Abstract
The title compound, C10H11N3O3, was synthesized by the reaction of 3,5-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-formyl-4-methyl-1H-pyrrole and hydrazine hydrate. The angle between the pyrrole ring and the pyridazinone ring is 0.93 (9)°. In the crystal, intermolecular N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen-bond interactions link the molecules into a two-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the biological activity of pyrrolopyridazine compounds, see: Chen et al. (2006 ▶); Hu et al. (2004 ▶); Swamy et al. (2005 ▶). For bond-length data, see Allen et al. (1987 ▶).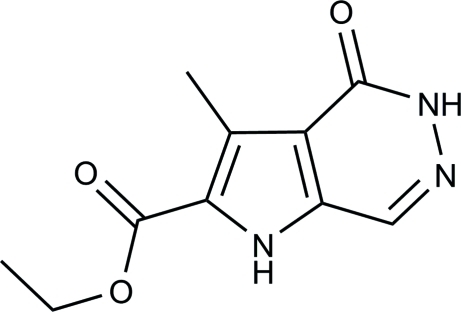
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H11N3O3
M r = 221.22
Monoclinic,
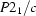
a = 8.0030 (16) Å
b = 9.774 (2) Å
c = 13.370 (3) Å
β = 90.17 (3)°
V = 1045.8 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.40 × 0.26 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.959, T max = 0.994
6834 measured reflections
2045 independent reflections
1676 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.120
S = 1.06
2045 reflections
156 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809055081/sj2715sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809055081/sj2715Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯O1i | 0.90 (3) | 1.90 (3) | 2.804 (2) | 175 (2) |
| N1—H1⋯N2ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.08 (2) | 2.925 (2) | 166.2 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 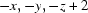 ; (ii)
; (ii) 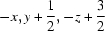 .
.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30660215).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
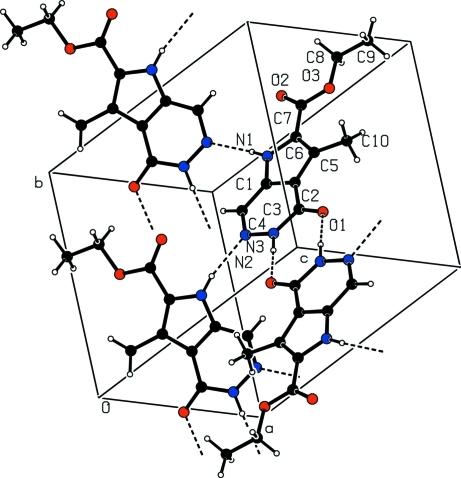
Pyridazine and its derivatives play an important role play an important role in medicine and as pesticides. One of the main techniques to synthesize pyridazines is to react 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds with hydrazine hydrate. Recently, the synthesis of pyrrolopyridazine compounds has aroused great interest because of their significant biological activity (Chen et al., 2006; Hu et al., 2004; Swamy et al., 2005). As part of our work to develop new types of pyrrolopyridazine compounds with potential biological activity, we report here the synthesis and structure of the title compound (1). In the molecule of compound (1), the torsion angles are N1—C1—C2—C3 179.21 (14) and N1—C1—C2—C5 0.20 (18)°. The dihedral angle between the pyrrole and pyridazinone rings is 0.93 (9)°, an indication that the pyrrolopyridazine system is reasonably planar. The C4═N2 and C3═O1 bond lengths in the molecule are 1.291 (2) and 1.2397 (19)°, respectively, showing their double-bond character (Allen et al., 1987). In the crystal structure, N—H···O and N—H···N hydrogen bonds form a two-dimensional network structure, Fig. 2.
Experimental
2.39 g (10 mmol) of the 3,5-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-2,4- dimethyl-1(H)-pyrrole was added to a mixed solvent of 60 ml THF and 60 ml glacial acetic acid at room temperature under stirring until all of the solid was dissolved. Then, 60 ml water and 21.93 g (40 mmol) cerous ammonium nitrate (CAN) were added consecutively and the mixture stirred at room temperature for 1.5 h until the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was poured into ice water and the white solid was separated (2.13 g, 84%). Recrystallization of the white solid from ethanol gave the compound 3,5-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-formyl-4-methyl-1(H)-pyrrole.
An aqueous solution of hydrazine hydrate (80%, 0.5 ml) was added into a solution of 3,5-bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-formyl-4-methyl- 1(H)-pyrrole (0.25 g, 1.0 mmol) in glacial acetic acid (20 ml) under stirring at room temperature. The reaction mixture was refluxed for 3 h till the reaction was complete. The reaction mixture was evaporated to remove the solvent of water and acetic acid at reduced pressure to yield the title compound (1) as a white solid (0.18 g, 82%). Recrystallization of the white solid from hot ethanol yielded colorless plate-like crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis.
Refinement
The H atoms bound to N1 and N3 were located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely with isotropic displacement parameters. All other H atoms were visible in difference maps and were subsequently treated as riding atoms with distances C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å. Uiso(H) was set equal to xUeq(parent atom), where x = 1.2 - 1.5.
Figures
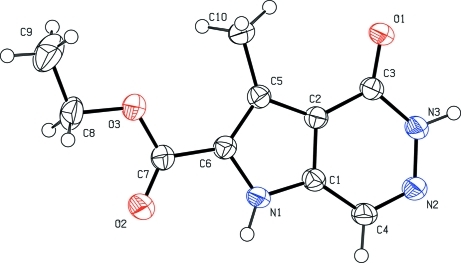
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound (1), showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of compound (1) showing the chain of molecules linked by N3–H3···O1 and N1–H1···N2 hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C10H11N3O3 | F(000) = 464 |
| Mr = 221.22 | Dx = 1.405 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 7501 reflections |
| a = 8.0030 (16) Å | θ = 2.6–26.4° |
| b = 9.774 (2) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 13.370 (3) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 90.17 (3)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 1045.8 (4) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.26 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2045 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1676 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.031 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.994 | k = −11→12 |
| 6834 measured reflections | l = −16→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.120 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0631P)2 + 0.2196P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2045 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 156 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.007 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.0960 (2) | 0.38216 (17) | 0.86245 (11) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.14214 (19) | 0.33040 (17) | 0.95543 (11) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.0970 (2) | 0.19196 (17) | 0.97885 (11) | 0.0295 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.0078 (2) | 0.30214 (18) | 0.79200 (12) | 0.0348 (4) | |
| H2 | −0.0209 | 0.3395 | 0.7303 | 0.042* | |
| C5 | 0.22621 (19) | 0.43535 (17) | 1.00880 (11) | 0.0287 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.2266 (2) | 0.54646 (17) | 0.94508 (11) | 0.0293 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.2897 (2) | 0.68717 (18) | 0.95437 (12) | 0.0324 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.4347 (2) | 0.8457 (2) | 1.05488 (15) | 0.0473 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.3500 | 0.9150 | 1.0436 | 0.057* | |
| H8B | 0.5247 | 0.8602 | 1.0076 | 0.057* | |
| C9 | 0.4995 (3) | 0.8551 (3) | 1.15900 (17) | 0.0665 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.5831 | 0.7860 | 1.1694 | 0.100* | |
| H9B | 0.4094 | 0.8414 | 1.2052 | 0.100* | |
| H9C | 0.5478 | 0.9438 | 1.1696 | 0.100* | |
| C10 | 0.2976 (2) | 0.4242 (2) | 1.11193 (12) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.2233 | 0.4670 | 1.1587 | 0.057* | |
| H10B | 0.4043 | 0.4690 | 1.1142 | 0.057* | |
| H10C | 0.3111 | 0.3295 | 1.1291 | 0.057* | |
| N1 | 0.14838 (18) | 0.51266 (15) | 0.85690 (10) | 0.0318 (4) | |
| N2 | −0.03348 (19) | 0.17759 (15) | 0.81245 (10) | 0.0362 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.01190 (19) | 0.12734 (16) | 0.90363 (10) | 0.0349 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.12783 (16) | 0.13034 (12) | 1.05782 (8) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.27522 (18) | 0.77051 (14) | 0.88893 (10) | 0.0506 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.36361 (16) | 0.71015 (13) | 1.04147 (9) | 0.0409 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.132 (2) | 0.565 (2) | 0.8057 (15) | 0.038 (5)* | |
| H3 | −0.028 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.9145 (16) | 0.067 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0348 (9) | 0.0251 (9) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0005 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0008 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0013 (7) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0275 (9) | 0.0268 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0017 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0503 (10) | 0.0287 (10) | 0.0253 (8) | −0.0019 (8) | −0.0054 (7) | 0.0011 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0271 (9) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0012 (6) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0321 (8) | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0286 (8) | −0.0002 (7) | −0.0028 (6) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0347 (9) | 0.0285 (10) | 0.0340 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | −0.0022 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0492 (11) | 0.0365 (12) | 0.0562 (12) | −0.0114 (9) | −0.0071 (9) | −0.0098 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0655 (14) | 0.0758 (18) | 0.0581 (14) | −0.0170 (13) | −0.0081 (11) | −0.0236 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0447 (10) | 0.0367 (11) | 0.0325 (9) | −0.0025 (8) | −0.0098 (7) | 0.0021 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0432 (8) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0268 (7) | −0.0024 (6) | −0.0058 (6) | 0.0050 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0515 (9) | 0.0298 (9) | 0.0272 (7) | −0.0048 (7) | −0.0059 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0502 (9) | 0.0255 (9) | 0.0290 (7) | −0.0063 (6) | −0.0053 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0569 (8) | 0.0305 (7) | 0.0317 (7) | −0.0077 (6) | −0.0101 (5) | 0.0078 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0723 (10) | 0.0319 (8) | 0.0475 (8) | −0.0113 (6) | −0.0173 (7) | 0.0092 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0514 (8) | 0.0324 (8) | 0.0389 (7) | −0.0092 (6) | −0.0101 (6) | −0.0006 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.345 (2) | C7—O3 | 1.324 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.391 (2) | C8—O3 | 1.453 (2) |
| C1—C4 | 1.412 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.487 (3) |
| C2—C5 | 1.418 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.435 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9700 |
| C3—O1 | 1.2396 (19) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C3—N3 | 1.368 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C4—N2 | 1.291 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (2) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C10 | 1.495 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C6—N1 | 1.374 (2) | N1—H1 | 0.86 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.470 (2) | N2—N3 | 1.3626 (19) |
| C7—O2 | 1.201 (2) | N3—H3 | 0.90 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.20 (14) | O3—C8—H8B | 110.1 |
| N1—C1—C4 | 130.09 (15) | C9—C8—H8B | 110.1 |
| C2—C1—C4 | 121.71 (16) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.4 |
| C1—C2—C5 | 108.11 (15) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.14 (14) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C5—C2—C3 | 133.74 (14) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—N3 | 119.96 (16) | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 126.47 (15) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N3—C3—C2 | 113.57 (14) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—C1 | 120.59 (15) | C5—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—H2 | 119.7 | C5—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C1—C4—H2 | 119.7 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C2 | 105.10 (14) | C5—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 128.68 (15) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—C5—C10 | 126.22 (15) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 109.79 (15) | C1—N1—C6 | 108.79 (14) |
| N1—C6—C7 | 116.94 (14) | C1—N1—H1 | 123.8 (13) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 133.26 (15) | C6—N1—H1 | 127.4 (13) |
| O2—C7—O3 | 124.61 (16) | C4—N2—N3 | 117.50 (14) |
| O2—C7—C6 | 122.72 (16) | N2—N3—C3 | 128.49 (16) |
| O3—C7—C6 | 112.68 (14) | N2—N3—H3 | 112.6 (14) |
| O3—C8—C9 | 107.89 (17) | C3—N3—H3 | 118.8 (14) |
| O3—C8—H8A | 110.1 | C7—O3—C8 | 115.92 (14) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110.1 | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C5 | 0.20 (18) | C10—C5—C6—C7 | −1.4 (3) |
| C4—C1—C2—C5 | −179.24 (15) | N1—C6—C7—O2 | −0.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.22 (14) | C5—C6—C7—O2 | −178.97 (18) |
| C4—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (2) | N1—C6—C7—O3 | −179.76 (14) |
| C1—C2—C3—O1 | −179.84 (16) | C5—C6—C7—O3 | 1.3 (3) |
| C5—C2—C3—O1 | −1.1 (3) | C2—C1—N1—C6 | −0.42 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—N3 | 0.1 (2) | C4—C1—N1—C6 | 178.97 (17) |
| C5—C2—C3—N3 | 178.82 (16) | C5—C6—N1—C1 | 0.49 (19) |
| N1—C1—C4—N2 | −179.01 (17) | C7—C6—N1—C1 | −178.65 (14) |
| C2—C1—C4—N2 | 0.3 (3) | C1—C4—N2—N3 | −0.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C5—C6 | 0.09 (18) | C4—N2—N3—C3 | 0.2 (3) |
| C3—C2—C5—C6 | −178.72 (17) | O1—C3—N3—N2 | 179.87 (16) |
| C1—C2—C5—C10 | −179.86 (15) | C2—C3—N3—N2 | −0.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—C5—C10 | 1.3 (3) | O2—C7—O3—C8 | −1.8 (3) |
| C2—C5—C6—N1 | −0.35 (18) | C6—C7—O3—C8 | 177.84 (15) |
| C10—C5—C6—N1 | 179.60 (15) | C9—C8—O3—C7 | 175.68 (16) |
| C2—C5—C6—C7 | 178.60 (17) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···O1i | 0.90 (3) | 1.90 (3) | 2.804 (2) | 175 (2) |
| N1—H1···N2ii | 0.86 (2) | 2.08 (2) | 2.925 (2) | 166.2 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+2; (ii) −x, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ2715).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2002). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chen, Z., Kim, S. H., Barbosa, S. A., Huynh, T., Tortolani, D. R., Leavitt, K. J., Wei, D. D., Manne, V., Ricca, C. S., Gullo-Brown, J., Poss, M. A., Vaccaro, W. & Salvati, M. E. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.16, 628–632. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hu, T., Stearns, B. A., Campbell, B. T., Arruda, J. M., Chen, C., Aiyar, J., Bezverkov, R. E., Santini, A., Schaffhauser, H., Liu, W., Venkatraman, S. & Munoz, B. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.14, 2031–2034. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Swamy, K. M. K., Park, M. S., Han, S. J., Kim, S. K., Kim, J. H., Lee, C., Bang, H., Kim, Y., Kim, S.-J. & Yoon, J. (2005). Tetrahedron, 61, 10227–10234.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809055081/sj2715sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809055081/sj2715Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report