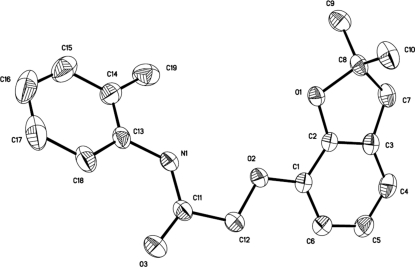
Abstract
In the title compound, C19H21NO3, the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the two benzene rings is 38.13 (12)°. The furan ring adopts an envelope-like conformation with the C atom bonded to the dimethyl groups displaced by 0.356 (2) Å from the plane through the other four atoms. In the crystal, molecules are linked into inversion dimers by weak C—H⋯O intermolecular interactions.
Related literature
The title compound is a derivative of Carbofuran, a popular carbamate insecticide, see: Tomlin (1994 ▶). For related structures, see: Xu et al. (2005 ▶); Li et al. (2009 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).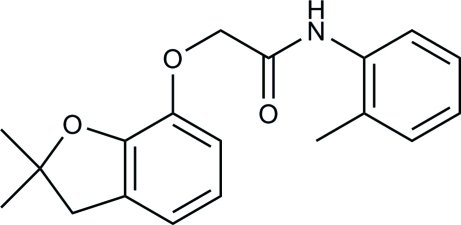
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H21NO3
M r = 311.37
Monoclinic,

a = 9.0868 (18) Å
b = 8.9708 (18) Å
c = 20.230 (4) Å
β = 92.18 (3)°
V = 1647.9 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.32 × 0.28 × 0.21 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.985, T max = 0.991
8246 measured reflections
2961 independent reflections
1649 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.130
S = 1.00
2961 reflections
211 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018672/jj2028sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018672/jj2028Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12—H12A⋯O3i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.561 (3) | 174 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2006 A A03Z460) for financial suppport.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), C19H21NO3, is a derivative of the commercial compound Carbofuran (Tomlin, 1994), which is a popular carbamate insecticide. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of the two aromatic rings is 38.13 (12)° (Fig. 1). The five-membered furan ring adopts an envelope-like conformation. All bond lengths (Allen et al. 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. The atom C1 deviates from the C1—C7/O1 plane with a distance of 0.356 (2) Å. Molecules are linked into dimers by weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions which helps stabilize crystal packing(Fig 2).
Experimental
0.10 mol of 2,2-dimethy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-ol , 0.12 mol chloroacetic acid, 0.25 mol sodium hydrate and 70 ml distilled water were stirred and heated under reflux for 3 h. The reaction mixture was then cooled to 283.15 K and 15 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid was added to give 2-(2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yloxy)acetic acid as an amber solid of 21.91 g, yield 98.5%. Subsequently, 0.10 mol of dry 2-(2,2-dimethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yloxy)acetic acid, 0.25 mol thionyl chloride and 80 ml anhydrous was stirred and heated at 353.15 K for 6h. The excess thionyl chloride was then removed under reduced pressure. The residue was cooled to 273.15 K, after which 0.10 mol o-toluidine and 0.20 mol triethylamine was added dropwise. After stirring for an additional 3 h, the reaction mixture was washed with water (3× 40 ml), and the excess toluene removed in vacuo. The residue was purified by recrystallization from a saturated ethanol solution, giving the title compound as a colourless crystalline solid. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethyl acetate solution at room temperature over a period of nine days. The identity of the title compound was confirmed by NMR and LC—MS spectroscopy.
Refinement
Methyl H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C–H = 0.96 Å, and torsion angles were refined, with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C). Other H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and refined as a riding model, with a N–H distance of 0.86 Å, C–H distances of 0.98Å (C3—H3), 0.93Å (aromatic H atoms) and 0.97Å (methylene H atoms). The constraint Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier) was applied.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram for the title compound. H atoms bonded to C atoms have been omitted for clarity. Dashed lines indicate weak C—H···O intermolecular interactions forminng dimers.
Crystal data
| C19H21NO3 | F(000) = 664 |
| Mr = 311.37 | Dx = 1.255 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 363.75 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0868 (18) Å | Cell parameters from 3600 reflections |
| b = 8.9708 (18) Å | θ = 1.4–28° |
| c = 20.230 (4) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 92.18 (3)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1647.9 (6) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.28 × 0.21 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII area-detector diffractometer | 2961 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1649 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.047 |
| φ and ω scan | θmax = 25.2°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −8→10 |
| Tmin = 0.985, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −10→9 |
| 8246 measured reflections | l = −19→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0561P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2961 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 211 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. 1H NMR in CDCl3 (300 MHz), delta: 1.49(s,6H,2CH3), 2.72(s,3H, ArCH3), 3.06(s,2H,CH2), 4.72 (s,2H, OCH2), 6.76~7.99(m,7H,C6H3,C6H4), 8.53(s,1H, NH). MS: 312.2(M+1) |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C7 | 0.4155 (3) | 0.3064 (3) | 0.23529 (11) | 0.0590 (7) | |
| H7A | 0.3140 | 0.2780 | 0.2254 | 0.071* | |
| H7B | 0.4243 | 0.3430 | 0.2804 | 0.071* | |
| C1 | 0.6148 (2) | 0.4224 (2) | 0.09104 (10) | 0.0478 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.5545 (2) | 0.3488 (2) | 0.14345 (10) | 0.0452 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.4665 (2) | 0.4205 (3) | 0.18741 (10) | 0.0508 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.5867 (3) | 0.5737 (3) | 0.08464 (11) | 0.0625 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.6271 | 0.6269 | 0.0503 | 0.075* | |
| C8 | 0.5210 (3) | 0.1749 (2) | 0.22464 (10) | 0.0534 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.4988 (3) | 0.6465 (3) | 0.12900 (12) | 0.0697 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.4804 | 0.7479 | 0.1239 | 0.084* | |
| C4 | 0.4384 (3) | 0.5705 (3) | 0.18046 (12) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.3795 | 0.6198 | 0.2101 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 0.6543 (3) | 0.1807 (3) | 0.27130 (12) | 0.0741 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.7220 | 0.1034 | 0.2601 | 0.111* | |
| H10B | 0.6243 | 0.1664 | 0.3159 | 0.111* | |
| H10C | 0.7014 | 0.2759 | 0.2677 | 0.111* | |
| C9 | 0.4475 (3) | 0.0248 (3) | 0.22421 (12) | 0.0761 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.3673 | 0.0243 | 0.1919 | 0.114* | |
| H9B | 0.4107 | 0.0046 | 0.2672 | 0.114* | |
| H9C | 0.5177 | −0.0505 | 0.2133 | 0.114* | |
| O1 | 0.57451 (16) | 0.20069 (15) | 0.15680 (7) | 0.0515 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.69720 (17) | 0.34027 (15) | 0.04836 (7) | 0.0554 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.83327 (19) | 0.16952 (19) | −0.03274 (8) | 0.0500 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.7740 | 0.1490 | −0.0019 | 0.060* | |
| C11 | 0.8592 (3) | 0.3146 (3) | −0.04218 (11) | 0.0540 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.9383 (2) | 0.36591 (19) | −0.08343 (9) | 0.0889 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.7796 (3) | 0.4201 (2) | 0.00151 (11) | 0.0569 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.8503 | 0.4844 | 0.0246 | 0.068* | |
| H12B | 0.7138 | 0.4823 | −0.0254 | 0.068* | |
| C13 | 0.8900 (3) | 0.0448 (2) | −0.06653 (10) | 0.0499 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.8094 (3) | −0.0865 (3) | −0.06628 (11) | 0.0611 (7) | |
| C17 | 1.0776 (4) | −0.0718 (4) | −0.12804 (13) | 0.0943 (11) | |
| H17 | 1.1673 | −0.0671 | −0.1486 | 0.113* | |
| C19 | 0.6654 (3) | −0.0952 (3) | −0.03299 (13) | 0.0822 (8) | |
| H19A | 0.6813 | −0.0796 | 0.0137 | 0.123* | |
| H19B | 0.6224 | −0.1918 | −0.0405 | 0.123* | |
| H19C | 0.6001 | −0.0199 | −0.0508 | 0.123* | |
| C15 | 0.8674 (4) | −0.2095 (3) | −0.09801 (14) | 0.0891 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.8155 | −0.2989 | −0.0985 | 0.107* | |
| C16 | 0.9987 (5) | −0.2025 (4) | −0.12855 (15) | 0.1031 (13) | |
| H16 | 1.0347 | −0.2863 | −0.1497 | 0.124* | |
| C18 | 1.0232 (3) | 0.0530 (3) | −0.09684 (10) | 0.0664 (7) | |
| H18 | 1.0761 | 0.1417 | −0.0963 | 0.080* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C7 | 0.0495 (15) | 0.0799 (17) | 0.0482 (14) | 0.0056 (13) | 0.0113 (11) | −0.0089 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0495 (14) | 0.0487 (14) | 0.0452 (13) | 0.0017 (11) | 0.0031 (11) | −0.0074 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0489 (14) | 0.0448 (13) | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0012 (11) | 0.0030 (11) | −0.0075 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0457 (14) | 0.0594 (15) | 0.0475 (14) | 0.0022 (12) | 0.0034 (11) | −0.0117 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0803 (19) | 0.0517 (15) | 0.0558 (15) | 0.0002 (13) | 0.0053 (14) | −0.0017 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0530 (15) | 0.0674 (15) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0041 (12) | 0.0144 (11) | 0.0004 (11) |
| C5 | 0.089 (2) | 0.0528 (14) | 0.0672 (17) | 0.0128 (14) | 0.0046 (15) | −0.0085 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0663 (18) | 0.0676 (17) | 0.0647 (17) | 0.0142 (14) | 0.0053 (14) | −0.0208 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0674 (18) | 0.103 (2) | 0.0522 (16) | 0.0144 (15) | 0.0057 (14) | 0.0012 (14) |
| C9 | 0.090 (2) | 0.0737 (18) | 0.0664 (17) | −0.0086 (16) | 0.0263 (15) | 0.0080 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0605 (10) | 0.0524 (9) | 0.0426 (9) | 0.0055 (8) | 0.0167 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0686 (11) | 0.0503 (9) | 0.0489 (9) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0242 (8) | 0.0000 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0523 (12) | 0.0438 (11) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0175 (9) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0602 (16) | 0.0583 (16) | 0.0444 (14) | −0.0096 (12) | 0.0129 (12) | 0.0007 (11) |
| O3 | 0.1140 (16) | 0.0713 (12) | 0.0856 (13) | −0.0173 (11) | 0.0584 (12) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0635 (16) | 0.0550 (14) | 0.0536 (14) | −0.0072 (12) | 0.0190 (12) | −0.0003 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0599 (16) | 0.0579 (15) | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0128 (12) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0787 (19) | 0.0548 (15) | 0.0485 (14) | 0.0045 (14) | −0.0137 (13) | −0.0024 (12) |
| C17 | 0.106 (3) | 0.128 (3) | 0.0505 (17) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0147 (17) | 0.0032 (18) |
| C19 | 0.088 (2) | 0.0724 (18) | 0.085 (2) | −0.0193 (16) | −0.0079 (17) | 0.0098 (15) |
| C15 | 0.134 (3) | 0.0651 (19) | 0.0653 (19) | 0.020 (2) | −0.029 (2) | −0.0111 (15) |
| C16 | 0.149 (4) | 0.100 (3) | 0.058 (2) | 0.063 (3) | −0.014 (2) | −0.0204 (19) |
| C18 | 0.0742 (18) | 0.0837 (18) | 0.0421 (14) | 0.0215 (15) | 0.0121 (13) | 0.0088 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C7—C3 | 1.495 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.540 (3) | O2—C12 | 1.423 (2) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9700 | N1—C11 | 1.337 (3) |
| C7—H7B | 0.9700 | N1—C13 | 1.418 (3) |
| C1—O2 | 1.378 (2) | N1—H1 | 0.8600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (3) | C11—O3 | 1.213 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.500 (3) |
| C2—O1 | 1.367 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.378 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.376 (3) | C13—C18 | 1.380 (3) |
| C6—C5 | 1.387 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.387 (3) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.390 (4) |
| C8—O1 | 1.492 (2) | C14—C19 | 1.497 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.503 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.374 (4) |
| C8—C10 | 1.508 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.386 (3) |
| C5—C4 | 1.376 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C19—H19A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C19—H19B | 0.9600 |
| C10—H10A | 0.9600 | C19—H19C | 0.9600 |
| C10—H10B | 0.9600 | C15—C16 | 1.366 (4) |
| C10—H10C | 0.9600 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C7—C8 | 102.93 (17) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C7—H7A | 111.2 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 111.2 | C2—O1—C8 | 106.68 (14) |
| C3—C7—H7B | 111.2 | C1—O2—C12 | 117.43 (16) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 111.2 | C11—N1—C13 | 129.02 (18) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.1 | C11—N1—H1 | 115.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 117.83 (18) | C13—N1—H1 | 115.5 |
| O2—C1—C6 | 124.60 (19) | O3—C11—N1 | 125.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.56 (19) | O3—C11—C12 | 118.5 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 113.71 (19) | N1—C11—C12 | 116.00 (18) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 124.27 (18) | O2—C12—C11 | 110.67 (18) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.0 (2) | O2—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.0 (2) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C7 | 132.5 (2) | O2—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C7 | 107.51 (19) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.6 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.1 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C18—C13—C14 | 121.3 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C18—C13—N1 | 120.9 (2) |
| O1—C8—C9 | 107.10 (17) | C14—C13—N1 | 117.8 (2) |
| O1—C8—C10 | 106.75 (18) | C13—C14—C15 | 117.6 (3) |
| C9—C8—C10 | 112.3 (2) | C13—C14—C19 | 121.1 (2) |
| O1—C8—C7 | 103.68 (16) | C15—C14—C19 | 121.3 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 114.1 (2) | C16—C17—C18 | 119.9 (3) |
| C10—C8—C7 | 112.06 (19) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.8 (2) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C14—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C14—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.0 (2) | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.5 | C14—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.5 | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 121.7 (3) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.2 |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C15—C16—C17 | 120.0 (3) |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C13—C18—C17 | 119.6 (3) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C13—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
| C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.2 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C12—H12A···O3i | 0.97 | 2.60 | 3.561 (3) | 174 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: JJ2028).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Li, W.-S., Li, L. & Li, J.-S. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2829–o2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tomlin, C. (1994). The Pesticide Manual. A World Compendium, 10th ed., pp 152-153. Bath: The British Crop Protection Council, The Bath Press.
- Xu, L.-Z., Yu, G.-P. & Yang, S.-H. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o1924–o1926.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018672/jj2028sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810018672/jj2028Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report