Abstract
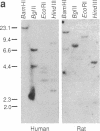
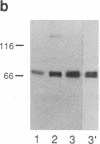
A component of soluble terminal complement complexes was identified and affinity-purified to homogeneity by using a monoclonal antibody previously developed against the soluble C5b-9 complex. The protein, which we have designated complement cytolysis inhibitor (CLI), has a molecular mass of 70 kDa and consists of two nonidentical, disulfide-linked subunits of 35 kDa. Partial amino acid sequences determined for the amino-termini of the two subunits were identical with those of a recently characterized serum protein called SP-40,40. An almost full-length cDNA clone of 1651 base pairs was isolated from a human liver cDNA library by using long synthetic oligonucleotides as probes. The encoded amino acid sequence of CLI consists of 427 amino acid residues preceded by a 21-residue-long typical signal peptide and shows an overall 75.6% amino acid sequence homology to sulfated glycoprotein 2 (SGP-2), a major Sertoli cell-derived protein of rat testis fluid. As in SGP-2, proteolytic processing between residues 206 and 207 yields the two disulfide-linked subunits of plasma CLI. CLI and SGP-2 were shown to be orthologous single-copy genes in humans and rats by Southern blotting experiments. In addition, CLI was immunologically identified in human seminal plasma. Functional studies with purified terminal complement components showed that CLI suppresses the cytolytic potential of nascent C5b-7 complexes at physiological blood plasma concentrations (approximately 50 micrograms/ml). Its presence on the surface of mature sperm cells and its relative abundance in seminal plasma (approximately 250 micrograms/ml) suggest that CLI protects sperm cells and epithelial tissues against complement attack in the male reproductive tract.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Jenne D., Hugo F. Electroimmunoassay-immunoblotting (EIA-IB) for the utilization of monoclonal antibodies in quantitative immunoelectrophoresis: the method and its applications. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jun 12;80(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Hydrophilic-amphiphilic transition of the terminal SC5b-8 complement complex through tryptic modification: biochemical and ultrastructural studies. Mol Immunol. 1982 Sep;19(9):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschuk O., Burdzy K., Fritz I. B. Purification and characterization of a cell-aggregating factor (clusterin), the major glycoprotein in ram rete testis fluid. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7714–7720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. Y., Mathur P. P., Grima J. Structural analysis of clusterin and its subunits in ram rete testis fluid. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):4079–4088. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collard M. W., Griswold M. D. Biosynthesis and molecular cloning of sulfated glycoprotein 2 secreted by rat Sertoli cells. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Podack E. R. Characterization of human S protein, an inhibitor of the membrane attack complex of complement. Demonstration of a free reactive thiol group. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 23;24(9):2368–2374. doi: 10.1021/bi00330a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griswold M. D., Roberts K., Bishop P. Purification and characterization of a sulfated glycoprotein secreted by Sertoli cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7265–7270. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger J. A., Jenne D., Stanley K. K., Tschopp J. Structural homology of human complement component C8 gamma and plasma protein HC: identity of the cysteine bond pattern. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):750–754. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M. Isolation of genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:180–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Weller P. F., Nicholson-Weller A. Release of C8 binding protein (C8bp) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1089–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Hugo F., Bhakdi S. Monoclonal antibodies to human plasma protein X alias complement S-protein. Biosci Rep. 1985 Apr;5(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01116907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Stanley K. K. Molecular cloning of S-protein, a link between complement, coagulation and cell-substrate adhesion. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3153–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirszbaum L., Sharpe J. A., Murphy B., d'Apice A. J., Classon B., Hudson P., Walker I. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40,40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):711–718. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Kolb L. M. Antithrombin III binding to SC5b-9 attack complexes of human complement: dissociation of a modified antithrombin III derivative subsequent to complex formation. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):496–504. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. F., Kirszbaum L., Walker I. D., d'Apice A. J. SP-40,40, a newly identified normal human serum protein found in the SC5b-9 complex of complement and in the immune deposits in glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI113531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular organization and function of the complement system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex of complement. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:503–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Yamamoto K. I., Lint T. F. Restriction of complement-mediated membrane damage by the eighth component of complement: a dual role for C8 in the complement attack sequence. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Coiled-coils in alpha-helix-containing proteins: analysis of the residue types within the heptad repeat and the use of these data in the prediction of coiled-coils in other proteins. Biosci Rep. 1982 Dec;2(12):1017–1024. doi: 10.1007/BF01122170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. I., Packman C. H., Leddy J. P. Inhibition of the lytic action of cell-bound terminal complement components by human high density lipoproteins and apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):795–808. doi: 10.1172/JCI110833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassi F., Hugo F., Muhly M., Khaled A., Ben Rachid M. S., Bhakdi S. A natural auto-inhibitory factor of the terminal complement pathway in serum of Ctenodactylus gondi. Mol Immunol. 1987 May;24(5):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönermark S., Rauterberg E. W., Shin M. L., Löke S., Roelcke D., Hänsch G. M. Homologous species restriction in lysis of human erythrocytes: a membrane-derived protein with C8-binding capacity functions as an inhibitor. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1772–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester S. R., Skinner M. K., Griswold M. D. A sulfated glycoprotein synthesized by Sertoli cells and by epididymal cells is a component of the sperm membrane. Biol Reprod. 1984 Dec;31(5):1087–1101. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod31.5.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarter T. H., Alexander N. J. Complement-inhibiting activity of seminal plasma. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.1984.tb00105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Jongeneel C. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated cytolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2641–2646. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Masson D., Schäfer S., Peitsch M., Preissner K. T. The heparin binding domain of S-protein/vitronectin binds to complement components C7, C8, and C9 and perforin from cytolytic T-cells and inhibits their lytic activities. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):4103–4109. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung P. S., Fritz I. B. Immunolocalization of clusterin in the ram testis, rete testis, and excurrent ducts. Biol Reprod. 1985 Aug;33(1):177–186. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod33.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane protein capable of inhibiting expression of homologous complement transmembrane channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]