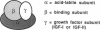Abstract
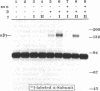
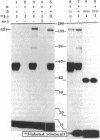
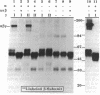
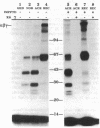
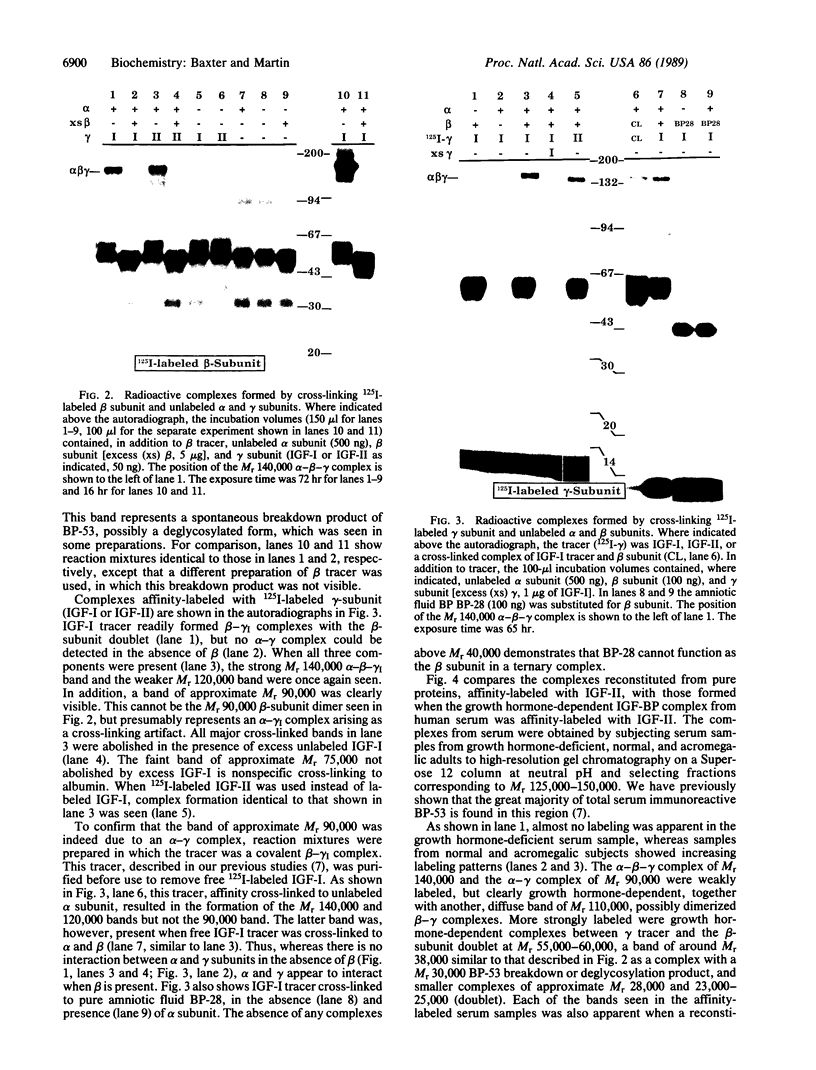
To determine the structure of the high molecular weight, growth hormone-dependent complex between the insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) and their binding proteins in human serum, we have reconstituted the complex from its purified component proteins and analyzed it by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography after covalent cross-linking. The proteins tested in reconstitution mixtures were an acid-labile Mr 84,000-86,000 glycoprotein doublet (alpha subunit), an acid-stable Mr 47,000-53,000 glycoprotein doublet with IGF-binding activity (BP-53 or beta subunit), and IGF-I or IGF-II (gamma subunit). In incubations containing any one of the three subunits 125I-labeled and the other two unlabeled, identical 125I-labeled alpha-beta-gamma complexes of Mr 140,000 were formed. Minor bands of Mr 120,000 and 90,000 were also seen, thought to represent a partially deglycosylated form of the alpha-beta-gamma complex, and an alpha-gamma complex arising as a cross-linking artifact. When serum samples from subjects of various growth hormone status were affinity-labeled with IGF-II tracer, a growth hormone-dependent Mr 140,000 band was seen, corresponding to the reconstituted alpha-beta-gamma complex. Other growth hormone-dependent labeled bands, of Mr 90,000 (corresponding to alpha-gamma), Mr 55,000-60,000 (corresponding to labeled beta-subunit doublet), and smaller bands of Mr 38,000, 28,000, and 23,000-25,000 (corresponding to labeled beta-subunit degradation products), were also seen in the affinity-labeled serum samples and in the complex reconstituted from pure proteins. All were immunoprecipitable with an anti-BP-53 antiserum. We conclude that the growth hormone-dependent Mr 140,000 IGF-binding protein complex in human serum has three components: the alpha (acid-labile) subunit, the beta (binding) subunit, and the gamma (growth factor) subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S. Purification of tracer for somatomedin C radioimmunoassay by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):485–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):265–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Beniac V. A. High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11843–11848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Tyler M. I., Howden M. E. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human plasma differs from other human IGF binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. The insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;91(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., de Mellow J. S. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor-II by radioreceptor assay using ovine placental membranes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Mar;24(3):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I-binding proteins in human amniotic fluid and in fetal and postnatal blood: evidence of immunological homology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):612–617. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Ward A. P., Goldberg A. C., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):916–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G. Purification of a high molecular weight somatomedin binding protein from human plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90959-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren H. J., Kahn C. R. Effect of cross-linking agents on insulin associated responses in adipocytes. Can J Biochem. 1982;60(10):987–1000. doi: 10.1139/o82-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Rosenfeld R. G., Kemp S. F. Plasma somatomedin-binding proteins in hypopituitarism: changes during growth hormone therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):100–104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. D., Powell D. R., Li C. H., Bohn H., Liu F., Hintz R. L. High molecular weight forms of insulin-like growth factor II and its binding protein identified by protein immunoblotting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1131–1137. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. H., Schalch D. S. Structure of somatomedin-binding protein: alkaline pH-induced dissociation of an acid-stable, 60,000 molecular weight complex into smaller components. Endocrinology. 1982 Sep;111(3):801–805. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-3-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. Covalent cross-linking of insulin-like growth factor-1 to a specific inhibitor from human serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. M., Nissley S. P., Moses A. C., Rechler M. M., Johnsonbaugh R. E. The growth hormone dependence of a somatomedin-binding protein in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):49–57. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Cachianes G., Henzel W. J., Winslow G. A., Spencer S. A., Hellmiss R., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Cloning and expression of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1176–1185. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]