References
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Johnston, L. L., Martin, D. P., Supkowski, R. M. & LaDuca, R. L. (2008). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 361, 2887–2894.
- Niu, Y., Hou, H., Wei, Y., Fan, Y., Zhu, Y., Du, C. & Xin, X. (2001). Inorg. Chem. Commun.4, 358–361.
- Palmer, D. (2007). CrystalMaker CrystalMaker Software, Bicester, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS, University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018799/lh5049sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018799/lh5049Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report