Abstract
The title heteroaryl chalcone, C21H14OS, is a second orthorhombic polymorph which crystallizes in the space group P212121. The structure was previously reported [Fun et al. (2009 ▶). Acta Cryst. E65, o2168-o2169] in the space group Pna21. The bond distances and angles are similar in both structures. In contrast, the overall crystal packing is different from that in the first orthorhombic Pna21 polymorph in which molecules were stacked into columns along the b axis and the thiophene units of two adjacent columns were stacked in a head to tail fashion. In the present polymorph, molecules are found to dimerize through a weak S⋯S interaction [3.6513 (7) Å] and these dimers are arranged into sheets parallel to the bc plane. There are no classical hydrogen bonds in the packing which features short C⋯O [3.2832 (2)–3.6251 (9) Å], C⋯S [3.4879 (17)–3.6251 (19) Å] and S⋯O [2.9948 (16) Å] contacts, together with C—H⋯π interactions. Similar contacts were found in the other polymorph.
Related literature
For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For the structure of the first polymorph, see: Fun et al. (2009 ▶). For background to and applications of chalcones, see: Chantrapromma et al. (2009 ▶); Patil & Dharmaprakash (2008 ▶); Saydam et al. (2003 ▶); Suwunwong et al. (2009 ▶); Svetlichny et al. (2007 ▶). For the stability of the temperature controller used in the data collection, see Cosier & Glazer, (1986 ▶).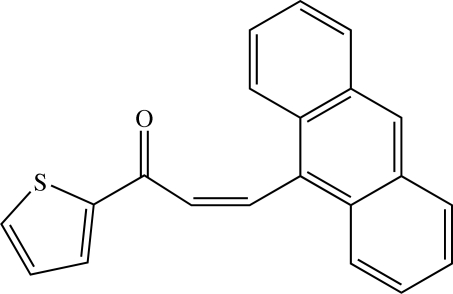
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H14OS
M r = 314.38
Orthorhombic,
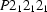
a = 5.5116 (1) Å
b = 14.8497 (2) Å
c = 18.3625 (3) Å
V = 1502.89 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.50 × 0.19 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.900, T max = 0.977
14062 measured reflections
4354 independent reflections
4035 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.108
S = 1.05
4354 reflections
254 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.79 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1830 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.04 (8)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810000061/sj2716sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810000061/sj2716Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg 1, Cg 2 and Cg 3 are the centroids of the S1/C18–C21, C1–C6 and C8–C13 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5—H5A⋯Cg1i | 0.91 (3) | 2.64 (3) | 3.443 (2) | 149 (2) |
| C15—H15A⋯Cg2ii | 0.95 (2) | 2.74 (2) | 3.565 (2) | 146.4 (17) |
| C21—H21A⋯Cg3iii | 1.04 (3) | 2.91 (3) | 3.711 (2) | 134.4 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 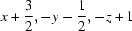 ; (ii)
; (ii) 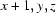 ; (iii)
; (iii) 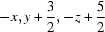 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) for research grant (RSA 5280033) and the Prince of Songkla University for financial support through the Crystal Materials Research Unit. The authors also thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Golden Goose grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811012.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In continuation of our study of chalcone derivatives (Chantrapromma et al., 2009; Fun et al., 2009; Suwunwong et al., 2009) which can be used for non-linear optical (NLO) materials (Patil & Dharmaprakash, 2008), fluorescent materials (Svetlichny et al., 2007) and bioactive compounds (Saydam et al., 2003), the title heteroaryl chalcone (I) was synthesized and its crystal structure was previously reported in the orthorhombic space group Pna21 (Fun et al., 2009). In the present work, the compound crystallized in the orthorhombic space group P212121 from an ethanol/acetone (1:1) solvent mixture, while the crystal of the Pna21 form crystallized from hot ethanol. (I) exhibits fluorescence with the maximum emission at 402 nm when the compound is excited at 335 nm.
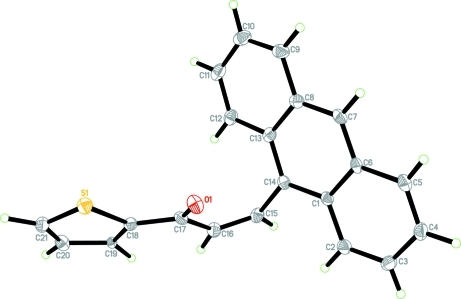
The molecule of (I) (Fig. 1) exists in an Z configuration with respect to the C15═C16 double bond and the torsion angle C14–C15–C16–C17 = -2.9 (3)° [compared to -3.7 (7)° in one molecule and -4.0 (7)° in the other in the Pna21 polymorph which contains two molecules in an asymmetric unit]. The molecule of the present polymorph is less twisted as indicated by the interplanar angles between thiophene and anthracene rings being 56.36 (7)° and the least squares plane through the prop-2-en-1-one unit (C15–C17/O1) makes interplanar angles of 12.2 and 68.00 (11)° with the thiophene and anthracene rings, respectively [the corresponding values are 75.07 (17), 13.1 (3) and 71.2 (3)° in one molecule and 76.32 (17), 15.2 (3) and 72.3 (3)° in the other for the Pna21 polymorph]. Bond distances are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987).
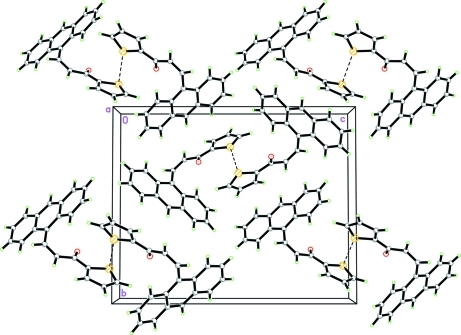
In the crystal packing (Fig. 2), molecules are found to dimerize through a non-bonding S···S interaction [S···S = 3.6513 (7) Å]. The dimers are arranged into sheets parallel to the bc plane. These sheets are stacked along the a axis. The intermolecular interactions and short contacts are almost similar in both polymorph. There is no classic hydrogen bond and the crystal is consolidated by short C···O [3.2832 (2)–3.6251 (9) Å], C···S [3.4879 (17)–3.6251 (19) Å] and S···O [2.9948 (16) Å] contacts, as well as C—H···π interactions (Table 1); Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the S1/C18–C21, C1–C6 and C8–C13 rings, respectively.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized as reported by Fun et al. (2009). Yellow block-shaped single crystals of the title compound suitable for x-ray structure determination were recrystallized from ethanol/acetone (1:1 v/v) by slow evaporation of the solvent at room temperature over several days, Mp. 400–401 K.
Refinement
The H atom attached to C19 was placed in a calculated position, with d(C—H) = 0.93 Å, Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C). The remaining H atoms were located from the difference maps and refined isotropically. The highest residual electron density peak is located at 0.04 Å from C19 and the deepest hole is 0.07 Å from C20. A total of 1830 Friedel pairs were used to determine the absolute configuration.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound viewed along the a axis. S···S contacts are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C21H14OS | Dx = 1.390 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 314.38 | Melting point = 400–401 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 4354 reflections |
| a = 5.5116 (1) Å | θ = 1.8–30.0° |
| b = 14.8497 (2) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| c = 18.3625 (3) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 1502.89 (4) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.50 × 0.19 × 0.11 mm |
| F(000) = 656 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4354 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 4035 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.025 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −7→5 |
| Tmin = 0.900, Tmax = 0.977 | k = −17→20 |
| 14062 measured reflections | l = −25→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.108 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0502P)2 + 0.8977P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4354 reflections | Δρmax = 0.79 e Å−3 |
| 254 parameters | Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1830 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.04 (8) |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cryosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 120.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.79023 (9) | 0.82740 (3) | 0.98167 (3) | 0.01920 (11) | |
| O1 | 0.6379 (3) | 0.74101 (10) | 0.84157 (8) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.6215 (3) | 0.62511 (12) | 0.66251 (10) | 0.0142 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.6199 (4) | 0.69201 (13) | 0.60656 (10) | 0.0176 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.747 (4) | 0.7404 (15) | 0.6071 (12) | 0.019 (6)* | |
| C3 | 0.4549 (4) | 0.68828 (13) | 0.55096 (10) | 0.0193 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.459 (4) | 0.7304 (16) | 0.5132 (14) | 0.022 (6)* | |
| C4 | 0.2761 (4) | 0.61930 (13) | 0.54827 (11) | 0.0198 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.150 (5) | 0.6169 (17) | 0.5090 (13) | 0.026 (6)* | |
| C5 | 0.2685 (4) | 0.55527 (13) | 0.60124 (10) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.155 (5) | 0.5111 (18) | 0.6021 (14) | 0.033 (7)* | |
| C6 | 0.4394 (3) | 0.55565 (12) | 0.65992 (10) | 0.0146 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.4332 (4) | 0.49043 (12) | 0.71450 (10) | 0.0169 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.311 (4) | 0.4456 (14) | 0.7129 (11) | 0.010 (5)* | |
| C8 | 0.6064 (4) | 0.48855 (12) | 0.76949 (10) | 0.0159 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.6059 (4) | 0.41897 (13) | 0.82390 (11) | 0.0213 (4) | |
| H9A | 0.479 (4) | 0.3744 (16) | 0.8218 (13) | 0.019 (6)* | |
| C10 | 0.7811 (4) | 0.41528 (14) | 0.87607 (11) | 0.0240 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.788 (5) | 0.3656 (16) | 0.9099 (13) | 0.022 (6)* | |
| C11 | 0.9682 (4) | 0.48106 (15) | 0.87753 (11) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| H11A | 1.103 (5) | 0.4744 (16) | 0.9123 (13) | 0.023 (6)* | |
| C12 | 0.9731 (4) | 0.54951 (14) | 0.82813 (10) | 0.0189 (4) | |
| H12A | 1.091 (5) | 0.5966 (17) | 0.8299 (13) | 0.027 (7)* | |
| C13 | 0.7917 (4) | 0.55659 (12) | 0.77254 (9) | 0.0156 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.7917 (3) | 0.62627 (12) | 0.72009 (9) | 0.0143 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.9746 (4) | 0.69969 (13) | 0.72208 (10) | 0.0172 (4) | |
| H15A | 1.077 (4) | 0.7024 (15) | 0.6807 (12) | 0.016 (6)* | |
| C16 | 1.0028 (4) | 0.76158 (13) | 0.77411 (10) | 0.0178 (4) | |
| H16A | 1.138 (5) | 0.8035 (17) | 0.7711 (13) | 0.026 (6)* | |
| C17 | 0.8452 (3) | 0.77098 (12) | 0.83955 (10) | 0.0153 (3) | |
| C18 | 0.9491 (3) | 0.82083 (12) | 0.90132 (9) | 0.0146 (3) | |
| C19 | 1.1727 (3) | 0.86783 (12) | 0.90518 (10) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H19A | 1.2863 | 0.8714 | 0.8678 | 0.018* | |
| C20 | 1.1971 (3) | 0.90888 (11) | 0.97520 (10) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H20A | 1.351 (5) | 0.9445 (17) | 0.9876 (14) | 0.031 (7)* | |
| C21 | 1.0083 (4) | 0.89174 (13) | 1.02086 (11) | 0.0198 (4) | |
| H21A | 0.993 (5) | 0.9095 (18) | 1.0753 (15) | 0.034 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0185 (2) | 0.0204 (2) | 0.0188 (2) | −0.00094 (17) | 0.00214 (18) | −0.00059 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0243 (7) | −0.0038 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | −0.0053 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0159 (8) | 0.0132 (8) | 0.0136 (8) | 0.0006 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0200 (9) | 0.0167 (8) | 0.0162 (8) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0234 (9) | 0.0181 (9) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0033 (7) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0009 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0211 (9) | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0174 (8) | 0.0038 (8) | −0.0038 (8) | −0.0049 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0182 (9) | 0.0167 (8) | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0007 (8) | −0.0057 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0143 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0007 (7) | −0.0001 (7) | −0.0056 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0187 (9) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0188 (8) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | −0.0038 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0192 (9) | 0.0142 (8) | 0.0143 (8) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0279 (11) | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0208 (9) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0215 (9) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0078 (9) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0032 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0254 (10) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0149 (8) | 0.0088 (9) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0007 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0182 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0166 (8) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0164 (8) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0038 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0146 (7) | 0.0144 (8) | 0.0141 (7) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0019 (7) | −0.0028 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0213 (9) | 0.0141 (8) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0002 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0170 (9) | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0165 (8) | −0.0033 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0000 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0118 (8) | 0.0167 (8) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0011 (7) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0151 (8) | 0.0125 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0125 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | −0.0024 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0125 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | −0.0024 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| C21 | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0040 (7) | −0.0012 (8) | −0.0017 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C21 | 1.696 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.96 (3) |
| S1—C18 | 1.7184 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.421 (3) |
| O1—C17 | 1.227 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.97 (2) |
| C1—C14 | 1.414 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.363 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.429 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.98 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.440 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.433 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.368 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.96 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 1.00 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.414 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.422 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.485 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.93 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.335 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.361 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.95 (2) |
| C4—H4A | 1.00 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.489 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.431 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.97 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.91 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.470 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.394 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.418 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.390 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.429 (2) |
| C7—H7A | 0.95 (2) | C19—H19A | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.437 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.360 (3) |
| C8—C13 | 1.438 (3) | C20—H20A | 1.02 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.361 (3) | C21—H21A | 1.04 (3) |
| C21—S1—C18 | 92.02 (10) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.5 (15) |
| C14—C1—C2 | 122.21 (17) | C10—C11—H11A | 119.4 (14) |
| C14—C1—C6 | 119.73 (17) | C11—C12—C13 | 121.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.05 (17) | C11—C12—H12A | 122.4 (16) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.81 (18) | C13—C12—H12A | 116.5 (16) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.0 (13) | C14—C13—C12 | 122.62 (18) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 119.1 (13) | C14—C13—C8 | 119.20 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.04 (18) | C12—C13—C8 | 118.16 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.8 (15) | C13—C14—C1 | 120.04 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 118.2 (15) | C13—C14—C15 | 121.37 (16) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.99 (18) | C1—C14—C15 | 118.55 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 118.0 (15) | C16—C15—C14 | 127.01 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 122.0 (15) | C16—C15—H15A | 118.3 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.99 (19) | C14—C15—H15A | 114.7 (14) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 122.6 (17) | C15—C16—C17 | 125.05 (17) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 116.4 (17) | C15—C16—H16A | 119.3 (15) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.47 (17) | C17—C16—H16A | 115.6 (15) |
| C7—C6—C1 | 119.43 (17) | O1—C17—C18 | 121.46 (17) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.10 (17) | O1—C17—C16 | 122.25 (17) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.27 (17) | C18—C17—C16 | 116.26 (16) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 119.8 (13) | C19—C18—C17 | 128.65 (16) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 118.9 (13) | C19—C18—S1 | 111.83 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 121.21 (18) | C17—C18—S1 | 119.51 (14) |
| C7—C8—C13 | 120.14 (17) | C18—C19—C20 | 109.67 (16) |
| C9—C8—C13 | 118.65 (18) | C18—C19—H19A | 125.2 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.1 (2) | C20—C19—H19A | 125.2 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 121.0 (14) | C21—C20—C19 | 113.75 (16) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 117.8 (14) | C21—C20—H20A | 126.4 (15) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.04 (18) | C19—C20—H20A | 119.8 (15) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 120.8 (16) | C20—C21—S1 | 112.71 (15) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 119.0 (16) | C20—C21—H21A | 127.5 (16) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 121.0 (2) | S1—C21—H21A | 119.7 (16) |
| C14—C1—C2—C3 | 179.06 (17) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 2.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.1 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C1 | 174.11 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (3) | C8—C13—C14—C1 | −4.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −3.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (3) | C8—C13—C14—C15 | 178.18 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.95 (18) | C2—C1—C14—C13 | −177.53 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.0 (3) | C6—C1—C14—C13 | 3.6 (3) |
| C14—C1—C6—C7 | 0.2 (3) | C2—C1—C14—C15 | 0.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.75 (17) | C6—C1—C14—C15 | −178.90 (16) |
| C14—C1—C6—C5 | −179.92 (16) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −64.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.2 (3) | C1—C14—C15—C16 | 118.4 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 176.94 (17) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −2.9 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −3.1 (3) | C15—C16—C17—O1 | −21.8 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −177.26 (17) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 160.02 (19) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | 2.3 (3) | O1—C17—C18—C19 | −172.54 (18) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 177.47 (19) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 5.7 (3) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −2.1 (3) | O1—C17—C18—S1 | 6.9 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.2 (3) | C16—C17—C18—S1 | −174.86 (13) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.3 (3) | C21—S1—C18—C19 | 0.62 (15) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.9 (3) | C21—S1—C18—C17 | −178.93 (15) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −179.56 (18) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 178.21 (17) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | −1.0 (3) | S1—C18—C19—C20 | −1.30 (19) |
| C7—C8—C13—C14 | 1.5 (3) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 1.5 (2) |
| C9—C8—C13—C14 | −178.92 (17) | C19—C20—C21—S1 | −1.1 (2) |
| C7—C8—C13—C12 | −177.10 (17) | C18—S1—C21—C20 | 0.27 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the S1/C18–C21, C1–C6 and C8–C13 rings, respectively. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5—H5A···Cg1i | 0.91 (3) | 2.64 (3) | 3.443 (2) | 149 (2) |
| C15—H15A···Cg2ii | 0.95 (2) | 2.74 (2) | 3.565 (2) | 146.4 (17) |
| C21—H21A···Cg3iii | 1.04 (3) | 2.91 (3) | 3.711 (2) | 134.4 (19) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+3/2, −y−1/2, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x, y+3/2, −z+5/2.
Footnotes
This paper is dedicated to His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej of Thailand (King Rama IX) for his sustainable development of the country.
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SJ2716).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chantrapromma, S., Suwunwong, T., Karalai, C. & Fun, H.-K. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o893–o894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Fun, H.-K., Suwunwong, T., Boonnak, N. & Chantrapromma, S. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o2168–o2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008). Mater. Lett.62, 451–453.
- Saydam, G., Aydin, H. H., Sahin, F., Kucukoglu, O., Erciyas, E., Terzioglu, E., Buyukkececi, F. & Omay, S. B. (2003). Leuk. Res 27, 57–64. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suwunwong, T., Chantrapromma, S., Karalai, C., Pakdeevanich, P. & Fun, H.-K. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o420–o421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Svetlichny, V. Y., Merola, F., Dobretsov, G. E., Gularyan, S. K. & Syrejshchikova, T. I. (2007). Chem. Phys. Lipids, 145, 13–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810000061/sj2716sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810000061/sj2716Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report