Abstract
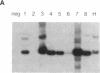
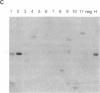
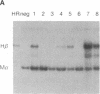
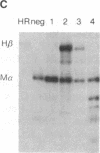
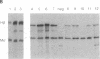
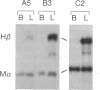
Several lines of evidence suggest that erythroid-specific DNase I hypersensitive sites (HS) located far upstream of the human beta-globin gene are important in regulating beta-globin gene expression. We used the polymerase chain reaction technique to amplify and clone an 882-base-pair DNA fragment spanning one of these HS, designated HSII, which is located 54 kilobases upstream of the beta-globin gene. The cloned HSII fragment was linked to a human beta-globin gene in either the genomic (HSII-beta) or antigenomic (HSII-beta) orientation. These two constructs and a beta-globin gene alone (beta) were injected into fertilized mouse eggs, and expression was analyzed in liver and brain from day-16 transgenic fetuses. Five of 7 beta-transgenic fetuses expressed human beta-globin mRNA, but the level of expression per gene copy was low, ranging from 0.93 to 22.4% of mouse alpha-globin mRNA (average 9.9%). In contrast, 11 of 12 HSII-beta transgenic fetuses expressed beta-globin mRNA at levels per gene copy ranging from 31.3 to 336.6% of mouse alpha-globin mRNA (average 139.5%). Only three fetuses containing intact copies of the HSII-beta construct were produced. Two of three expressed human beta-globin mRNA at levels per gene copy of 179.2 and 387.1%. Expression of human beta-globin mRNA was tissue-specific in all three types of transgenic fetuses. These studies demonstrate that a small DNA fragment containing a single erythroid-specific HS can stimulate high-level human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Townes T. M. Two 3' sequences direct adult erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Costantini F. An embryonic pattern of expression of a human fetal globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):685–689. doi: 10.1038/319685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Kan Y. W. The inactive beta globin gene on a gamma delta beta thalassemia chromosome has a normal structure and functions normally in vitro. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):766–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P., Pirastu M., Kan Y. W., Gobert-Jones J. A., Stephens A. D., Lehmann H. A distant gene deletion affects beta-globin gene function in an atypical gamma delta beta-thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1554–1558. doi: 10.1172/JCI112136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisseroth A., Nienhuis A., Lawrence J., Giles R., Turner P., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal localization of human beta globin gene on human chromosome 11 in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1456–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzierzak E. A., Papayannopoulou T., Mulligan R. C. Lineage-specific expression of a human beta-globin gene in murine bone marrow transplant recipients reconstituted with retrovirus-transduced stem cells. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):35–41. doi: 10.1038/331035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Thompson C., Elder J. T., Groudine M. A developmentally stable chromatin structure in the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E. F., Lawn R. M., Maniatis T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human beta-like globin gene cluster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):959–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Papayannopoulou T. Human fetal to adult hemoglobin switching: changes in chromatin structure of the beta-globin gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7551–7555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Vanin E., deLange T., Flavell R. A., Grosveld F. G. Beta-globin gene inactivation by DNA translocation in gamma beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):662–666. doi: 10.1038/306662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebo R. V., Carrano A. V., Burkhart-Schultz K., Dozy A. M., Yu L. C., Kan Y. W. Assignment of human beta-, gamma-, and delta-globin genes to the short arm of chromosome 11 by chromosome sorting and DNA restriction enzyme analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5804–5808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Powers P. A., Smithies O. Nucleotide sequence of 16-kilobase pairs of DNA 5' to the human epsilon-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14901–14910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magram J., Chada K., Costantini F. Developmental regulation of a cloned adult beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):338–340. doi: 10.1038/315338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli R., Kioussis D., Vanin E., Bartram K., Groffen J., Hurst J., Grosveld F. G. Gamma delta beta-thalassaemias 1 and 2 are the result of a 100 kbp deletion in the human beta-globin cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7017–7029. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudel M., Costantini F. A 3' enhancer contributes to the stage-specific expression of the human beta-globin gene. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):954–961. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Konings A., Oort M., Roos D., Bernini L., Flavell R. A. gamma-beta-Thalassaemia studies showing that deletion of the gamma- and delta-genes influences beta-globin gene expression in man. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):637–642. doi: 10.1038/283637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]