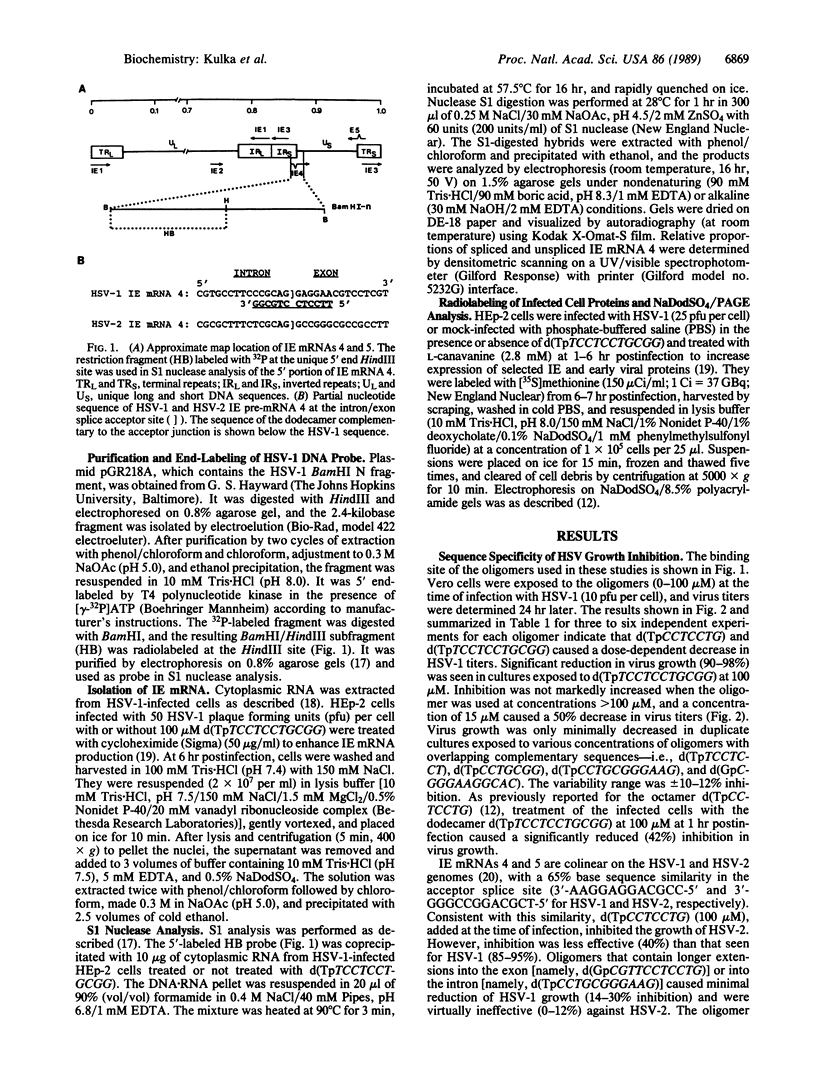
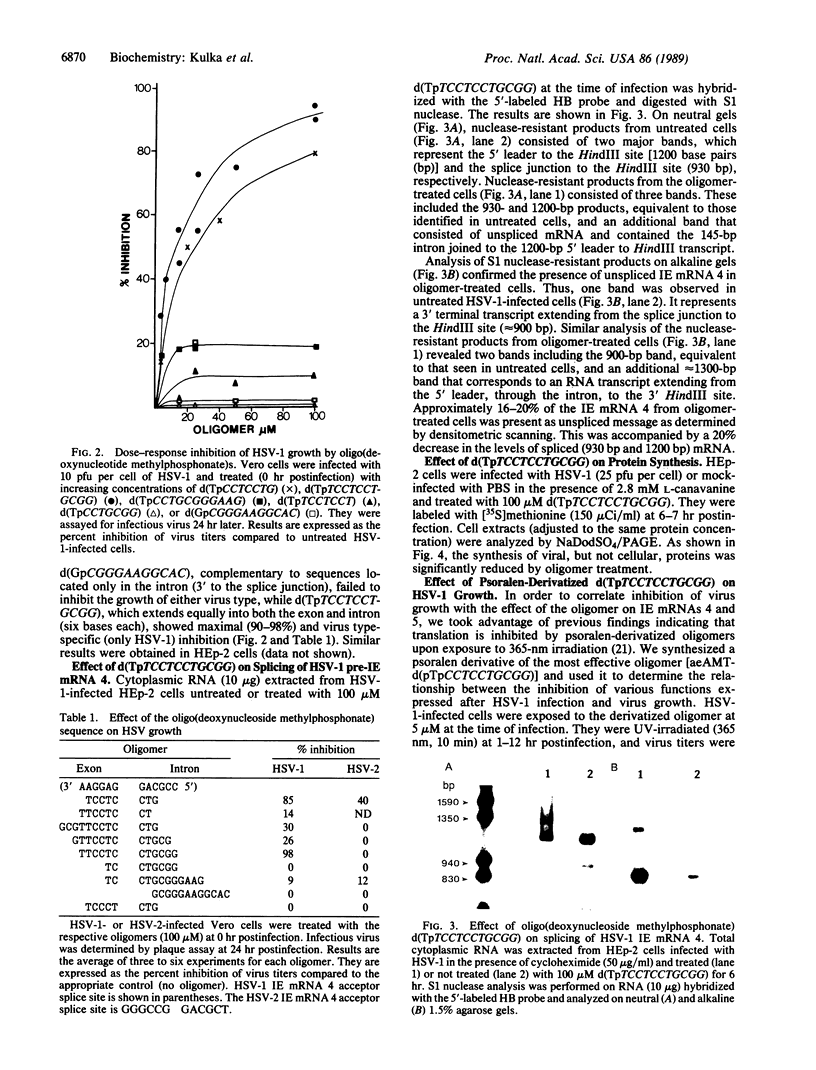
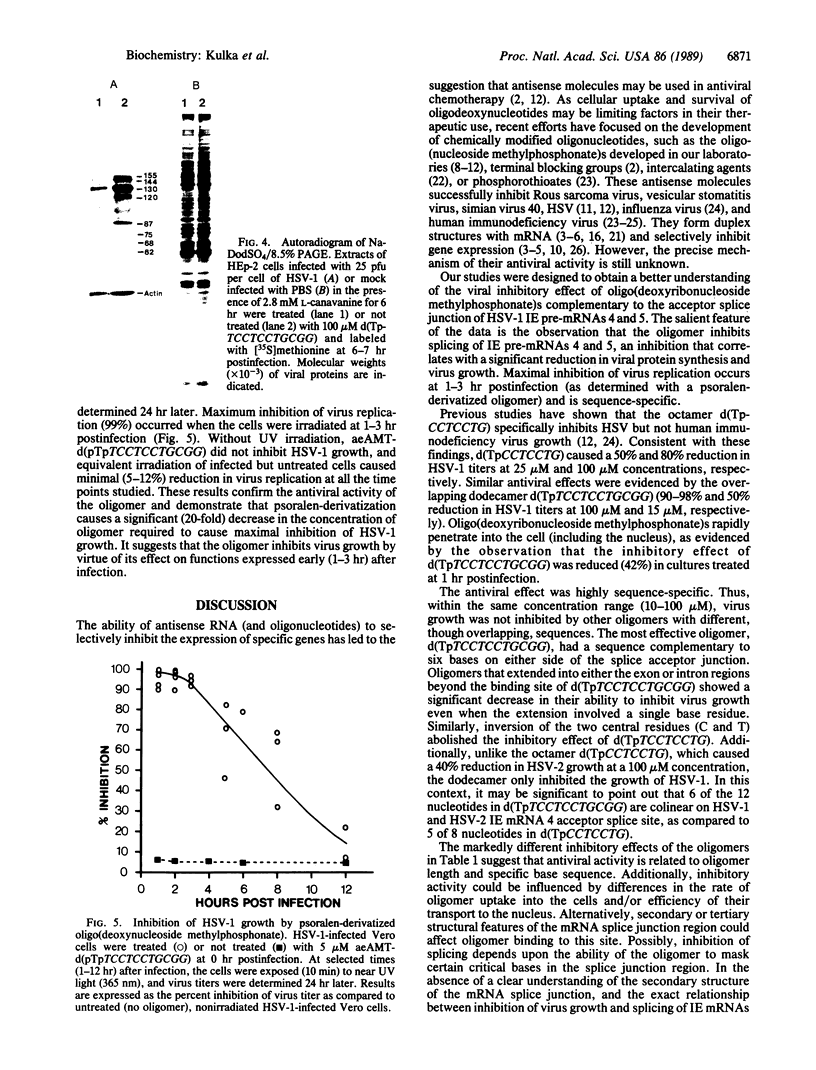
Abstract
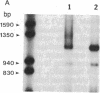
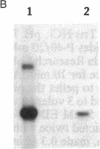
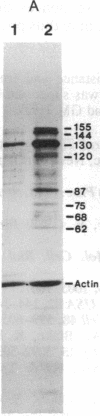
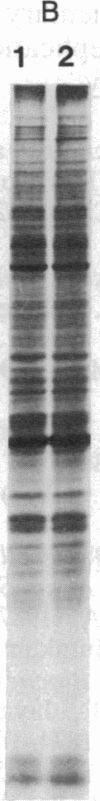
Oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5 caused specific inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 growth. The dodecamer d(TpTCCTCCTGCGG) (deoxynucleoside methylphosphonate residues in italic) caused 50% and 98% decreases in herpes simplex virus type 1 titers at concentrations of 15 microM and 100 microM, respectively. d(TpTCCTCCTGCGG) inhibited viral but not cellular protein synthesis and decreased splicing of immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Inhibition was highly sequence specific. A psoralen derivative of d(TpTCCTCCTGCGG) that can covalently bind to complementary sequences after exposure to 365-nm irradiation caused 90-98% inhibition of virus growth in cells treated with oligomer (5 microM) and irradiated at 1-3 hr postinfection. The data suggest that oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate)s of appropriate sequence and derivatization may be effective as antiviral agents.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris C. H., Blake K. R., Miller P. S., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus protein synthesis and infection by sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6268–6275. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua A., Erickson R. P., Hieber V. Antisense RNA inhibits endogenous gene expression in mouse preimplantation embryos: lack of double-stranded RNA "melting" activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):831–835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake K. R., Murakami A., Spitz S. A., Glave S. A., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O., Miller P. S. Hybridization arrest of globin synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates and cells by oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6139–6145. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. The regulation of transcription of viral and cellular genes by herpesvirus immediate-early gene products (review). Anticancer Res. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4A):589–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontichiaro K. L., Beck T. W., Millette R. L. In vitro transcription of herpes simplex virus genes: identification of a new initiation site and second intervening sequence in the immediate-early RNA-5 gene. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.235-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild J., Agrawal S., Civeira M. P., Sarin P. S., Sun D., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus replication by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5507–5511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemont B., Verrier B., Epstein A. L., Machuca I. Expression of immediate-early genes in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected XC cells: lack of ICP22 (68K) polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1984 Aug;65(Pt 8):1331–1340. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-8-1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Cushman C. D., Miller P. S. Photochemical cross-linking of psoralen-derivatized oligonucleoside methylphosphonates to rabbit globin messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9113–9121. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Chow L. T. Incomplete splicing and deficient accumulation of the fiber messenger RNA in monkey cells infected by human adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):221–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. L., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Lin S. B., Miller P. S. Interaction of psoralen-derivatized oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates with single-stranded DNA. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3197–3203. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukura M., Shinozuka K., Zon G., Mitsuya H., Reitz M., Cohen J. S., Broder S. Phosphorothioate analogs of oligodeoxynucleotides: inhibitors of replication and cytopathic effects of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Ackermann M., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a viable herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant lacking coding sequences of the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.807-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Injected anti-sense RNAs specifically block messenger RNA translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., McParland K. B., Jayaraman K., Ts'o P. O. Biochemical and biological effects of nonionic nucleic acid methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1874–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. S., Reddy M. P., Murakami A., Blake K. R., Lin S. B., Agris C. H. Solid-phase syntheses of oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5092–5097. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Melton D. A. Antisense RNA injections in fertilized frog eggs reveal an RNA duplex unwinding activity. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):599–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Clements J. B. Detailed structural analysis of two spliced HSV-1 immediate-early mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2241–2256. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Halliburton I. W., Meignier B., Silver S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 mutant deleted in the alpha 22 gene: growth and gene expression in permissive and restrictive cells and establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.338-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The junctions between the repetitive and the short unique sequences of the herpes simplex virus genome are determined by the polypeptide-coding regions of two spliced immediate-early mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):451–466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaia J. A., Rossi J. J., Murakawa G. J., Spallone P. A., Stephens D. A., Kaplan B. E., Eritja R., Wallace R. B., Cantin E. M. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus by using an oligonucleoside methylphosphonate targeted to the tat-3 gene. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3914–3917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3914-3917.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Stephenson M. L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Selective inhibition of the cytopathic effect of type A influenza viruses by oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to an intercalating agent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9909–9919. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]