Abstract
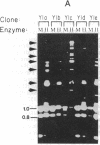
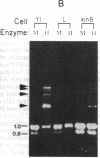
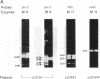
DNA fragments encoding the mouse steroid 21-hydroxylase (C21 or Cyp21A1) gene are de novo methylated when introduced into the mouse adrenocortical tumor cell line Y1 by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Although CCGG sequences within the C21 gene are de novo methylated, CCGG sites within flanking vector sequences, other mammalian gene sequences driven by the C21 promoter, and the neomycin-resistance gene, which was cotransfected with the C21 gene, do not become methylated. At least two separate signals for de novo methylation are encoded within the gene since three fragments derived from the C21 gene were methylated de novo. Specific de novo methylation of C21-derived sequences does not occur in L cells or Y1 kin8 cells; this suggests that the cellular factors needed for de novo methylation of the C21 gene are not ubiquitous. Most DNA sequences are not de novo methylated when introduced into somatic cells and DNA sequences other than the C21 gene are not de novo methylated when introduced into Y1 cells. Several groups have suggested that de novo methylation occurs in early embryonic cells and that somatic cells strictly maintain their methylation pattern by a semiconservative methyltransferase. Our results suggest that de novo methylation of specific nucleotide sequences can occur in some mammalian somatic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnett T. S., Gallimore P. H. Introduction of cloned human papillomavirus 1a DNA into rat fibroblasts: integration, de novo methylation and absence of cellular morphological transformation. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1063–1072. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone A. M., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Remethylation at sites 5' of the murine Lyt-2 gene in association with shutdown of Lyt-2 expression. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Galbraith L. J., Seidman J. G., White P. C., Parker K. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis of murine 21-hydroxylase genes: mutations affecting gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9601–9605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbre P. D., King R. J. Progression to steroid insensitivity can occur irrespective of the presence of functional steroid receptors. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Ryden T., Bourgeois S. Role of de novo DNA methylation in the glucocorticoid resistance of a T-lymphoid cell line. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):621–623. doi: 10.1038/302621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebara M. M., Drevon C., Harcourt S. A., Steingrimsdottir H., James M. R., Burke J. F., Arlett C. F., Lehmann A. R. Inactivation of a transfected gene in human fibroblasts can occur by deletion, amplification, phenotypic switching, or methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1459–1464. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Marx M. Stable propagation of the active transcriptional state of an immunoglobulin mu gene requires continuous enhancer function. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):645–654. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler J. D., Schimmer B. P., Flynn T. R., Szyf M., Seidman J. G., Parker K. L. An enhancer element and a functional cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase are required for expression of adrenocortical 21-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13068–13073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M. E., Okamura T., Dee A., Adler B., John M. C., White P. C., Simpson E. R., Waterman M. R. Bovine steroid 21-hydroxylase: regulation of biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2846–2853. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare M. J., Neville A. M. Steroid metabolism by adult rat adrenocortical cells in monolayer culture. J Endocrinol. 1973 Sep;58(3):447–462. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0580447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Chaplin D. D., Wong M., Seidman J. G., Schimmer B. P. Molecular analysis of 21-hydroxylase gene expression in mouse adrenal cells. Endocr Res. 1986;12(4):409–427. doi: 10.3109/07435808609035448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Chaplin D. D., Wong M., Seidman J. G., Smith J. A., Schimmer B. P. Expression of murine 21-hydroxylase in mouse adrenal glands and in transfected Y1 adrenocortical tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7860–7864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack Y., Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. Methylation of foreign DNA sequences in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6463–6467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. A., Gutmann N. S., Tsao J., Schimmer B. P. Mutations in cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and corticotropin (ACTH)-sensitive adenylate cyclase affect adrenal steroidogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Szyf M. DNA methylation patterns. Formation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonian M. H., Hornsby P. J., Ill C. R., O'Hare M. J., Gill G. N. Characterization of cultured bovine adrenocortical cells and derived clonal lines: regulation of steroidogenesis and culture life span. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):99–108. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H. The inheritance of methylation patterns in vertebrates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):285–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumura Y., Buonassisi V., Sato G. Clonal analysis of differentiated function in animal cell cultures. I. Possible correlated maintenance of differentiated function and the diploid karyotype. Cancer Res. 1966 Mar;26(3):529–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaller D. M., Yu H., Eckhardt L. A. Genes activated in the presence of an immunoglobulin enhancer or promoter are negatively regulated by a T-lymphoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1932–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]