Abstract
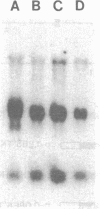
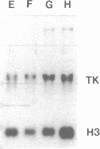
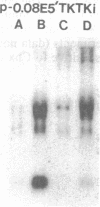
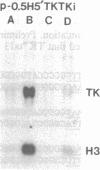
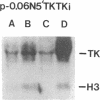
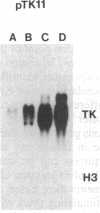
The levels of thymidine kinase (TK; EC 2.7.1.21) mRNA were determined in nine established cell lines derived from TK-ts13, a temperature-sensitive mutant cell line that arrests in late G1 phase of the cell cycle at the restrictive temperature. The derivative cell lines carried either a cDNA or a minigene of human TK under the control of TK promoters of different lengths. A tenth cell line carried a human TK cDNA under the control of a simian virus 40 promoter. Two different assays were used to determine the S-phase-specific regulation of human TK mRNA levels in quiescent cells stimulated to proliferate. Results from these two assays indicated that (i) the first two introns of the human TK gene had no effect on the S-phase-specific regulation of TK mRNA levels, although the presence of introns increased the amount of TK mRNA; (ii) similar amounts of TK mRNA were present in cells containing constructs with an 83-base-pair (bp) promoter as with other TK promoters comprising up to approximately 4000 bp of 5' flanking sequence; (iii) a 456-bp promoter was fully S-phase-regulated, whereas the 83-bp promoter was only partially regulated; (iv) a 63-bp promoter was much less regulated than an 83-bp promoter; and (v) the crucial element in the 20-bp fragment comprising bp -83 to -64 has been localized, by site-directed mutagenesis, to the CCAAT element at -70.
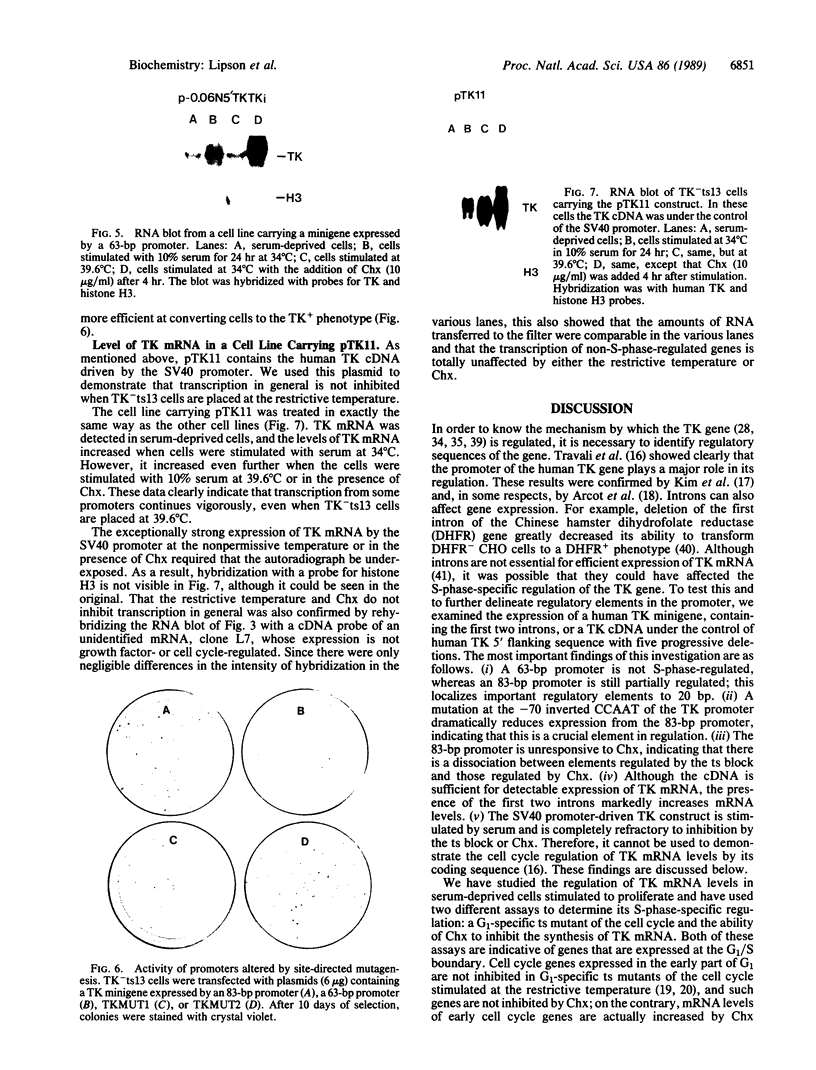
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcot S. S., Flemington E. K., Deininger P. L. The human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Deletion analysis and specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Deininger P. L. Human thymidine kinase gene: molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA expressible in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2316–2320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent T. P., Butler J. A., Crathorn A. R. Variations in phosphokinase activities during the cell cycle in synchronous populations of HeLa cells. Nature. 1965 Jul 10;207(993):176–177. doi: 10.1038/207176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Reffel A. C., Stiles C. D. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Control of thymidine kinase mRNA during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Bradshaw H. D., Jr, Traina-Dorge V., Slagel V., Deininger P. L. Sequence, structure and promoter characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Ashihara T., Baserga R. Characterization of ts13 cells a temperature-sensitive mutant of the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 May;2(3):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Chang H., Baserga R. Stimulated DNA synthesis in frog nuclei by cytoplasmic extracts of temperature-sensitive mammalian cells. Science. 1978 Aug 18;201(4356):651–652. doi: 10.1126/science.675253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. K., Kainz M. S., Merrill G. F. Introns are inconsequential to efficient formation of cellular thymidine kinase mRNA in mouse L cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4576–4581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. K., Merrill G. F. Regulation of thymidine kinase protein levels during myogenic withdrawal from the cell cycle is independent of mRNA regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11625–11643. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. R., Aller P., Yuan Z. A., Gibson C. W., Baserga R. Cell-cycle-specific cDNAs from mammalian cells temperature sensitive for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6004–6008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. R., Marashi F., Baserga R., Stein J., Stein G. Expression of histone genes in a G1-specific temperature-sensitive mutant of the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3731–3735. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Müllner E., Seiser C., Wintersberger E. Cell cycle regulated synthesis of stable mouse thymidine kinase mRNA is mediated by a sequence within the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):741–752. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide T., Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Ferrari S., Philiponis V., Baserga R. Expression of growth-regulated genes in tsJT60 cells, a temperature-sensitive mutant of the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7041–7046. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Wells S., Lau Y. F., Lee A. S. Sequences contained within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene can direct cell-cycle regulation of heterologous fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Kelly T. J. Genetic analysis of the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Matkovich D. A. Genetic determinants of growth phase-dependent and adenovirus 5-responsive expression of the Chinese hamster thymidine kinase gene are contained within thymidine kinase mRNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2262–2266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. F., Zhao S. Y., Ruddle F. H. Genomic cloning and preliminary characterization of the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6528–6532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield J. W. The periodic synthesis of thymidine kinase in mouse fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Gibson C. W., Hirschhorn R. R., Rittling S., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Expression of thymidine kinase and dihydrofolate reductase genes in mammalian ts mutants of the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3269–3274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino R., Hayashi K., Sugimura T. C-myc transcript is induced in rat liver at a very early stage of regeneration or by cycloheximide treatment. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):697–698. doi: 10.1038/310697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Hauschka S. D., McKnight S. L. tk Enzyme expression in differentiating muscle cells is regulated through an internal segment of the cellular tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittling S. R., Gibson C. W., Ferrari S., Baserga R. The effect of cycloheximide on the expression of cell cycle dependent genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):327–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y. M., Hirschhorn R. R., Mercer W. E., Surmacz E., Tsutsui Y., Soprano K. J., Baserga R. Gene transfer: DNA microinjection compared with DNA transfection with a very high efficiency. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1145–1154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L., Kelly T. J. Regulation of human thymidine kinase during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8350–8358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart P., Ito M., Stewart C., Conrad S. E. Induction of cellular thymidine kinase occurs at the mRNA level. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1490–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Mueller G. C. Thymidine kinase activity in synchronized HeLa cell cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):535–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Basilico C. Temperature sensitive mutants of BHK cells affected in cell cycle progression. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Sep;92(3):425–436. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Lipson K. E., Jaskulski D., Lauret E., Baserga R. Role of the promoter in the regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venolia L., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Polyadenylation of Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase genomic genes and minigenes after gene transfer. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):491–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01534491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl A. F., Geis A. M., Spain B. H., Wong S. W., Korn D., Wang T. S. Gene expression of human DNA polymerase alpha during cell proliferation and the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5016–5025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]