Abstract
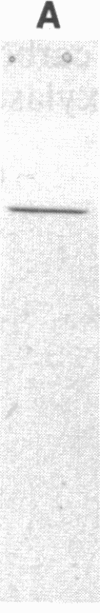
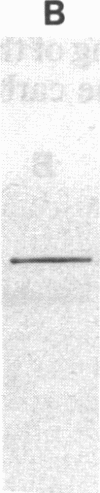
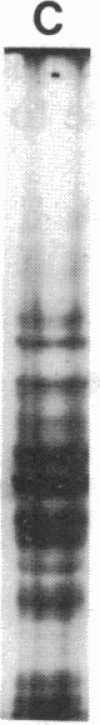
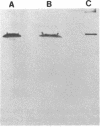
The vitamin K-dependent carboxylase catalyzes the posttranslational modification of specific glutamic acid residues to form gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues within the vitamin K-dependent proteins. This enzyme recognizes the gamma-carboxylation recognition site on the propeptide of the precursor forms of the vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation proteins. To purify this enzyme to homogeneity, the carboxylase from bovine liver microsomes was solubilized with 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS), the protein was fractionated with ammonium sulfate, and then the enzyme was isolated by affinity chromatography using a synthetic peptide based upon the structure of the prothrombin propeptide. Elution with 10 mM propeptide yielded a single major band on SDS gel electrophoresis with a molecular weight of 77,000. In the presence of high concentrations of propeptide, only minimal carboxylase activity was measurable. Antibodies to the protein inhibited the carboxylase activity in crude preparations. In an alternative affinity purification strategy the propeptide was coupled through an NH2-terminal cysteine to an activated thiol-Sepharose column. The carboxylase-propeptide complex was eluted at 25 degrees C by reductive cleavage of the enzyme-propeptide complex in the presence of detergent and phospholipids. The eluted protein (Mr, 77,000) contained both stable vitamin K-dependent carboxylase and vitamin K epoxidase activity. The protein, purified by either method, was detected as a single band (Mr, 77,000) in a Western blot using anti-carboxylase antibodies. A 10,000-fold purification of carboxylase activity from crude microsomes was estimated. Purified bovine liver vitamin K-dependent carboxylase should facilitate the study of its structure and of the mechanism of action of vitamin K as a cofactor in the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom J. W., Mann K. G. Metal ion induced conformational transitions of prothrombin and prothrombin fragment 1. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4430–4438. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield L. M., Sinsky T. A., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: purification of the rat liver microsomal enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Jul;202(2):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle T. L., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K dependent carboxylase: subcellular location of the carboxylase and enzymes involved in vitamin K metabolism in rat liver. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1161–1167. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2087–2097. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Grant G. A., Suttie J. W. Purification of an apparent rat liver prothrombin precursor: characterization and comparison to normal rat prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1595–1600. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Sadowski J. A., Suttie J. W. A new carboxylation reaction. The vitamin K-dependent incorporation of H-14-CO3- into prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4744–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W., Jackson C. M. The functional significance of vitamin K action. Difference in phospholipid binding between normal and abnormal prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4095–4099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Solubilization and properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Rudinski M. S., Schach B. G., Berkner K. L., Kumar A. A., Hagen F. S., Sprecher C. A., Insley M. Y., Davie E. W. Propeptide of human protein C is necessary for gamma-carboxylation. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):7003–7011. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Partial purification and properties of the enzyme-substrate complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15008–15011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Suttie J. W. Rat liver prothrombin precursors: purification of a second, more basic form. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5387–5393. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard B. R., Jacobs M., Ulrich M. M., Walsh C., Furie B., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. In vitro modification of synthetic peptides containing the gamma-carboxylation recognition site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14145–14150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. P., Gardner E. J., Cooper T. G., Olson R. E. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of peptide-bound glutamate. The active species of "CO2" utilized by the membrane-bound preprothrombin carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7738–7742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen M. J., Cantor A. B., Furie B. C., Brown C. L., Shoemaker C. B., Furie B. Recognition site directing vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylation resides on the propeptide of factor IX. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J. E., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Control of enzyme activity by the "propeptide" region of factor X. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15334–15337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6461–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Jenny R. J., Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Nesheim M. E., Tracy P. B., Hibbard L. S., Bloom J. W. Assembly of the prothrombinase complex. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):106–107. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84624-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Automated synthesis of peptides. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):178–185. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L. Role of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. An unusual protein transition required for the calcium-dependent binding of prothrombin to phospholipid. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5648–5656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Zytkovicz T. H., Howard J. B. The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6347–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Differentiation of metal ion-induced transitions of prothrombin fragment 1. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):840–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. A. Role of vitamin-K-dependent proteins in bone metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr. 1988;8:565–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.08.070188.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabiet M. J., Jorgensen M. J., Furie B., Furie B. C. Effect of propeptide mutations on post-translational processing of factor IX. Evidence that beta-hydroxylation and gamma-carboxylation are independent events. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14895–14898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. V., Swanson J. C., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: effect of detergent concentrations, vitamin K status, and added protein precursors on activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Apr 1;222(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soute B. A., Ulrich M. M., Vermeer C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: increased efficiency of the carboxylation reaction. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Feb 3;57(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Furie B. C., Blumenstein M., Keyt B., Furie B. Metal binding properties of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Implications for the vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3898–3906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Fernlund P., Egan W., Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730–2733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuchbury T., Shipton M., Norris R., Malthouse J. P., Brocklehurst K., Herbert J. A., Suschitzky H. A reporter group delivery system with both absolute and selective specificity for thiol groups and an improved fluorescent probe containing the 7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole moiety. Biochem J. 1975 Nov;151(2):417–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1510417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W., Larson A. E., Canfield L. M., Carlisle T. L. Relationship between vitamin K-dependent carboxylation and vitamin K epoxidation. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2605–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Mechanism of action of vitamin K: synthesis of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;8(2):191–223. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:459–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai M. M., Furie B. C., Furie B. Conformation-specific antibodies directed against the bovine prothrombin . calcium complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2790–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich M. M., Furie B., Jacobs M. R., Vermeer C., Furie B. C. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation. A synthetic peptide based upon the gamma-carboxylation recognition site sequence of the prothrombin propeptide is an active substrate for the carboxylase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9697–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: evidence for cofractionation of carboxylase and epoxidase activities, and for carboxylation of a high-molecular-weight microsomal protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Suttie J. W. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: evidence for cofractionation of carboxylase and epoxidase activities, and for carboxylation of a high-molecular-weight microsomal protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Mar;214(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Diuguid D. L., Liebman H. A., Rabiet M. J., Kasper C. K., Furie B. C., Furie B., Stafford D. W. Factor IX San Dimas. Substitution of glutamine for Arg-4 in the propeptide leads to incomplete gamma-carboxylation and altered phospholipid binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11401–11406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Metz M., Vermeer C., Soute B. A., van Scharrenburg G. J., Slotboom A. J., Hemker H. C. Partial purification of bovine liver vitamin K-dependent carboxylase by immunospecific adsorption onto antifactor X. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]