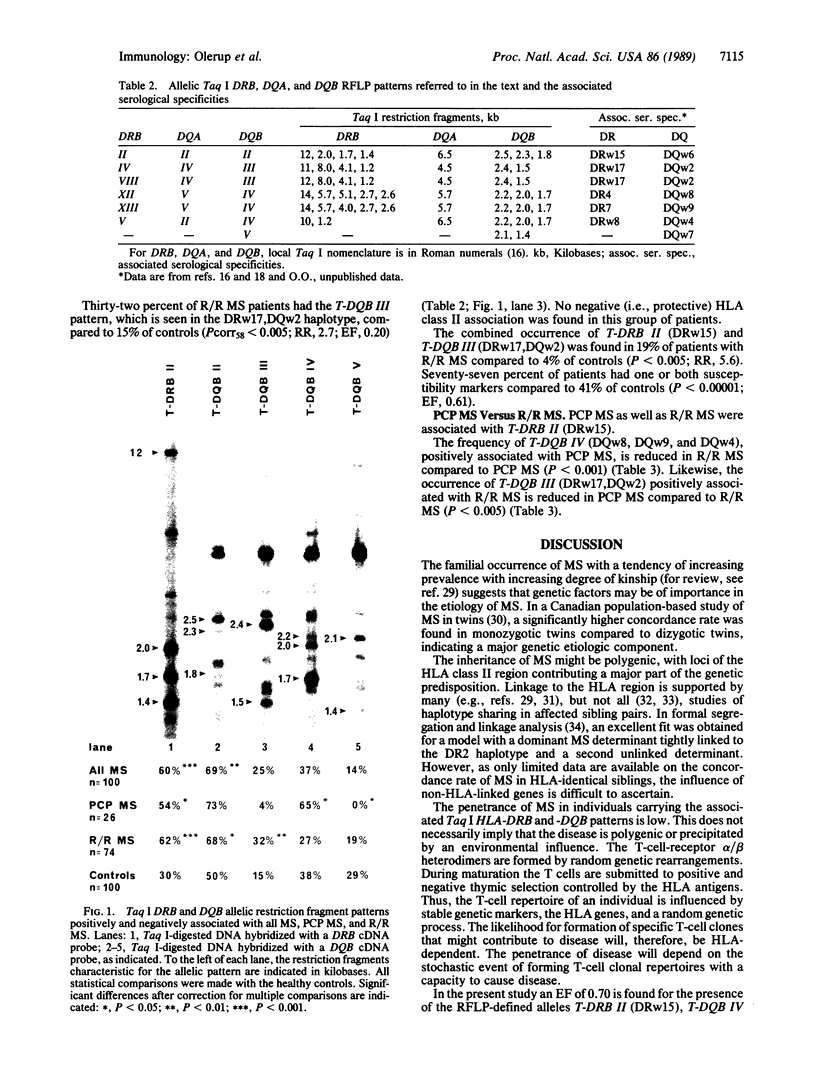
Abstract
HLA class II gene polymorphism was investigated in 100 patients with clinically definite multiple sclerosis (MS) by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of Taq I-digested DNA using DRB, DQA, and DQB cDNA probes. Twenty-six patients had primarily chronic progressive MS and 74 had relapsing/remitting MS. The latter group included patients with a secondary progressive evolution of symptoms. Both clinical forms of MS were found to be associated with the DRw15,DQw6 haplotype. In addition, primarily chronic progressive MS was positively associated with the DQB1 restriction fragment pattern seen in DR4,DQw8, DR7,DQw9, and DRw8, DQw4 haplotypes, as well as negatively associated with the Taq I DQB1 allelic pattern corresponding to the serological specificity DQw7. Relapsing/remitting MS was positively associated with the DQB1 allelic pattern observed in the DRw17,DQw2 haplotype. These three DQB1 alleles are in strong negative linkage disequilibria with DRw15. The two susceptibility markers of each clinical form of MS act additively in determining the genetic susceptibility, as the relative risks for individuals carrying both markers roughly equal the sum of respective risks. Different alleles of the DQB1 locus defined by restriction fragment length polymorphisms contribute to susceptibility and resistance to primarily chronic progressive MS as well as to susceptibility to relapsing/remitting MS. The observed immunogenetic heterogeneity between the different clinical forms of MS favors the hypothesis that primarily chronic progressive MS and relapsing/remitting MS are two distinct disease entities.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengtsson B. O., Thomson G. Measuring the strength of associations between HLA antigens and diseases. Tissue Antigens. 1981 Nov;18(5):356–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1981.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. L., Bidwell E. A., Laundy G. J., Klouda P. T., Bradley B. A. Allogenotypes defined by short DQ alpha and DQ beta cDNA probes correlate with and define splits of HLA-DQ serological specificities. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):513–522. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidwell J. DNA-RFLP analysis and genotyping of HLA-DR and DQ antigens. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91351-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson B., Wallin J., Böhme J., Möller E. HLA-DR-DQ haplotypes defined by restriction fragment analysis. Correlation to serology. Hum Immunol. 1987 Oct;20(2):95–113. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Le Gall I., Marcadet A., Font M. P., Lalouel J. M., Dausset J. Clusters of HLA class II beta restriction fragments describe allelic series. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7870–7874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Confavreux C., Aimard G., Devic M. Course and prognosis of multiple sclerosis assessed by the computerized data processing of 349 patients. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):281–300. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Bulman D. E., Sadovnick A. D., Paty D. W., Warren S., Hader W., Murray T. J., Seland T. P., Duquette P., Grey T. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1638–1642. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebers G. C., Paty D. W., Stiller C. R., Nelson R. F., Seland T. P., Larsen B. HLA-typing in multiple sclerosis sibling pairs. Lancet. 1982 Jul 10;2(8289):88–90. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91702-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. A., Batchelor J. R., McDonald W. I., Hing S. N., Dodi I. A., Fielder A. H., Hern J. E., Downie A. W. Multiple sclerosis in north-east Scotland. An association with HLA-DQw1. Brain. 1987 Feb;110(Pt 1):181–196. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts A., Gony J., Martin-Mondiére C., Poirier J. C., Schmid M., Schuller E., Degos J. D., Dausset J. HLA and multiple sclerosis: population and families study. Tissue Antigens. 1985 Apr;25(4):187–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1985.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Emmoth E., Larhammar D., Böhme J., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Ronne H., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Mutations and selection in the generation of class II histocompatibility antigen polymorphism. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1655–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. Z., Tiwari J. L., Haile R. W., Terasaki P. I., Morton N. E. HLA-linked and unlinked determinants of multiple sclerosis. Immunogenetics. 1982;15(5):509–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00345910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Bugawan T. L., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Allelic sequence variation of the HLA-DQ loci: relationship to serology and to insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jersild C., Fog T., Hansen G. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A., Dupont B. Histocompatibility determinants in multiple sclerosis, with special reference to clinical course. Lancet. 1973 Dec 1;2(7840):1221–1225. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes D., Strominger J. L. Human class II major histocompatibility complex genes and proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:991–1028. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.005015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurdi A., Ayesh I., Abdallat A., Maayta U. Different B lymphocyte alloantigens associated with multiple sclerosis in Arabs and North Europeans. Lancet. 1977 May 28;1(8022):1123–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Schenning L., Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Claesson L., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Complete amino acid sequence of an HLA-DR antigen-like beta chain as predicted from the nucleotide sequence: similarities with immunoglobulins and HLA-A, -B, and -C antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. P., Kvaale G., Riise T., Nyland H., Aarli J. A. Multiple sclerosis--more than one disease? Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Aug;72(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. S., Bell J. I., Rust N. A., McDevitt H. O. Structural and functional variability among DQ beta alleles of DR2 subtypes. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00345459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz U., Alter M. Clinical factors associated with increased disability in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1970;46(1):53–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1970.tb05604.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. III. Evaluation of IgG synthesis within the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):397–401. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigand M., Oger J. J., Fauchet R., Sabouraud O., Genetet B. HLA profiles in multiple sclerosis suggest two forms of disease and the existence of protective haplotypes. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Mar;53(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrosu M. G., Muntoni F., Murru M. R., Spinicci G., Pischedda M. P., Goddi F., Cossu P., Pirastu M. Sardinian multiple sclerosis is associated with HLA-DR4: a serologic and molecular analysis. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1749–1753. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moen T., Bratlie A., Kiss E., Bruserud O., Thorsby E. Identification of four SB antigens by cloned cells. Population studies of Norwegians. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Oct;22(4):298–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moen T., Stien R., Bratlie A., Bondevik E. Distribution of HLA-SB antigens in multiple sclerosis. Tissue Antigens. 1984 Aug;24(2):126–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1984.tb02116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum N., Hartzman R., Jakobsen B. K., Morling N., Platz P., Robbins F. M., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A. The HLA-DP polymorphism in Denmark investigated by local and international PLT reagents. Definition of two "new" DP antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Aug;28(2):105–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum N., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Morling N., Sandberg-Wollheim M., Platz P., Svejgaard A. HLA-DP antigens are involved in the susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Tissue Antigens. 1988 May;31(5):235–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1988.tb02088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Fredrikson S., Olsson T., Kam-Hansen S. HLA class II genes in chronic progressive and in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):327–327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90907-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Kostulas V., Link H. Improved detection of oligoclonal IgG in cerebrospinal fluid by isoelectric focusing in agarose, double-antibody peroxidase labeling, and avidin-biotin amplification. Clin Chem. 1984 Jul;30(7):1246–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser S., Poser W., Schlaf G., Firnhaber W., Lauer K., Wolter M., Evers P. Prognostic indicators in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1986 Nov;74(5):387–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1986.tb03531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMACHER G. A., BEEBE G., KIBLER R. F., KURLAND L. T., KURTZKE J. F., MCDOWELL F., NAGLER B., SIBLEY W. A., TOURTELLOTTE W. W., WILLMON T. L. PROBLEMS OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS: REPORT BY THE PANEL ON THE EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTAL TRIALS OF THERAPY IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:552–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenning L., Larhammar D., Bill P., Wiman K., Jonsson A. K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Both alpha and beta chains of HLA-DC class II histocompatibility antigens display extensive polymorphism in their amino-terminal domains. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosstein L., Terasaki P. I., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. High association of an HL-A antigen, W27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 5;288(14):704–706. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304052881403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. J., McLeod J. G., Basten A., Bashir H. V. HLA family studies and multiple sclerosis: A common gene, dominantly expressed. Hum Immunol. 1981 Aug;3(1):13–29. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez B., O'Rourke D., Van Eerdewegh P. Power of the affected-sib-pair method to defect disease susceptibility loci of small effect: an application to multiple sclerosis. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Jul;12(3):309–326. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swingler R. J., Kirk P. F., Darke C., Compston D. A. HLA and multiple sclerosis in south east Wales. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Sep;50(9):1153–1155. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.9.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termijtelen A., Naipal-van den Berge S., Suwandi-Thung L., van Rood J. J. Recognition of DP determinants with typing reagents prepared with lymphocytes from Dutch unrelated individuals. Tissue Antigens. 1985 Oct;26(4):234–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1985.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiercy J. M., Gorski J., Jeannet M., Mach B. Identification and distribution of three serologically undetected alleles of HLA-DR by oligonucleotide.DNA typing analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):198–202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lambalgen R., Sanders E. A., D'Amaro J. Sex distribution, age of onset and HLA profiles in two types of multiple sclerosis. A role for sex hormones and microbial infections in the development of autoimmunity? J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;76(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verjans E., Theys P., Delmotte P., Carton H. Clinical parameters and intrathecal IgG synthesis as prognostic features in multiple sclerosis. Part I. J Neurol. 1983;229(3):155–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00313739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLF B. On estimating the relation between blood group and disease. Ann Hum Genet. 1955 Jun;19(4):251–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1955.tb01348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Mach B. Allelic polymorphism and complexity of the genes for HLA-DR beta-chains--direct analysis by DNA-DNA hybridization. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):372–374. doi: 10.1038/300372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Moerloose P., Jeannet M., Martins-da-Silva B., Werner-Favre C., Rohr J., Gauthier G. Increased frequency of HLA--DRw2 and DRw3 in multiple sclerosis. Tissue Antigens. 1979 May;13(5):357–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1979.tb00808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]