Abstract
In the title compound, C9H14N2O2, the pyrrolidine and piperazine rings adopt envelope and boat conformations, respectively. The chiral centers were assigned on the basis of the known stereogenic center of an enantiomerically pure starting material and the trans relationship between the H atoms attached to these centers. The crystal packing is stabilized by an intermolecular hydrogen bond between the N—H group and a carbonyl O atom of the diketopiperazine group, forming zigzag C(5) chains along [010].
Related literature
For general background to the chemistry and biological properties of diketopiperazines, see: Herbert & Kelleher (1994 ▶); Ciajolo et al. (1995 ▶); Morley et al. (1981 ▶); Kazuharu et al. (1990 ▶); Funabashi et al. (1994 ▶); Moyroud et al. (1996 ▶); Caballero et al. (2003 ▶); Onishi et al. (2003 ▶); Alberch et al. (2004 ▶); von Nussbaum et al. (2003 ▶). For related structures, see: Hendea et al. (2006 ▶).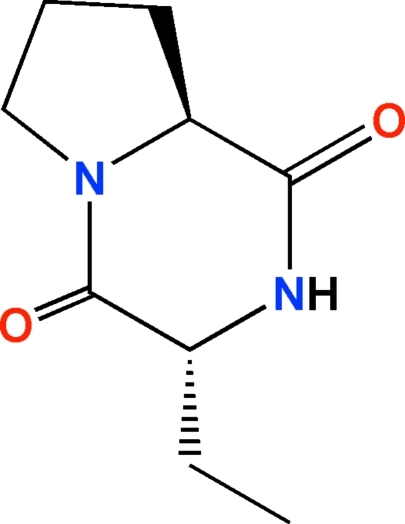
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H14N2O2
M r = 182.22
Monoclinic,
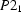
a = 6.8657 (4) Å
b = 9.9258 (17) Å
c = 7.0040 (5) Å
β = 90.892 (6)°
V = 477.25 (9) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.46 × 0.40 × 0.33 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
1290 measured reflections
1200 independent reflections
937 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.032
3 standard reflections every 200 reflections intensity decay: 1%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.120
S = 1.09
1200 reflections
119 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4 Software (Enraf–Nonius, 1989 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 Software; data reduction: HELENA (Spek, 1996 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810001856/bh2268sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810001856/bh2268Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O4i | 0.87 | 1.98 | 2.817 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry code: (i) 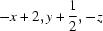 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), the Fundação de Apoio à Pesquisa Científica e Tecnológica do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC) and the Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia (INCT)–Catálise for financial assistance.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
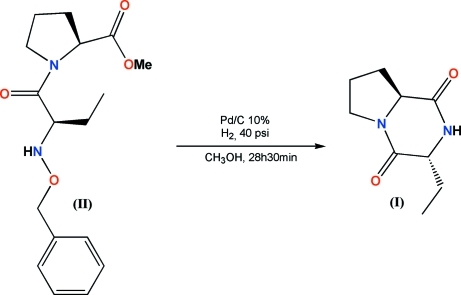
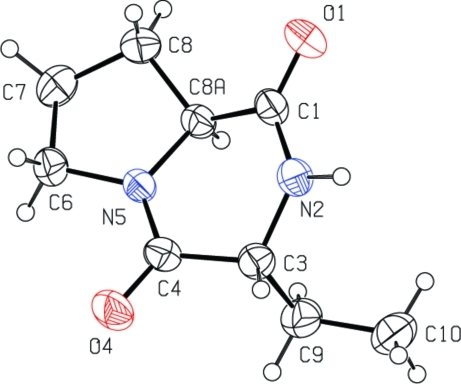
Diketopiperazine (DKP) backbone is an important pharmacophore in medicinal chemistry, which is conformationally restrained by six-membered ring with side chains that are oriented in a spatially defined manner (Herbert & Kelleher, 1994; Ciajolo et al., 1995). DKPs are quite common in nature and many natural products with the DKP scaffold have been isolated encompassing a wide range of biological activities (Morley et al., 1981; Kazuharu et al., 1990; Funabashi et al., 1994; Moyroud et al., 1996). Several secondary metabolites of microorganisms with interesting biological properties contain a proline-derived diketopiperazine as part of their molecular skeleton (Caballero et al., 2003; Onishi et al., 2003; Alberch et al., 2004; von Nussbaum et al., 2003). During our work on the synthesis of L-proline-based DKPs, we prepared L-proline methyl ester derivative (II) which, under hydrogenolysis condition, led to the title compound (I, Fig. 1). Despite its full chemical characterization and the known configuration of the starting material L-proline, the absolute configuration at C3 was tentatively assigned as being R due to the trans relationship of the hydrogen atoms attached to carbons C3 and C8a based on 1H-NMR and NOE experiments. The crystallographic data unambiguously confirmed the trans relationship of the above mentioned hydrogen atoms and consequently the R configuration of the chiral center at C3 (Fig. 2).
The molecular structure of (I) consists of a bicycle system formed by pyrrolidine and piperazine fused rings (Hendea et al., 2006). The five-membered pyrrolidine ring shows an envelope conformation, which is enveloped at C8. Piperazine ring shows perfect boat conformation, where N2, C1, C4 and N5 atoms lie on the basal plane (r.m.s. deviation: 0.0016 Å) and C3 and C8a are out of the basal mean plane by 0.39 Å (average) toward the same direction.
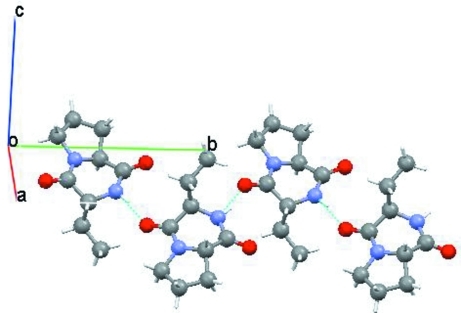
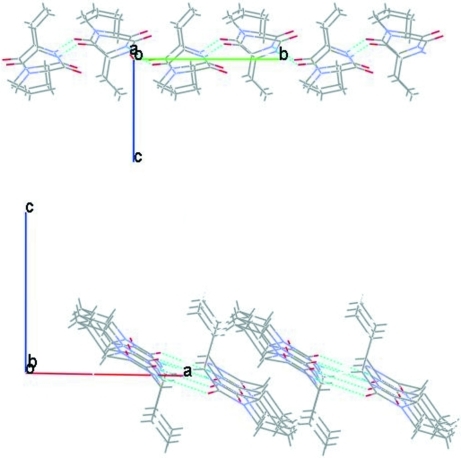
Strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds between the N—H group and the carbonyl O atom of the diketopiperazine neighboring groups contribute to the stabilization of the crystal structure. N2—H2···O4i [symmetry code: (i) -x + 2, y + 1/2, -z] interactions promote the formation of parallel one-dimensional zigzag C(5) chains running on the 21 screw axis along [010] (Fig. 3). Furthermore, the molecules of (I) are stacked viewing in perpendicular projection of the chains, along [100], and viewing in parallel projection of the chains, along [010] (Fig. 4).
Experimental
To a solution of L-proline methyl ester derivative (II) (0.084 mmol) in methanol (6 ml) was added Pd/C (10%, 18 mg, three portions of 6 mg of the catalyst were added each 10 h) and the mixture was shaken under 40 psi of hydrogen at room temperature for 28 h and 30 min [TLC control, alumina, ethyl acetate/hexane (1:3 v/v)]. After filtration of the catalyst, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and column chromatography of the residue over alumina with ethyl acetate afforded compound (I) as a white solid, with 84% yield. A careful crystallization from ethyl acetate/hexane (1:3 v/v) provided crystals (mp. 133.5–134.5°C) suitable for X-ray analysis.
Refinement
All non-H atoms were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters. H atoms were placed at their idealized positions with distances of 0.98, 0.97 and 0.96 Å for CH, CH2 and CH3, respectively. Uiso of the H atoms were fixed at 1.2 times for methine and methylene and 1.5 times for methyl of the Ueq of the carrier C atom. Hydrogen atom of the cyclic piperazine amine group was found in a difference map and treated with a riding model and its Uiso was also fixed at 1.2 times Ueq of the parent N atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Synthetic route.
Fig. 2.
The molecular structure of the title compound with labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 40% probability level.
Fig. 3.
Polymeric chain along b axis formed by intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Symmetry code: -x + 2, y + 1/2, -z
Fig. 4.
Partial packing of the title compound showing the stacking of the molecules along [100] (top) and along [010] (bottom).
Crystal data
| C9H14N2O2 | F(000) = 196 |
| Mr = 182.22 | Dx = 1.268 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Melting point: 407 K |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.8657 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| b = 9.9258 (17) Å | θ = 3.6–15.6° |
| c = 7.0040 (5) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 90.892 (6)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 477.25 (9) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.46 × 0.40 × 0.33 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.032 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 3.0° |
| graphite | h = −9→9 |
| ω–2θ scans | k = −13→0 |
| 1290 measured reflections | l = −9→0 |
| 1200 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections every 200 reflections |
| 937 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: 1% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.120 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0525P)2 + 0.0801P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1200 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 119 parameters | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 constraints |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6671 (5) | 0.5429 (3) | 0.1100 (4) | 0.0446 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.8672 (4) | 0.3662 (3) | −0.0490 (4) | 0.0446 (7) | |
| H3 | 1.0083 | 0.3519 | −0.0400 | 0.054* | |
| C4 | 0.7726 (4) | 0.2617 (3) | 0.0781 (4) | 0.0428 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.5113 (5) | 0.2151 (3) | 0.3021 (5) | 0.0481 (7) | |
| H6A | 0.5912 | 0.1966 | 0.4145 | 0.058* | |
| H6B | 0.4732 | 0.1304 | 0.2435 | 0.058* | |
| C7 | 0.3339 (5) | 0.2985 (4) | 0.3527 (5) | 0.0646 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.3015 | 0.2867 | 0.4860 | 0.077* | |
| H7B | 0.2223 | 0.2732 | 0.2741 | 0.077* | |
| C8 | 0.3944 (5) | 0.4437 (4) | 0.3131 (5) | 0.0603 (9) | |
| H8A | 0.2816 | 0.5001 | 0.2878 | 0.072* | |
| H8B | 0.4681 | 0.4810 | 0.4199 | 0.072* | |
| C8A | 0.5200 (4) | 0.4315 (3) | 0.1373 (4) | 0.0415 (6) | |
| H8AA | 0.4353 | 0.4263 | 0.0237 | 0.050* | |
| C9 | 0.8066 (5) | 0.3439 (4) | −0.2576 (5) | 0.0572 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.8351 | 0.2514 | −0.2924 | 0.069* | |
| H9B | 0.6670 | 0.3568 | −0.2705 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.9082 (6) | 0.4374 (5) | −0.3946 (5) | 0.0691 (11) | |
| H10A | 1.0466 | 0.4307 | −0.3753 | 0.104* | |
| H10B | 0.8673 | 0.5284 | −0.3720 | 0.104* | |
| H10C | 0.8751 | 0.4124 | −0.5235 | 0.104* | |
| N2 | 0.8290 (4) | 0.5027 (2) | 0.0198 (4) | 0.0486 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.9129 | 0.5629 | −0.0171 | 0.058* | |
| N5 | 0.6154 (3) | 0.3007 (2) | 0.1667 (3) | 0.0396 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.6391 (4) | 0.6573 (2) | 0.1630 (4) | 0.0643 (7) | |
| O4 | 0.8399 (4) | 0.1481 (2) | 0.0937 (4) | 0.0655 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0549 (17) | 0.0338 (15) | 0.0452 (15) | 0.0027 (13) | −0.0003 (13) | 0.0037 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0380 (15) | 0.0432 (17) | 0.0528 (16) | 0.0016 (12) | 0.0064 (13) | 0.0008 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0405 (15) | 0.0384 (15) | 0.0494 (16) | 0.0032 (13) | 0.0012 (13) | −0.0032 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0556 (18) | 0.0402 (16) | 0.0486 (16) | −0.0063 (14) | 0.0040 (14) | 0.0026 (14) |
| C7 | 0.061 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0009 (19) | 0.0250 (16) | 0.005 (2) |
| C8 | 0.065 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0113 (17) | 0.0253 (16) | 0.0011 (17) |
| C8A | 0.0415 (14) | 0.0351 (14) | 0.0480 (15) | 0.0053 (13) | 0.0043 (12) | 0.0018 (12) |
| C9 | 0.066 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0507 (17) | −0.0062 (16) | 0.0063 (16) | −0.0058 (15) |
| C10 | 0.077 (2) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0526 (19) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0156 (17) | −0.0057 (19) |
| N2 | 0.0534 (15) | 0.0378 (14) | 0.0549 (15) | −0.0127 (12) | 0.0085 (12) | −0.0031 (11) |
| N5 | 0.0416 (13) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0457 (13) | 0.0024 (10) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0018 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0847 (18) | 0.0346 (12) | 0.0737 (16) | 0.0033 (12) | 0.0073 (14) | −0.0050 (12) |
| O4 | 0.0627 (14) | 0.0468 (14) | 0.0875 (17) | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0180 (12) | 0.0095 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.210 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| C1—N2 | 1.347 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C8A | 1.512 (4) | C8—C8A | 1.519 (4) |
| C3—N2 | 1.464 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.519 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C9 | 1.529 (4) | C8A—N5 | 1.468 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9800 | C8A—H8AA | 0.9800 |
| C4—O4 | 1.223 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.513 (5) |
| C4—N5 | 1.312 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9700 |
| C6—N5 | 1.467 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| C6—C7 | 1.519 (5) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9700 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9700 | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.527 (6) | N2—H2 | 0.8717 |
| O1—C1—N2 | 123.9 (3) | C8A—C8—H8B | 111.1 |
| O1—C1—C8A | 122.5 (3) | C7—C8—H8B | 111.1 |
| N2—C1—C8A | 113.6 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.0 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 111.0 (2) | N5—C8A—C1 | 111.6 (2) |
| N2—C3—C9 | 113.7 (3) | N5—C8A—C8 | 102.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—C9 | 110.4 (3) | C1—C8A—C8 | 115.7 (3) |
| N2—C3—H3 | 107.1 | N5—C8A—H8AA | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 107.1 | C1—C8A—H8AA | 109.0 |
| C9—C3—H3 | 107.1 | C8—C8A—H8AA | 109.0 |
| O4—C4—N5 | 122.8 (3) | C10—C9—C3 | 113.3 (3) |
| O4—C4—C3 | 121.2 (3) | C10—C9—H9A | 108.9 |
| N5—C4—C3 | 116.0 (3) | C3—C9—H9A | 108.9 |
| N5—C6—C7 | 103.6 (3) | C10—C9—H9B | 108.9 |
| N5—C6—H6A | 111.0 | C3—C9—H9B | 108.9 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 111.0 | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.7 |
| N5—C6—H6B | 111.0 | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6B | 111.0 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.0 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 104.5 (3) | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 110.8 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 110.8 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7B | 110.8 | C1—N2—C3 | 125.6 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 110.8 | C1—N2—H2 | 119.3 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.9 | C3—N2—H2 | 114.5 |
| C8A—C8—C7 | 103.4 (3) | C4—N5—C6 | 123.2 (3) |
| C8A—C8—H8A | 111.1 | C4—N5—C8A | 124.3 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 111.1 | C6—N5—C8A | 112.5 (2) |
| N2—C3—C4—O4 | −152.4 (3) | O1—C1—N2—C3 | −179.1 (3) |
| C9—C3—C4—O4 | 80.6 (4) | C8A—C1—N2—C3 | 0.2 (4) |
| N2—C3—C4—N5 | 28.2 (4) | C4—C3—N2—C1 | −31.8 (4) |
| C9—C3—C4—N5 | −98.8 (3) | C9—C3—N2—C1 | 93.3 (3) |
| N5—C6—C7—C8 | −23.9 (4) | O4—C4—N5—C6 | 3.8 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—C8A | 36.4 (4) | C3—C4—N5—C6 | −176.8 (3) |
| O1—C1—C8A—N5 | −147.5 (3) | O4—C4—N5—C8A | −173.9 (3) |
| N2—C1—C8A—N5 | 33.2 (3) | C3—C4—N5—C8A | 5.4 (4) |
| O1—C1—C8A—C8 | −31.1 (4) | C7—C6—N5—C4 | −175.5 (3) |
| N2—C1—C8A—C8 | 149.7 (3) | C7—C6—N5—C8A | 2.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—C8A—N5 | −33.9 (3) | C1—C8A—N5—C4 | −37.8 (4) |
| C7—C8—C8A—C1 | −155.4 (3) | C8—C8A—N5—C4 | −162.1 (3) |
| N2—C3—C9—C10 | 59.2 (4) | C1—C8A—N5—C6 | 144.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—C9—C10 | −175.3 (3) | C8—C8A—N5—C6 | 20.0 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O4i | 0.87 | 1.98 | 2.817 (3) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BH2268).
References
- Alberch, L., Bailey, P. D., Clingan, P. D., Mills, T. J., Price, R. A. & Pritchard, R. G. (2004). Eur. J. Org. Chem. pp. 1887–1890.
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Caballero, E., Avendano, C. & Menendez, J. C. (2003). J. Org. Chem.68, 6944–6951. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ciajolo, M. R., Balboni, G., Picone, D., Salvadori, S., Tancredi, T., Temussi, P. A. & Tuzi, A. (1995). Int. J. Pept. Protein Res.46, 134–138. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Enraf–Nonius (1989). CAD-4 Software Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Funabashi, Y., Horiguchi, T., Iinuma, S., Tanida, S. & Harada, S. (1994). J. Antibiot.47, 1202–1218. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hendea, D., Laschat, S., Baro, A. & Frey, W. (2006). Helv. Chim. Acta, 89, 1894–1909.
- Herbert, R. H. & Kelleher, F. (1994). Tetrahedron Lett.35, 5497–5500.
- Kazuharu, I., Nakamura, K., Kurohashi, M., Nakanishi, T. & Ichii, T. (1990). Phytochemistry, 29, 35–39.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst.39, 453–457.
- Morley, J. E., Levine, A. S. & Prasad, C. (1981). Brain Res.210, 475–478. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Moyroud, J., Gelin, J., Chêne, A. & Mortier, J. (1996). Tetrahedron, 52, 8525–8534.
- Nussbaum, F. von (2003). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.42, 3068–3071.
- Onishi, T., Sebahar, P. R. & Williams, R. M. (2003). Org. Lett.5, 3135–3137. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (1996). HELENA University of Utrecht, The Netherlands.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810001856/bh2268sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810001856/bh2268Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report