Abstract
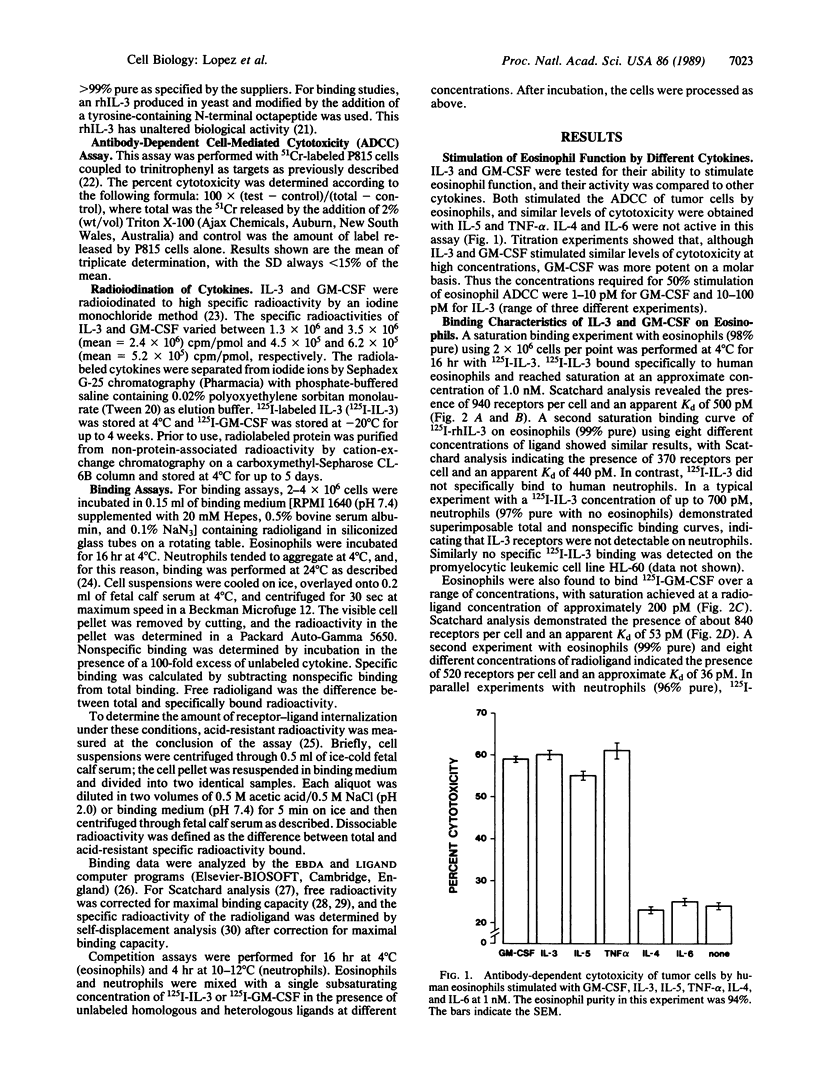
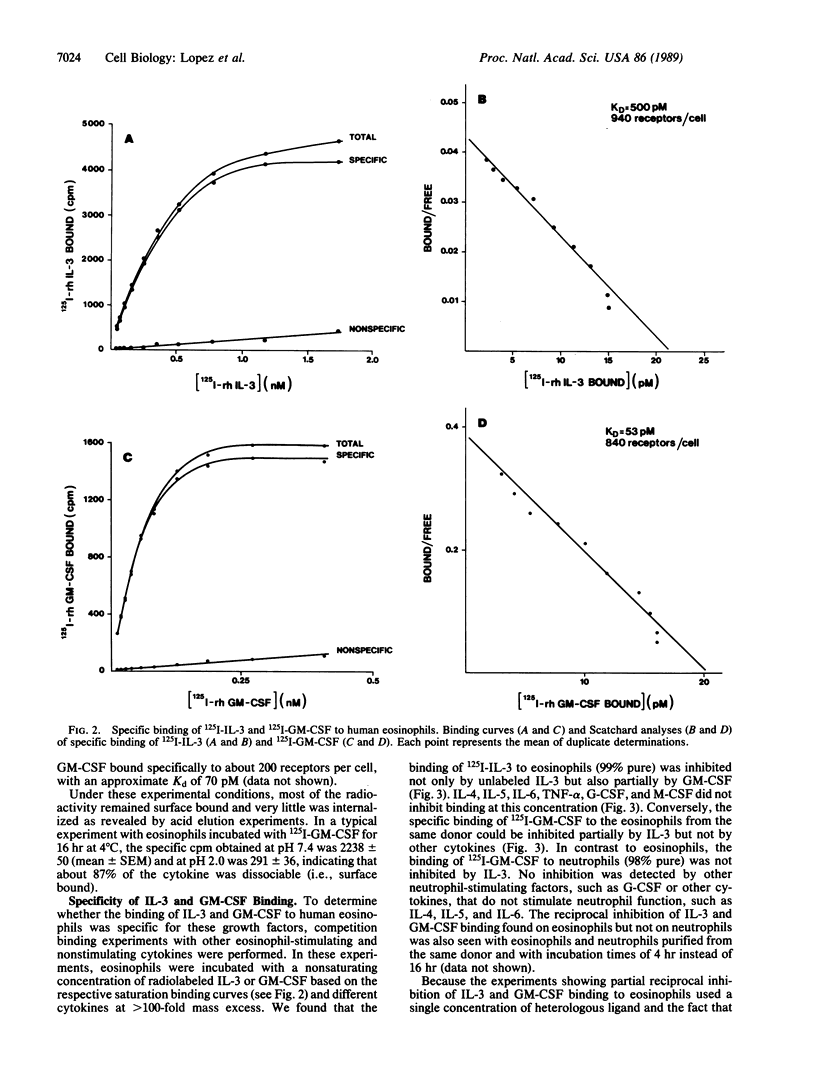
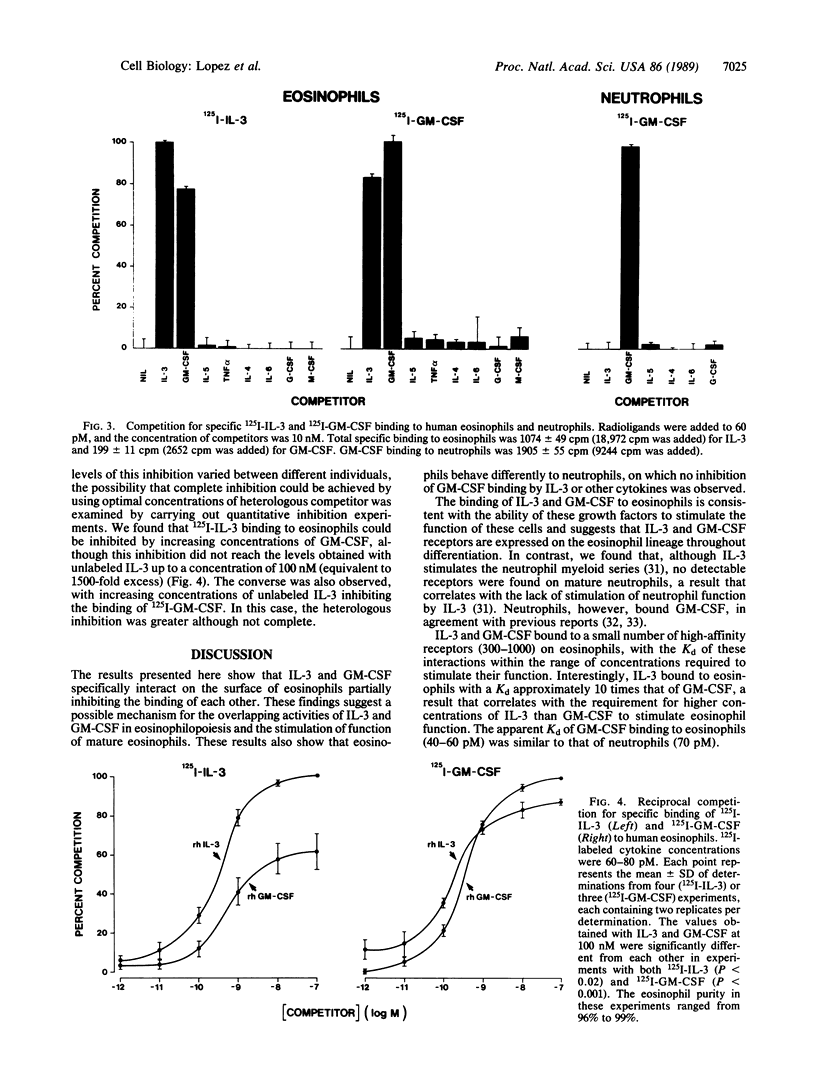
125I-labeled recombinant human interleukin 3 (IL-3) bound, at 4 degrees C, to a single class of high-affinity receptors on human eosinophils with an apparent dissociation constant (Kd) of 470 pM, but it did not bind to human neutrophils. 125I-labeled recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) also bound to a single class of high-affinity receptors on eosinophils with an apparent Kd of 44 pM and on neutrophils with an apparent Kd of 70 pM. These binding characteristics were consistent with the biological activities of IL-3 and GM-CSF on eosinophils and with the lack of stimulation of neutrophil function by IL-3. Specificity studies under conditions shown to prevent receptor internalization showed that the binding of 125I-labeled IL-3 to eosinophils was partially inhibited by GM-CSF but not by other cytokines. Reciprocal experiments with 125I-labeled GM-CSF showed that IL-3 but not other cytokines partially inhibited binding to eosinophils. In contrast, the binding of 125I-labeled GM-CSF to neutrophils was not inhibited by IL-3 or other cytokines tested. Quantitative inhibition binding experiments on eosinophils showed that the reciprocal inhibition between IL-3 and GM-CSF was not complete up to a concentration of heterologous ligand of 100 nM. These results show that (i) IL-3 binds to eosinophils but not neutrophils and (ii) IL-3 and GM-CSF specifically interact on the surface of eosinophils, providing a possible mechanism for the overlapping activities of IL-3 and GM-CSF on these cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. C., Radicella J. P., Charreau E. H. Measurement of specific radioactivities in labelled hormones by self-displacement analysis. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):259–264. doi: 10.1042/bj2120259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell H. D., Tucker W. Q., Hort Y., Martinson M. E., Mayo G., Clutterbuck E. J., Sanderson C. J., Young I. G. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the gene encoding human eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin 5). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6629–6633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D., Bernasconi C., Verdonck P. J., Postma A., Hows J., van der Does-van den Berg A., Rees J. K., Castelli G., Morra E., Galton D. A. The association of eosinophilia with lymphoblastic leukaemia or lymphoma: a study of seven patients. Br J Haematol. 1980 Aug;45(4):523–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb07174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Ling N., Guillemin R., Massagué J. A surface component on GH3 pituitary cells that recognizes transforming growth factor-beta, activin, and inhibin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17225–17228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras M. A., Bale W. F., Spar I. L. Iodine monochloride (IC1) iodination techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:277–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R., Vadas M. A., Butterworth A. E., de Brito P. A., Carvalho E. M., David R. A., Bina J. C., Andrade Z. A. Enhanced helminthotoxic capacity of eosinophils from patients with eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 1980 Nov 13;303(20):1147–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198011133032004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J., Billing P., Kaufman S., Eghtesady P., Williams R. E., Gasson J. C. Characterization of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1834–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue R. E., Wang E. A., Stone D. K., Kamen R., Wong G. G., Sehgal P. K., Nathan D. G., Clark S. C. Stimulation of haematopoiesis in primates by continuous infusion of recombinant human GM-CSF. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):872–875. doi: 10.1038/321872a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R., Sanders V. M., Vitetta E. S. Interactions between receptors for interleukin 2 and interleukin 4 on lines of helper T cells (HT-2) and B lymphoma cells (BCL1). J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):379–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Kaufman S. E., Weisbart R. H., Tomonaga M., Golde D. W. High-affinity binding of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Takada K., Kameya T., Shimosato Y., Tsuchiya R., Okabe T. Large cell carcinoma of the lung associated with marked eosinophilia. A case report. Cancer. 1984 Nov 15;54(10):2313–2317. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841115)54:10<2313::aid-cncr2820541044>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Beau M. M., Epstein N. D., O'Brien S. J., Nienhuis A. W., Yang Y. C., Clark S. C., Rowley J. D. The interleukin 3 gene is located on human chromosome 5 and is deleted in myeloid leukemias with a deletion of 5q. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5913–5917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Dyson P. G., To L. B., Elliott M. J., Milton S. E., Russell J. A., Juttner C. A., Yang Y. C., Clark S. C., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin-3 stimulation of hematopoiesis in humans: loss of responsiveness with differentiation in the neutrophilic myeloid series. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1797–1804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Sanderson C. J., Gamble J. R., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):219–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., To L. B., Yang Y. C., Gamble J. R., Shannon M. F., Burns G. F., Dyson P. G., Juttner C. A., Clark S., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of proliferation, differentiation, and function of human cells by primate interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2761–2765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Gamble J. R., Begley C. G., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Waltersdorph A., Wong G., Clark S. C., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates in vitro mature human neutrophil and eosinophil function, surface receptor expression, and survival. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI112705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Computer-assisted analysis of complex concentration-response data. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Apr;13(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J. Effects of purified bacterially synthesized murine multi-CSF (IL-3) on hematopoiesis in normal adult mice. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):46–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D., Begley C. G., Johnson G. R., Nicola N. A., Vadas M. A., Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Wong G. G., Clark S. C., Wang E. A. Biologic properties in vitro of a recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):37–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Binding of iodinated multipotential colony-stimulating factor (interleukin-3) to murine bone marrow cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Aug;128(2):180–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Binding of the differentiation-inducer, granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, to responsive but not unresponsive leukemic cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3765–3769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Friend D., Gillis S., Urdal D. L. Characterization of the cell surface receptor for human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):251–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Friend D., Price V., Anderson D., Singer J., Prickett K. S., Urdal D. L. Heterogeneity in human interleukin-3 receptors. A subclass that binds human granulocyte/macrophage colony stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5420–5427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular and cellular biology of eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin-5) and its effects on human and mouse B cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Ziltener H. J., Leslie K. B. Structural homologies among the hemopoietins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieff C. A., Niemeyer C. M., Nathan D. G., Ekern S. C., Bieber F. R., Yang Y. C., Wong G., Clark S. C. Stimulation of human hematopoietic colony formation by recombinant gibbon multi-colony-stimulating factor or interleukin 3. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):818–823. doi: 10.1172/JCI113139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein D. S., Owen W. F., Gasson J. C., DiPersio J. F., Golde D. W., Bina J. C., Soberman R., Austen K. F., David J. R. Enhancement of human eosinophil cytotoxicity and leukotriene synthesis by biosynthetic (recombinant) granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3290–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Baker E., Callen D. F., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Sanderson C. J., Garson O. M., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Interleukin-5 is at 5q31 and is deleted in the 5q- syndrome. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):1150–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Konishi M., Mizuta T., Noma T., Honjo T. Molecular cloning and structure of the human interleukin-5 gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16580–16584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., David J. R., Butterworth A., Pisani N. T., Siongok T. A. A new method for the purification of human eosinophils and neutrophils, and a comparison of the ability of these cells to damage schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1228–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas M. A., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Activation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity of human neutrophils and eosinophils by separate colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):795–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F., Nicola N. A., Metcalf D., Burgess A. W. Hierarchical down-modulation of hemopoietic growth factor receptors. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Kovacic S., Kriz R., Wolf S., Clark S. C., Wellems T. E., Nienhuis A., Epstein N. The human genes for GM-CSF and IL 3 are closely linked in tandem on chromosome 5. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):958–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



